1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll discuss two popular devices used in network security: gateway and firewall. We’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of using them in a network.
Finally, we’ll highlight the core differences between them to guide the readers in choosing the correct device.
2. Introduction to Network Security
Network security consists of guidelines and procedures that are recommended to implement to secure a computer network. It also protects the components of a computer network, including hardware and software. Furthermore, it safeguards data from unauthorized access and preserves its integrity.
Various technologies, processes, and practices work together to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. The goal of network security is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of networked systems, as well as computing devices. Additionally, it aims to prevent unauthorized access, theft of data, and malicious activity such as malware infections.
Network security can be divided into two main areas: network encryption and network monitoring. Network encryption is used to protect the transmission of data over a network. Furthermore, network monitoring is the process of gathering information from the computers on the network and using it to detect problems that could compromise the network’s security.
Some common network security components include gateways, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs). We’ll discuss how gateways and firewalls work in order to provide network security in detail.
3. Gateway
3.1. Introduction
Gateways play an important role in enabling secure and efficient communication between different networks. Additionally, they provide a layer of protection against potential threats. A gateway is simply a device that we place at the entrance to a network. It receives all the incoming traffic from the outside networks and sends outgoing traffic from the networking components of a network.
A gateway can function as a router, directing traffic between different networks based on IP addresses and other information contained in packets:
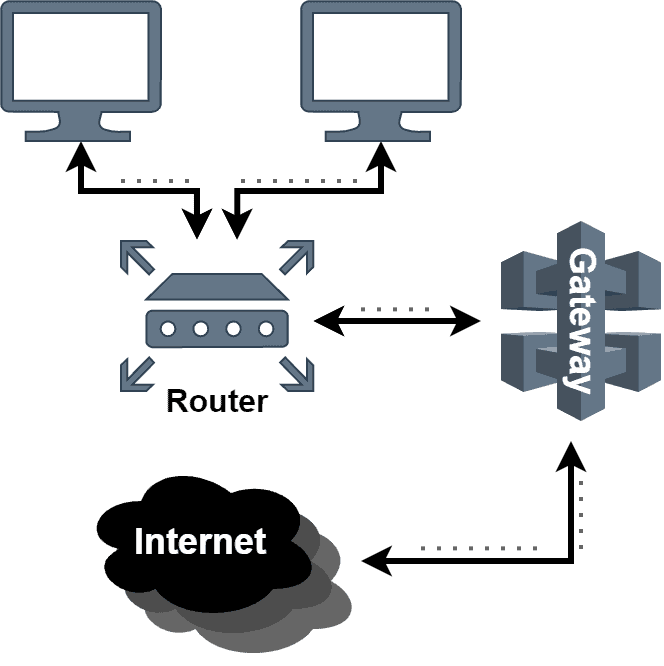
Additionally, a gateway can distribute network traffic across various servers. Hence, it boosts network performance and minimizes the risk of overloading any single server.
When a gateway receives data packets, it investigates them against preset rules. A data packet generally contains a source IP address, a destination IP address, and a port number. Based on the information contained in the packet, the gateway determines the best route for the packet to take to reach its destination. It may involve forwarding the packet to another network or forwarding the packet to a device within the same network.
Thus, a gateway behaves as a bridge between networks, allowing communication between devices on different networks. Additionally, it helps to ensure the security and efficiency of network traffic.
3.2. Advantages
Let’s discuss the advantages of using gateways.
A gateway allows different network parts to be segmented and isolated. It improves network security and reduces the risk of unauthorized access or malicious activity. Additionally, by distributing network traffic evenly across multiple servers, a gateway can help improve network performance and reduce the risk of overloading any single server.
A gateway permits the sharing of a single public IP address on a local network by multiple devices using the network address translation (NAT) technique. Additionally, it allows for conserving public IP addresses and simplifying network configuration.
Furthermore, we can use a gateway to set up a virtual private network (VPN), allowing remote employees or partners to securely access a local network.
3.3. Disadvantages
While gateways offer many benefits for computer networks, it’s important to carefully consider their disadvantages and determine whether they are the best solution for a particular network before deploying them.
Some disadvantages of a gateway include complexity, performance overhead, and a single point of failure.
Setting up and configuring a gateway can be complex, particularly for users without extensive networking experience. Additionally, we need a network administrator in order to monitor the performance of the network. Furthermore, If a gateway fails, it can disrupt network traffic. As a result, it might prevent devices on different networks from communicating with one another.
The process of routing and analyzing network traffic can add latency to network communication. As a result, it can reduce overall network performance.
4. Firewall
4.1. Introduction
A firewall is a security device that detects and blocks malicious activities in a network. The main purpose is to prevent unauthorized access while allowing authorized communication in a network. In order to make a decision for incoming traffic, it uses a set of predefined rules.
Additionally, we can place them at the perimeter of a network, between an internal network and the Internet, to protect against external threats. Furthermore, firewalls can also be placed on individual computers to protect against internal and external threats.
We set some rules in a firewall to guide it to determine what traffic is allowed to pass through the firewall and what traffic should be blocked. Furthermore, these security rules can be based on various criteria, such as port numbers, protocols, and IP addresses.
Firewalls can also include additional security features, such as virtual private networks (VPN), intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and application layer filters, to provide additional protection for networks.
Let’s take a look at the network architecture where we added a firewall in order to protect the systems connected to a network from attackers:

4.2. Advantages
Firewalls are an essential component of network security. They provide several advantages, including protection against unauthorized access, protection against cyber threats, and traffic control.
One of the primary benefits of employing a firewall in network security is that it gives a high level of network protection. Because all network traffic must travel via the firewall, harmful traffic is inspected and blocked in real-time. Hence, firewalls can prevent unauthorized access to a network by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Additionally, firewalls can help protect against cyber threats such as viruses, malware, and hacking by inspecting traffic and blocking any malicious activity.
Finally, firewalls allow network administrators to control the traffic in and out of a network based on specific policies and rules.
4.3. Disadvantages
While firewalls can provide a significant level of protection for a network, it has some drawbacks. Some of the issues are added complexity, increased latency, and the risk of overreliance.
Firewalls can be complex to configure and manage, particularly for larger networks. This can make it challenging for administrators to maintain an effective security posture. Additionally, they can add latency to network traffic, slowing communication and negatively impacting performance.
Some organizations may rely too heavily on firewalls as their sole method of protection, which can leave them vulnerable to attacks that can bypass firewalls, such as phishing or social engineering.
5. Differences
Let’s take a look at the core differences between a gateway and a firewall:
6. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we discussed two popular network security devices: gateway and firewall. We presented the advantages and disadvantages of using them in a network. Finally, we highlighted the core differences between them.