Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
Introduction to Delta Lake
Last updated: November 15, 2025
1. Overview
A data lake is a centralized repository that stores vast amounts of structured and unstructured data. It’s scalable and cost-efficient, but traditional data lakes often struggle with data quality, consistency, and manageability.
Delta Lake is an open-source storage layer that solves these challenges by providing ACID-compliant transactions (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability), schema enforcement, data versioning, and unified batching and streaming support.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore what Delta Lake is, why it’s needed, its architecture, core features, and how it works.
2. Problem With Traditional Data Lakes
While data lakes are flexible and inexpensive, they come with several limitations that affect analytics and machine learning workloads.
2.1. Data Reliability
Traditional data lakes lack ACID transactions. When multiple users or jobs write to the same dataset, it can result in dirty reads, partial writes, or corrupted files. Without built-in data versioning, it isn’t easy to roll back to a previous state or reproduce historical analyses.
2.2. Schema and Consistency
Schema drift occurs when the structure of datasets changes over time. This leads to inconsistent data and fragile downstream processes, making analytics and machine learning pipelines error-prone.
2.3. Performance and Pipeline Complexity
Large datasets can cause queries to slow down, especially when indexing or caching is not implemented. Moreover, organizations often maintain separate pipelines for batching and streaming, increasing complexity and maintenance overhead.
3. Key Features of Delta Lake
Delta Lake is an open-source storage layer that brings reliability to data lakes. Furthermore, it works seamlessly with big data processing engines such as Apache Spark and provides several features to address problems with traditional data lakes.
3.1. ACID Transactions
Delta Lake ensures data integrity with ACID transactions. This means writes are all-or-nothing, preventing data corruption and allowing multiple users to read and write to the same table simultaneously without conflicts.
3.2. Schema Enforcement and Evolution
Delta Lake validates incoming data against the table schema. Invalid records are rejected. At the same time, controlled changes like adding new columns are supported. This balance keeps data consistent without blocking growth.
3.3. Time Travel and Versioning
Delta Lake maintains a history of every change made to a table. Each commit in the log creates a new version of the table. We can query past versions to reproduce old reports, debug issues, or run audits. This makes data both reproducible and trustworthy.
3.4. Performance Optimizations
Delta Lake provides built-in optimizations that work together to accelerate queries. By using data skipping to avoid scanning irrelevant files by leveraging metadata, Delta Lake reduces unnecessary I/O.
With z-ordering, related records are stored close to each other, speeding up queries that filter on multiple columns.
Finally, file compaction reduces the overhead of handling too many small files by merging them into larger, more efficient ones, ensuring faster and more reliable query execution.
3.5. Unified Batch and Streaming
Delta Lake simplifies data architecture by treating a table as both a batch source and a streaming source or sink. This unified approach eliminates the need for separate systems for historical and real-time data.
We can ingest data into a Delta table through a streaming job and then perform batch analytics on that same table using a separate query, all while ensuring data consistency.
4. Architecture
At its core, Delta Lake is a storage layer that sits on top of existing cloud or on-premises object stores. It enhances these storage systems with a transaction log and rich metadata management.
The architecture is designed to be scalable, fault-tolerant, and engine-agnostic, while delivering strong consistency guarantees.
4.1. The Data Layer
The fundamental building block of Delta Lake is the parquet file format. Parquet is a columnar storage format that is highly efficient for analytical queries.
Data is written to parquet files in the underlying storage system, which can be any cloud-based object store, including Amazon S3, Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS), Google Cloud Storage (GCS), or Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
Because it works with our current storage layer instead of replacing it, we can introduce Delta Lake gradually without migrating to a proprietary platform.
Parquet stores the actual data records, organized into partitions and often optimized for common query patterns. Moreover, these files remain compatible with any engine that can read Parquet, even without leveraging Delta Lake’s advanced features.
4.2. The Metadata Layer
For every Delta table, Delta Lake maintains a transaction log in a dedicated directory named _delta_log alongside the data files. This log is a series of JSON files (and Parquet checkpoints for performance) that record every change made to the table: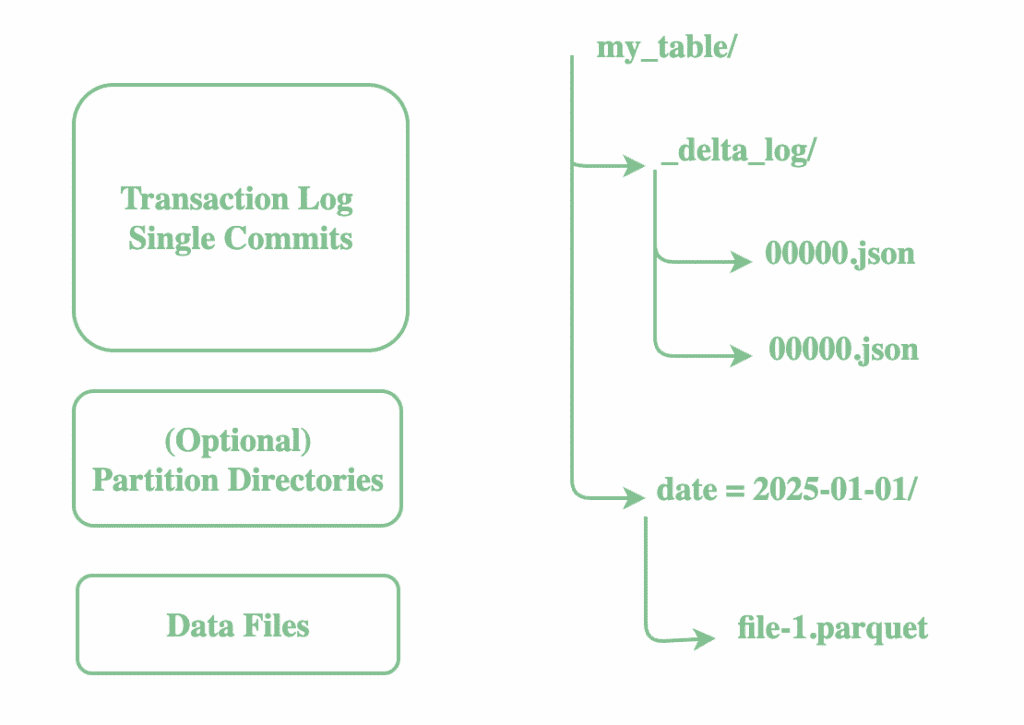
This log powers ACID transactions, supports time travel, and allows safe concurrent reads and writes. Each write to a Delta table appends a new JSON commit file containing:
- Added or removed data files
- Schema definition
- Partitioning information
- File statistics (min/max values, null counts, etc.)
This transaction log is the source of truth for the Delta table. Thus, to read the current state of a Delta table, the engine reads the transaction log to determine which data files are ‘active’ and what the current schema is.
4.3. The Compute Layer
The compute layer in Delta Lake is engine-agnostic, meaning it can work with various processing engines. While Apache Spark is the most commonly used engine, Delta Lake can also be queried using Trino, Presto, Flink, and Hive.
The engine first reads the _delta_log to determine the latest snapshot of the table when it executes a query. Using the metadata from the log, it identifies the specific Parquet files to scan.
Similarly, when we write new data, Delta Lake appends it as a Parquet file and updates the _delta_log. This prevents partial writes from corrupting the dataset and, once successful, records a new JSON entry capturing the updated state, schema, and file statistics.
To further enhance performance, the system applies optimizations such as caching, data skipping, and clustered reads during query execution.
5. Accessing Delta Lake
We must configure our environment to recognize the Delta format before we start creating and querying Delta tables. Open source Apache Spark does not bundle Delta Lake by default, so depending on where we run Spark, we may need to take a few additional steps.
5.1. Apache Spark
For vanilla Spark deployments, we need to explicitly add the Delta Lake library and configure Spark to understand Delta’s extended SQL features. To achieve this, we first need to add the Maven dependency in the pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.delta</groupId>
<artifactId>delta-core_2.12</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>We then instruct Spark to use Delta’s custom extensions and catalog. Spark applies this configuration when it creates the session:
SparkSession spark = SparkSession.builder()
.appName("DeltaExample")
.config("spark.sql.extensions", "io.delta.sql.DeltaSparkSessionExtension")
.config("spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog", "org.apache.spark.sql.delta.catalog.DeltaCatalog")
.getOrCreate();
We now create Delta tables using Spark DataFrame or SQL. Let’s now create a sample table at a temporary location and register it as a Delta table in Spark SQL:
public static String preparePeopleTable(SparkSession spark) {
try {
String tablePath = Files.createTempDirectory("delta-table-").toAbsolutePath().toString();
Dataset<Row> data = spark.createDataFrame(
java.util.Arrays.asList(
new Person(1, "Alice"),
new Person(2, "Bob")
),
Person.class
);
data.write().format("delta").mode("overwrite").save(tablePath);
spark.sql("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS people");
spark.sql("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS people USING DELTA LOCATION '" + tablePath + "'");
return tablePath;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}Now let’s verify that the table we created is indeed a Delta table:
@Test
void givenDeltaLake_whenUsingDeltaFormat_thenPrintAndValidate() {
Dataset<Row> df = spark.sql("DESCRIBE DETAIL people");
df.show(false);
Row row = df.first();
assertEquals("file:"+tablePath, row.getAs("location"));
assertEquals("delta", row.getAs("format"));
assertTrue(row.<Long>getAs("numFiles") >= 1);
}With these configurations, Spark knows how to interpret Delta’s transaction log and metadata. This means we can run SQL commands like MERGE INTO, VACUUM, or time-travel queries that are unique to Delta Lake.
5.2. Databricks
Delta Lake is fully integrated and enabled by default in Databricks. As a result, we can immediately create Delta tables using SQL or the DataFrame API, and explore advanced functionality like schema evolution, upserts, and time travel without any manual setup.
Additionally, Databricks provides notebook or console-based interfaces where users can query Delta Lake without needing to write connection logic themselves.
This seamless integration allows us to focus on building pipelines and analyzing data, rather than managing dependencies or configurations.
5.3. Other Engines
Delta Lake isn’t limited to Spark. It also works with other engines such as Trino, Presto, Flink, and Hive.
Tools like Trino and Presto connect through the Delta connector plugin, while Flink has its own dedicated Delta connector library. Hive also integrates with Delta through separate connectors.
The key thing to remember is that these connectors are not included by default and must be installed on your cluster before you can query Delta tables.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we explored the fundamentals of Delta Lake, including its key features and functionality.
Delta Lake transforms raw data lakes into reliable, high-performance platforms with ACID transactions, schema enforcement, time travel, and unified batch/streaming, ensuring accurate, consistent, and accessible data for any workload.
As always, the examples in this article are available over on GitHub.

















