Yes, we're now running our Black Friday Sale. All Access and Pro are 33% off until 2nd December, 2025:
What Is an Eavesdropping Attack?
Last updated: March 18, 2024
1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll discuss eavesdropping attacks with a practical example.
Furthermore, we’ll present the variants of eavesdropping attacks and some crucial prevention methods.
2. Eavesdropping Attack
An eavesdropping attack, also known as a wiretapping or listening attack, is a popular cyber attack in networking. In this attack, an attacker intercepts and listens to communications between two parties without their knowledge or consent.
An eavesdropping attack can be performed by physically tapping into a communication line or wire. Additionally, the attackers can use specialized software or hardware to intercept as well as decode wireless communication.
Eavesdropping attacks are a big threat to the integrity and confidentiality of the data. It allows an attacker to gather sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial data, or personal conversations, without the victim’s knowledge. Furthermore, attackers can use the extracted information for various malicious purposes, such as identity theft, extortion, or espionage.
Let’s look at the general steps in order to launch an eavesdropping attack:
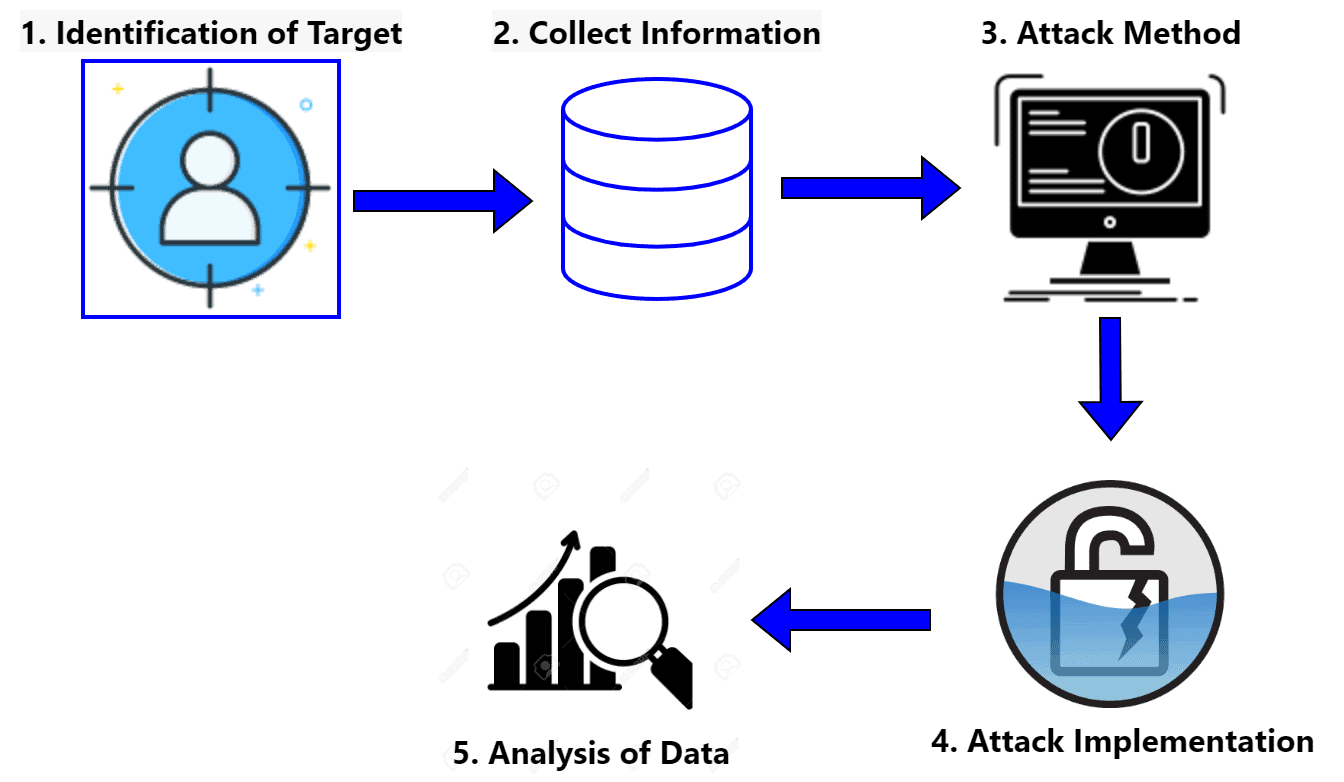
The first step is identifying a target for the attack, such as a specific individual or organization. As soon as the attacker identifies the target, it starts gathering information about it. Some useful information the attacker wants to extract includes the communication systems and vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
The next step is to choose an appropriate method for the successful execution of the attack. There’re several different methods that an attacker can use. Some examples are intercepting communication over unsecured networks, using malware to gain access to a device, or using hardware devices.
The next step is to execute the chosen method in the target system and intercept the target’s communication. Finally, the attacker analyzes the intercepted communication and extracts valuable information. They might also exfiltrate or remove data for further analysis.
3. Variants
An attacker can use several types of eavesdropping attacks to intercept and listen to communication between two parties. Some common eavesdropping attacks are man-in-the-middle (MITM), sniffing, physical wiretapping, eavesdropping on public Wi-Fi, and malware-based eavesdropping.
In a man-in-the-middle attack, an attacker intercepts communication between two parties. It acts as a relay, forwarding messages between the parties while secretly intercepting and reading them. MITM attacks can have severe consequences for both parties involved. For example, an attacker could intercept and alter financial transactions, leading to financial loss for one or both parties.
A sniffing attack involves using specialized software or hardware known as a sniffer. Specialized software or hardware captures and decodes wireless communication. The aim is to gather sensitive information or gain unauthorized access to networks or devices.
Physical wiretapping involves tapping into a communication line or wire to intercept and listen to communication. It can be done by splicing into a wire. Additionally, we can also use specialized wiretapping equipment.
We can always find some unencrypted public Wi-Fi networks. Unencrypted networks make it easy for attackers to intercept and listen to communication. These attacks can be particularly dangerous for people who use public Wi-Fi to conduct sensitive transactions, such as online banking or shopping.
Finally, attackers can design malware to intercept and transmit sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial data. The malware is typically delivered to the target through a phishing email or a malicious website. Malware-based eavesdropping attacks can be challenging to detect and prevent. These types of malware are often designed to operate in the background without the victim’s knowledge.
4. Example
Let’s talk about some practical examples of eavesdropping attacks.
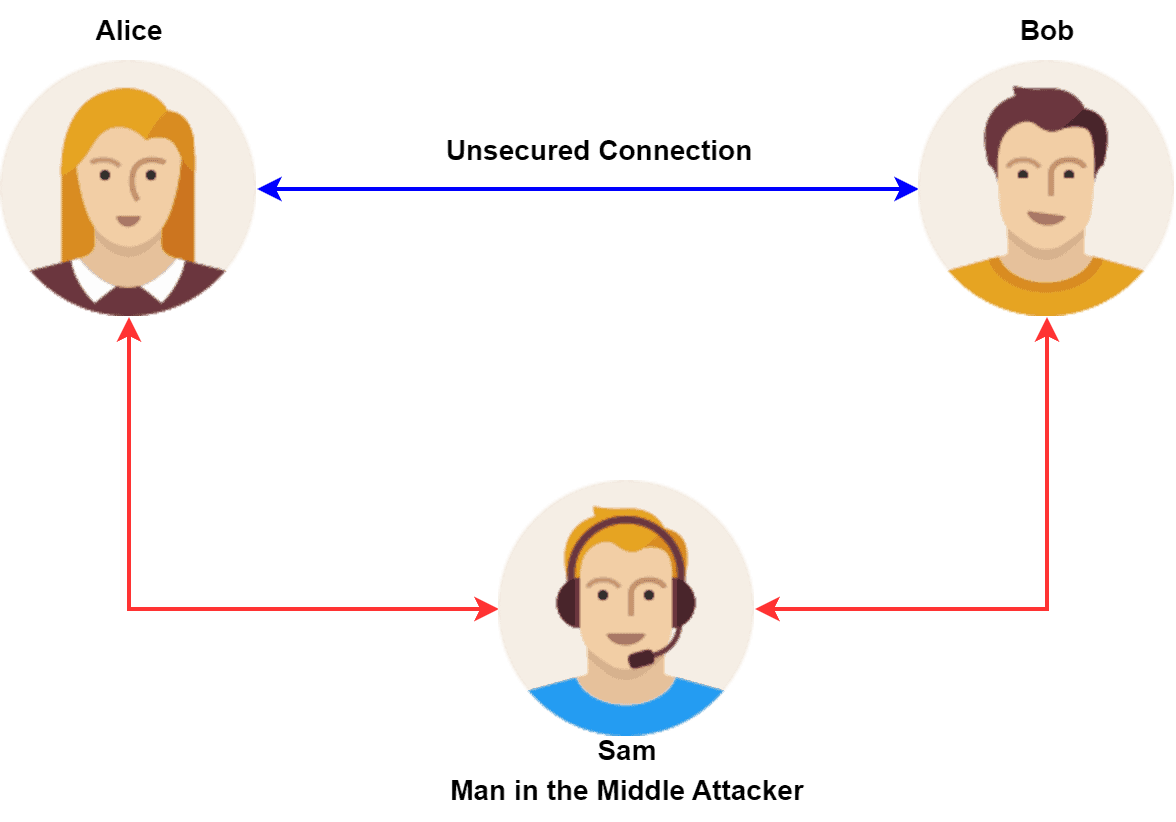
The first example explores a man-in-the-middle attack. Suppose Alice and Bob are communicating over an unsecured network. An attacker named Sam wants to intercept their communication. Sam can set up a fake wireless access point and trick Alice and Bob into connecting to it.
In this way, Sam can insert herself into the middle of the communication between Alice and Bob. Furthermore, Sam can intercept and read all of the messages sent between Alice and Bob. Additionally, Sam can potentially modify or inject new messages into the conversation:
Let’s consider another scenario where two individuals, Alice and Bob, communicate with each other over a public Wi-Fi network at a coffee shop. An attacker, Sam, is also connected to the same Wi-Fi network. Additionally, he can use software tools to intercept and read the data exchanged between Alice and Bob.
Sam can use various techniques, such as packet sniffing or man-in-the-middle attacks, to gain access to their communications. Additionally, Sam can access sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card information, and other sensitive data.
5. Impact
Eavesdropping attacks can have significant impacts on a network. Additionally, individuals and organizations relying on the network may face implications. An eavesdropping attack’s potential effects include loss of sensitive information, damage to reputation, loss of trust, financial losses, and legal consequences.
Eavesdropping attacks can allow attackers to intercept and listen to sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial data, or personal conversations. The attackers can use such sensitive information for various malicious purposes, such as identity theft, extortion, or espionage. Additionally, an eavesdropping attack that is successful in intercepting sensitive information can damage the reputation of the affected individuals or organizations.
If an eavesdropping attack is discovered, it can cause a loss of trust in the affected individuals or organizations. Additionally, it can result in financial losses, such as the cost of repairing damage or restoring lost data or the loss of business due to a damaged reputation.
Finally, an eavesdropping attack may violate laws or regulations, such as privacy laws or data protection regulations. It can result in legal and regulatory consequences for the affected individuals or organizations.
6. Prevention Techniques
We can use several techniques to prevent eavesdropping attacks. Some popular techniques include encryption, virtual private networks, secure communication protocols, firewalls, and network segmentation.
Encrypting communication makes it difficult for attackers to intercept and read messages. In order to encrypt communication, we can use different types of encryption algorithms, such as symmetric key algorithms and public key algorithms. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is an example of a symmetric key algorithm. Additionally, Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA) is a widely used public key algorithm.
Virtual private networks (VPNs) create a secure, encrypted connection between a device and a remote server. They can help to prevent eavesdropping attacks by encrypting communication and making it difficult for attackers to intercept.
Several secure communication protocols can be used to prevent eavesdropping attacks, such as HTTPS, SFTP, and SSH. These protocols use encryption and other security measures to protect communication from being intercepted. Firewalls can also prevent unauthorized access to communication lines or devices. By using a set of rules, it controls incoming and outgoing network traffic.
Finally, network segmentation is a widespread technique utilized to prevent eavesdropping attacks. Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller and isolated segments. Furthermore, it can help to prevent attackers from accessing sensitive information or systems.
On top of all the techniques, educating employees and users about the risks of eavesdropping attacks and the importance of using secure communication methods can help prevent these attacks.
7. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we discussed eavesdropping attacks with a practical example.
Furthermore, we presented the variants of eavesdropping attacks and some prevention methods.