Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
How Do I Generate a Dashboard Report in JMeter?
Last updated: January 8, 2024
1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll explore the JMeter dashboard report generation. JMeter is a popular testing tool written in Java. We use JMeter for load, performance, and stress testing. Besides generating rich statistical data, an important feature is to display the test results in a useful visual format. JMeter does that exactly and allows us to generate dashboard reports besides text reports in multiple formats.
2. Prerequisites
We need a Spring Boot app with the JMeter maven plugin. We have set up a sample Spring Boot MVC app with three endpoints. The endpoints return a greeting message, a quote of the day, and the server time. This is all we need to run our JMeter tests and generate a dashboard report.
3. Run JMeter Tests
Now, let’s look into running the JMeter tests against our app endpoints.
3.1. Create a JMeter Test Plan
Using JMeter GUI, we’ll generate a JMeter test plan.
Let’s create a test plan ReportsDashboardExample.jmx by using the JMeter GUI:
${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/dashboard/ReportsDashboardExample.jmxBesides saving our test plan in a file, we can also load an existing one back into our JMeter GUI. Furthermore, we can review and update it according to our needs. In our case, we have a very simple test plan which is enough for our demo purposes.
When we execute our test plan ReportsDashboardExample.jmx, it generates the test results into a CSV file ReportsDashboardExample.csv.
Next, let’s generate the JMeter dashboard reports. JMeter uses our test results available in the ReportsDashboardExample.csv file to generate the dashboard reports.
3.2. Configure the JMeter Maven Plugin
The JMeter Maven Plugin configurations are important:
<configuration>
<testFilesDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/dashboard</testFilesDirectory>
<resultsDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/dashboard</resultsDirectory>
<generateReports>true</generateReports>
<ignoreResultFailures>true</ignoreResultFailures>
<testResultsTimestamp>false</testResultsTimestamp>
</configuration>The generateReports element set to true instructs the plugin to generate the dashboard reports. The JMeter generates the reports under the target/jmeter directory by default. However, we can override the default behavior as well.
3.3. Generate the Dashboard Report
In order to run the JMeter tests, we have created a Maven profile named dashboard. Setting the environment variable named ‘env’ to the value of ‘dash’ maps and activates the dashboard profile:
...
<profile>
<id>dashboard</id>
<activation>
<property>
<name>env</name>
<value>dash</value>
</property>
</activation>
...The Maven command to run our code using this profile is:
mvn clean install -Denv=dashAlthough we can alter the global settings, setting up a separate profile isolates our specific dependencies, plugins, and configurations. This allows us to avoid touching any of the other profiles and global sections in our pom.xml.
3.4. View the Dashboard Reports
During the test run, the generated logs give us the reports destination path besides other information:
[INFO] Will generate HTML report in [PATH_TO_REPORT]Open the index.html from this path, and we get the dashboard view:
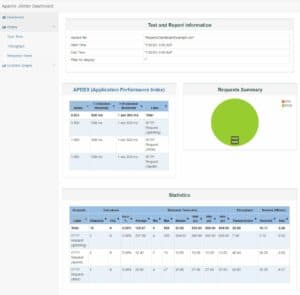
This dashboard presents the statistics from our tests in a nice format for each of the three endpoints. The corresponding charts support our tabular data. The pie chart is all green, which indicates all of our tests are successful. However, we can introduce some errors too to make it more real. For example, we can create an HTTP Request Sampler that points to a non-existing endpoint. Consequently, this will introduce a red area in the pie chart, too.
This concludes our dashboard report generation exercise. Next, we take a look at our project configurations.
4. The Maven Goals
One of our targets is to run a sample app in our test env. Hence, our JMeter tests are able to use the target endpoints from our local test env. Let’s dive into the corresponding pom.xml configurations.
4.1. The Spring Boot Maven Plugin
In our case, we want the Maven goals to run the Spring Boot app as a daemon. Therefore, we use the start and stop goals from the spring-boot-maven-plugin. Moreover, these two goals wrap the goals from the JMeter Maven plugin.
The Spring Boot Maven plugin start goal keeps the web server running until we stop it:
<execution>
<id>launch-web-app</id>
<goals>
<goal>start</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.baeldung.dashboard.DashboardApplication</mainClass>
</configuration>
</execution>The last goal in our Maven profile is the corresponding stop goal:
<execution>
<id>stop-web-app</id>
<goals>
<goal>stop</goal>
</goals>
</execution>4.2. The JMeter Maven Plugin
We wrap the goals from the JMeter Maven Plugin between Spring Boot start and stop goals. We want to keep the Spring Boot app running while the JMeter tests complete their execution. Our pom.xml file defines the configure, jmeter, and results goals from the jmeter-maven-plugin. Moreover, the execution with id jmeter-tests executes two goals: the jmeter goal and the results goal:
...
<execution>
<id>jmeter-tests</id>
<goals>
<goal>jmeter</goal>
<goal>results</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
...In some cases, if an error occurs, the last goal that stops the server fails to execute, thus resulting in the web server running forever. However, we can manually stop the web server. We’ll have to find out the process id for our Spring Boot app and then kill the process manually from our command line or Bash shell.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we’ve learned about the generation of JMeter dashboard reports. Getting visual reports is always a more useful, efficient, and easy way to analyze data than mere text.
In our case, we’re using JMeter to test web endpoints. JMeter also covers other use cases as well. A few examples are testing RESTful services, databases, and messaging services.
We can also add assertions to create pass/fail criteria. The JMeter GUI gives an easier interface to build your test plans. In production, however, we use Non-GUI mode for JMeter because the GUI mode is resource-intensive.
We can also use a cluster of resources to run our JMeter tests with a bigger load. This is a typical configuration for JMeter testing at scale.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















