Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
Distributed Performance Testing with JMeter
Last updated: January 8, 2024
1. Overview
In this article, we’ll explore distributed performance testing using JMeter.
2. What Is Distributed Performance Testing?
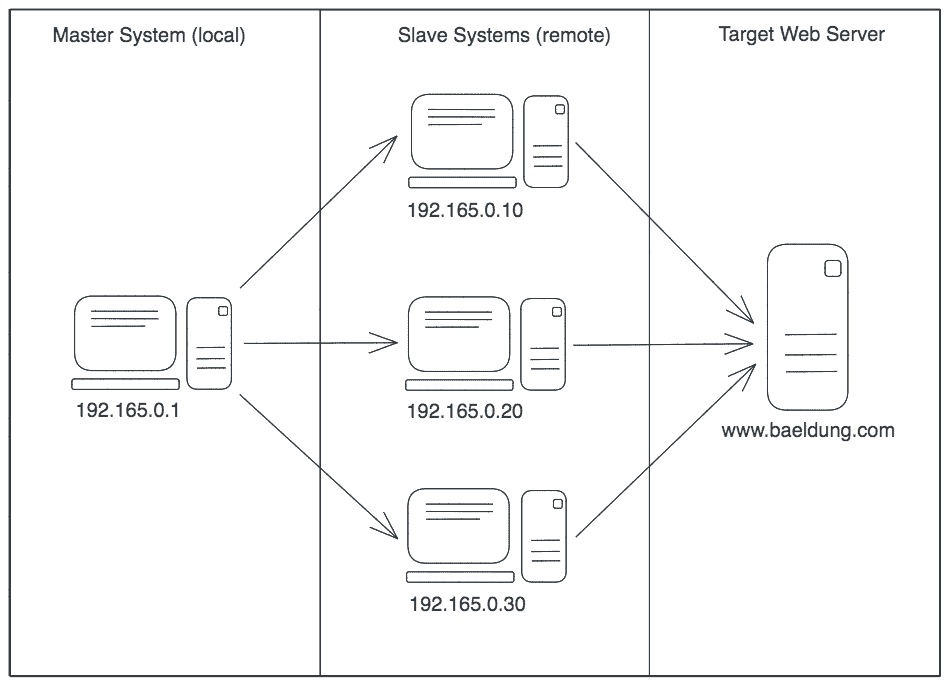
Distributed performance testing means using multiple systems with the master-slave configuration to test a web application or a server’s performance.
In this process, we’ll use a local client as a master that handles the test execution using multiple remote clients, and each remote client acting as a slave will execute the test on our target server.
Each slave system executes the load tests following the exact condition set by the master. Therefore, the distributed performance testing helps us achieve a higher number of concurrent users requesting the target server.
In simple terms, the outline of the distributed performance testing using JMeter will look like:
3. Setup
3.1. Prerequisites
We should follow a few prerequisites for a smooth setup and test run:
- Multiple computers with JMeter installed on each
- Firewalls on the systems are turned off, or required ports are opened for connection
- All systems (master/slave) are on the same subnet
- JMeter on each system can access the target server
- Use the same version of Java and JMeter on all systems (master and slave)
- For simplicity, disable the SSL for RMI
Now that we have our systems ready, let’s configure the slave and master systems.
3.2. Configure the Slave System
On the slave system, we’ll go to the jmeter/bin directory and execute the jmeter-server.bat file on Windows. Or, we can run the jmeter-server file on Unix.
3.3. Configure the Master System
On the master system, we’ll go to the jmeter/bin directory and edit the remote_hosts property in the jmeter.properties file to add IP addresses (comma-separated) of the slave systems:
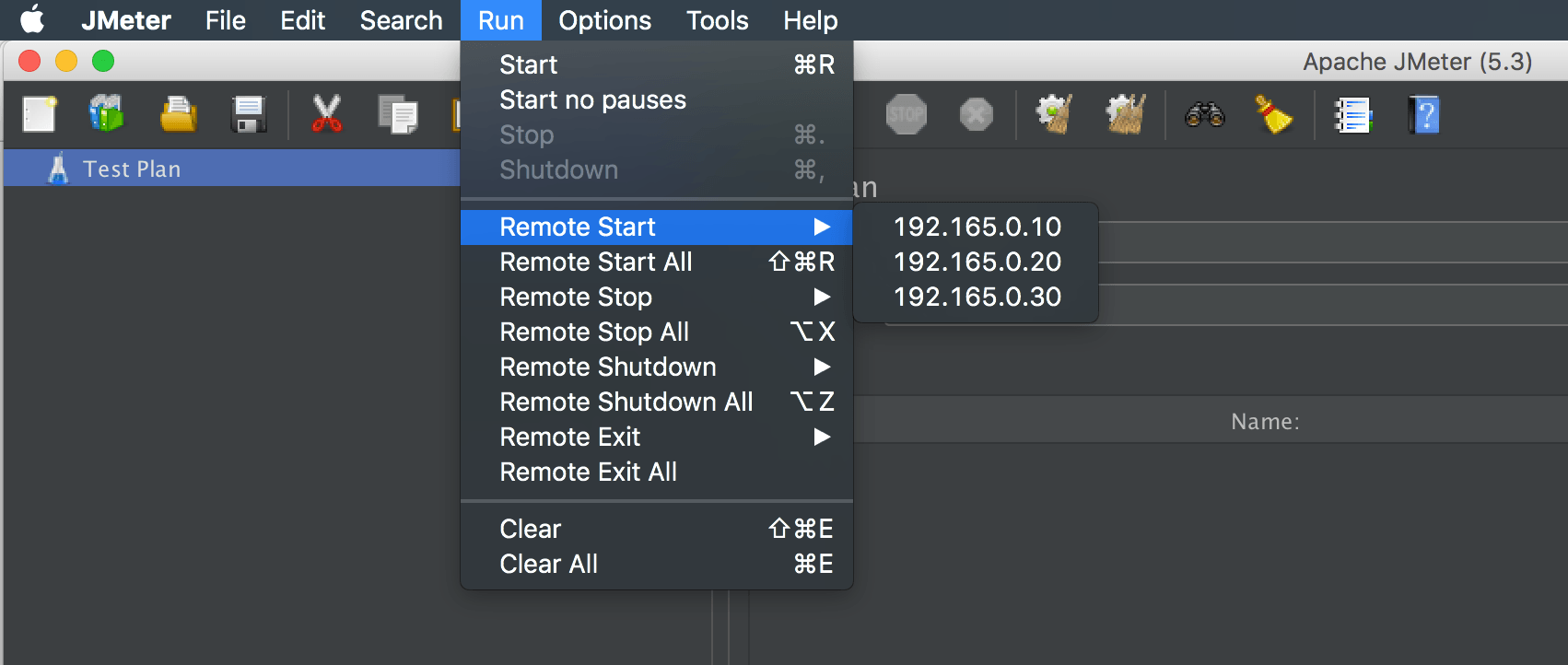
remote_hosts=192.165.0.10,192.165.0.20,192.165.0.30Here, we’ve added three slave systems.
So, by starting the JMeter (master) in the GUI mode, we can confirm all the slaves listed in the Run > Remote Start option:
That’s it! We’re ready to start the JMeter master system to execute tests on the target server using multiple clients.
4. Remote Testing
For remote testing, we can run JMeter in GUI mode for simplicity. However, we should run it using CLI mode when performing actual tests.
First, we’ll create a simple test plan in the master system that contains the HTTP Request sampler to request our baeldung.com server, and a View Results Tree listener.
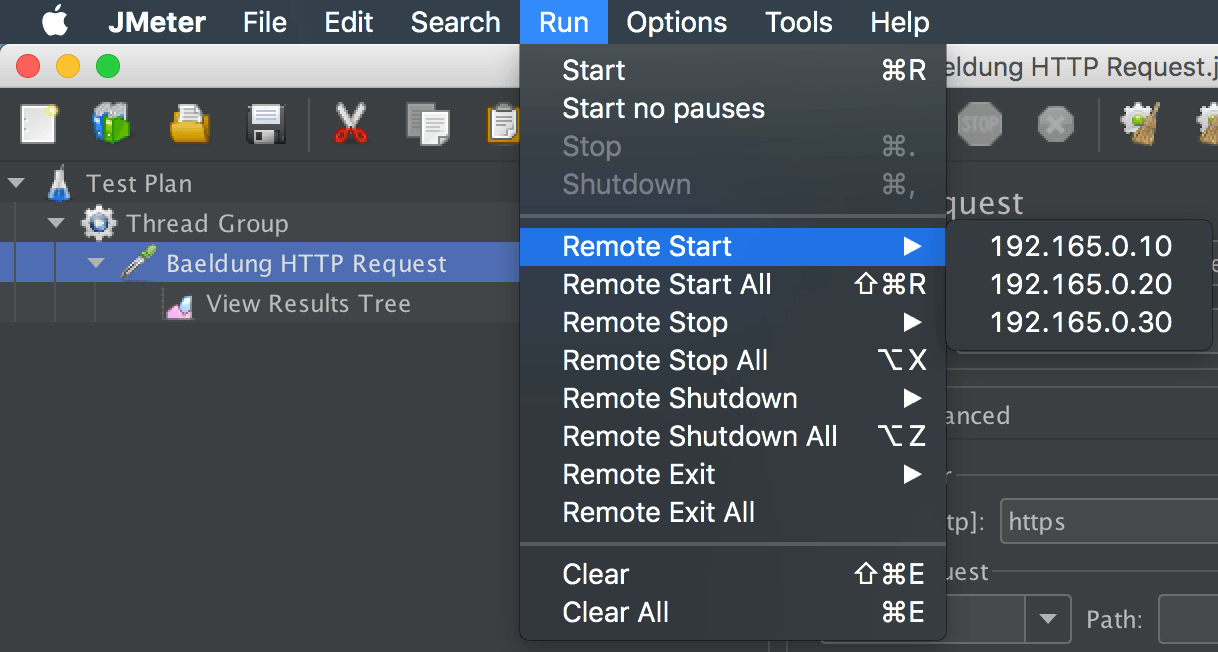
4.1. Starting a Single Slave
Then, we can choose which slave system to run using GUI mode by using the Run > Remote Start option:
4.2. Starting All Slaves
Similarly, we can choose to run all slave systems by using the Run > Remote Start All option:
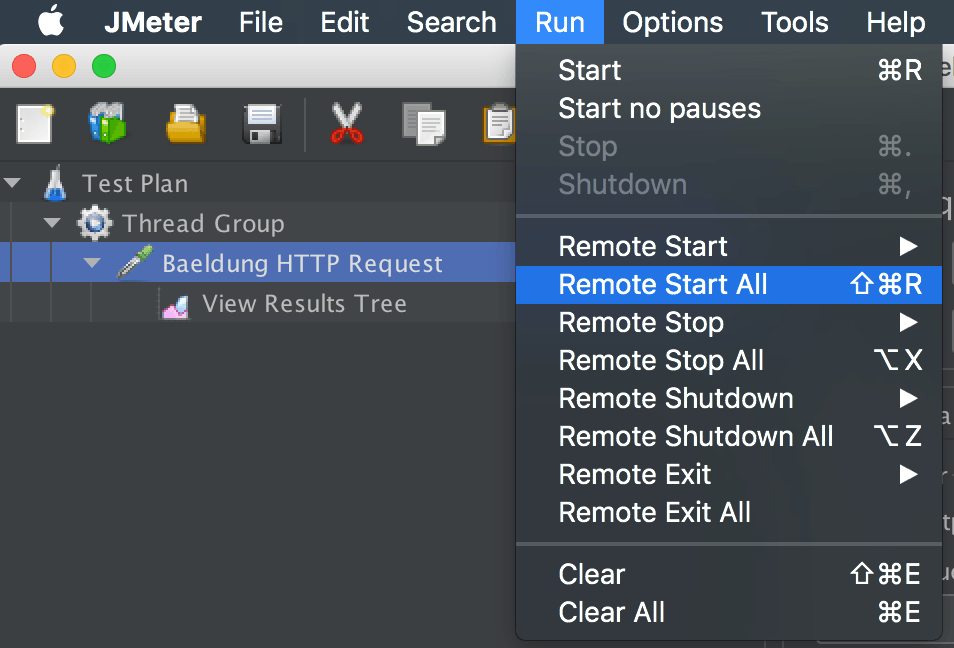
Additionally, a few options are available to handle test execution on the slave systems like Remote Stop, Remote Stop All, and Remote Shutdown All.
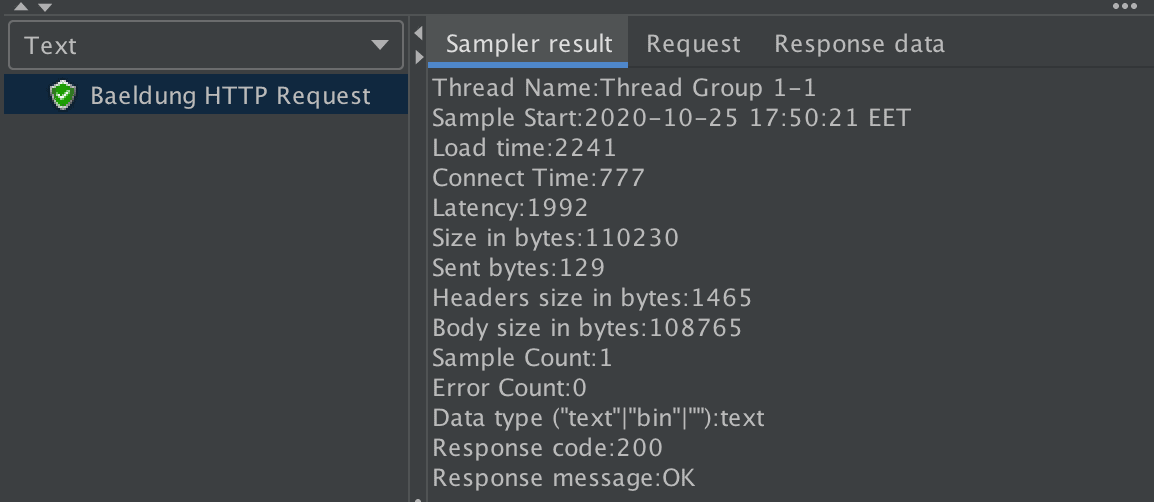
4.3. Test Results
Finally, we can see the test results in the local JMeter (master) once test execution finishes:
Also, on the remote JMeter systems (slaves), we can find logs about the start/stop of the test execution:
Starting the test on host 192.165.0.10 @ Sun Oct 25 17:50:21 EET 2020
Finished the test on host 192.165.0.10 @ Sun Oct 25 17:50:25 EET 20205. Conclusion
In this quick tutorial, we’ve seen how to get started with distributed performance testing using JMeter.
First, we looked at a few prerequisites for a smooth setup and test run. Then, we configured our slaves and master systems for a distributed performance testing environment.
Last, we started the slave systems, ran tests from a master system, and observed the results.

















