Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
What Causes java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread
Last updated: January 8, 2024
1. Introduction
In this tutorial, we’ll discuss the cause and possible remedies of the java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread error.
2. Understanding the Problem
2.1. Cause of the Problem
Most Java applications are multithreaded in nature, consisting of multiple components, performing specific tasks, and executed in different threads. However, the underlying operating system (OS) imposes a cap on the maximum number of threads that a Java application can create.
The JVM throws an unable to create new native thread error when the JVM asks the underlying OS for a new thread, and the OS is incapable of creating new kernel threads also known as OS or system threads. The sequence of events is as follows:
- An application running inside the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) requests for a new thread
- The JVM native code sends a request to the OS to create a new kernel thread
- The OS attempts to create a new kernel thread which requires memory allocation
- The OS refuses native memory allocation because either
- The requesting Java process has exhausted its memory address space
- The OS has depleted its virtual memory
- The Java process then returns the java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread error
2.2. Thread Allocation Model
An OS typically has two types of threads – user threads (threads created by a Java application) and kernel threads. User threads are supported above the kernel threads and the kernel threads are managed by the OS.
Between them, there are three common relationships:
- Many-To-One – Many user threads map to a single kernel thread
- One-To-One – One user thread map to one kernel thread
- Many-To-Many – Many user threads multiplex to a smaller or equal number of kernel threads
3. Reproducing the Error
We can easily recreate this issue by creating threads in a continuous loop and then make the threads wait:
while (true) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.HOURS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}Since we are holding on to each thread for an hour, while continuously creating new ones, we will quickly reach the max number of threads from the OS.
4. Solutions
One way to address this error is to increase the thread limit configuration at the OS level.
However, this is not an ideal solution because the OutOfMemoryError likely indicates a programming error. Let’s look at some other ways to solve this problem.
4.1. Leveraging Executor Service Framework
Leveraging Java’s executor service framework for thread administration can address this issue to a certain extent. The default executor service framework, or a custom executor configuration, can control thread creation.
We can use the Executors#newFixedThreadPool method to set the maximum number of threads that can be used at a time:
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
Runnable runnableTask = () -> {
try {
TimeUnit.HOURS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Handle Exception
}
};
IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10)
.forEach(i -> executorService.submit(runnableTask));
assertThat(((ThreadPoolExecutor) executorService).getQueue().size(), is(equalTo(5)));In the above example, we first create a fixed-thread pool with five threads and a runnable task which makes the threads wait for one hour. We then submit ten such tasks to the thread pool and asserts that five tasks are waiting in the executor service queue.
Since the thread pool has five threads, it can handle a maximum of five tasks at any time.
4.2. Capturing and Analyzing the Thread Dump
Capturing and analyzing the thread dump is useful for understanding a thread’s status.
Let’s look at a sample thread dump and see what we can learn:
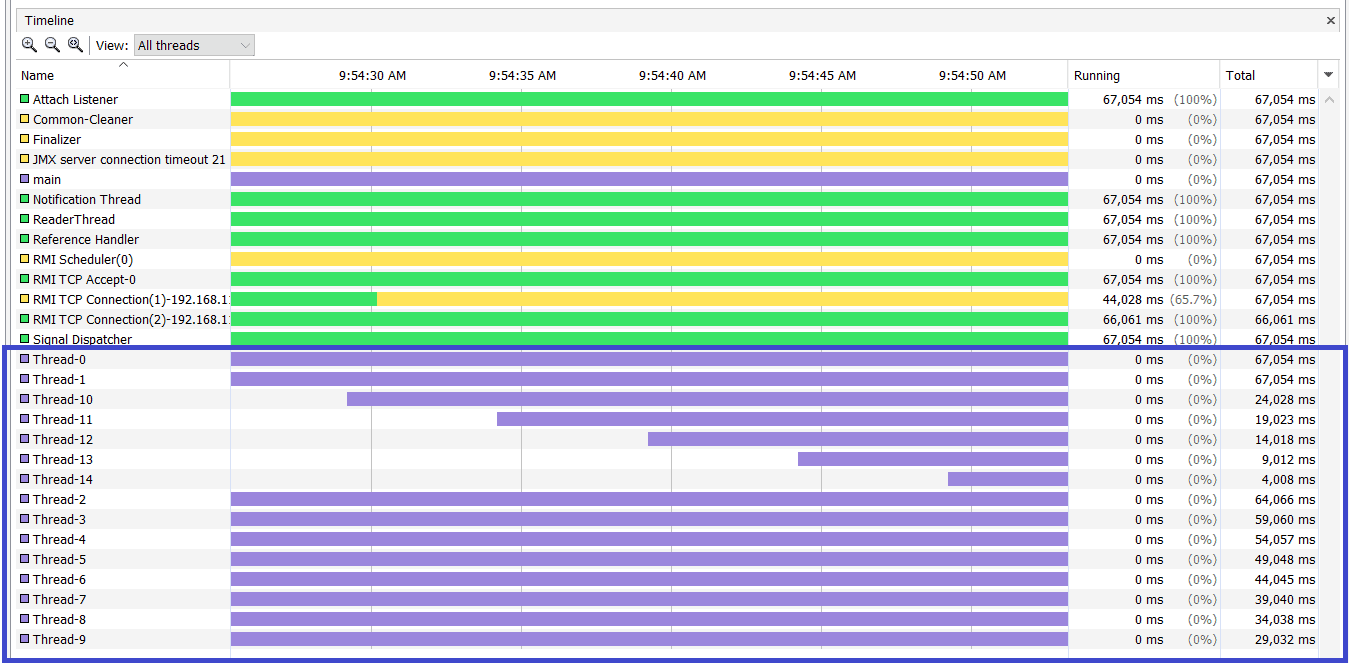
The above thread snapshot is from Java VisualVM for the example presented earlier. This snapshot clearly demonstrates the continuous thread creation.
Once we identify that there’s continuous thread creation, we can capture the thread dump of the application to identify the source code creating the threads:
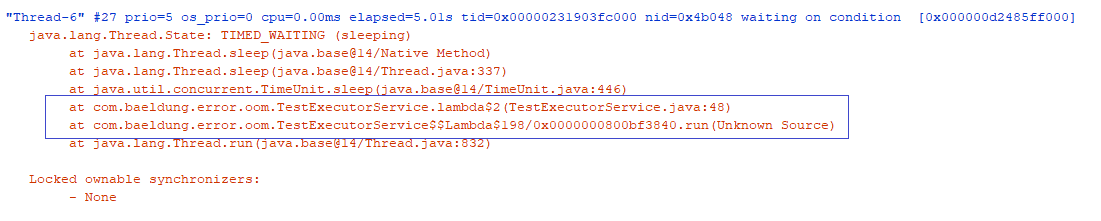
In the above snapshot, we can identify the code responsible for the thread creation. This provides useful insight to take appropriate measures.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we learned about the java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: unable to create new native thread error, and we saw that it’s caused by excessive thread creation in a Java application.
We explored some solutions to address and analyze the error by looking at the ExecutorService framework and thread dump analysis as two useful measures to tackle this issue.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.
















