1. Introduction
In this tutorial, we’re going to discuss how to choose the proper collection interface and class in the Java library. We skip legacy collections, such as Vector, Stack, and Hashtable in our discussion as we need to avoid using them in favor of the new collections. Concurrent collections deserve a separate topic, so we don’t discuss them either.
2. Collection Interfaces in the Java Library
It’s very useful to know the organization of the collection interfaces and classes in the Java library before trying to use them efficiently. The Collection interface is the root of all the collection interfaces. List, Set, and Queue interfaces extend the Collection.
Maps in the Java library are not treated as regular collections, so the Map interface doesn’t extend Collection. Here’s the diagram for interface relationships in the Java library:
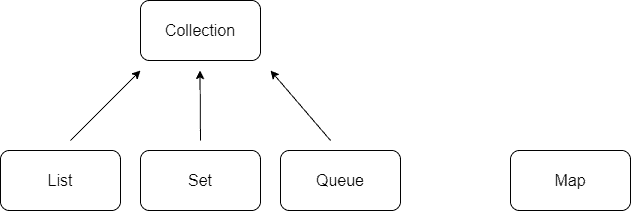
Any concrete collection implementation (collection class) is derived from one of the collection interfaces. The semantics of collection classes are defined by their interfaces, as concrete collections provide specific implementations for operations that their parent interfaces define. Consequently, we need to choose the proper collection interface before selecting the suitable collection class.
3. Choose the Right Collection Interface
Choosing the right collection interface is somewhat straightforward. Indeed, the diagram below shows a logical interface selection flow:
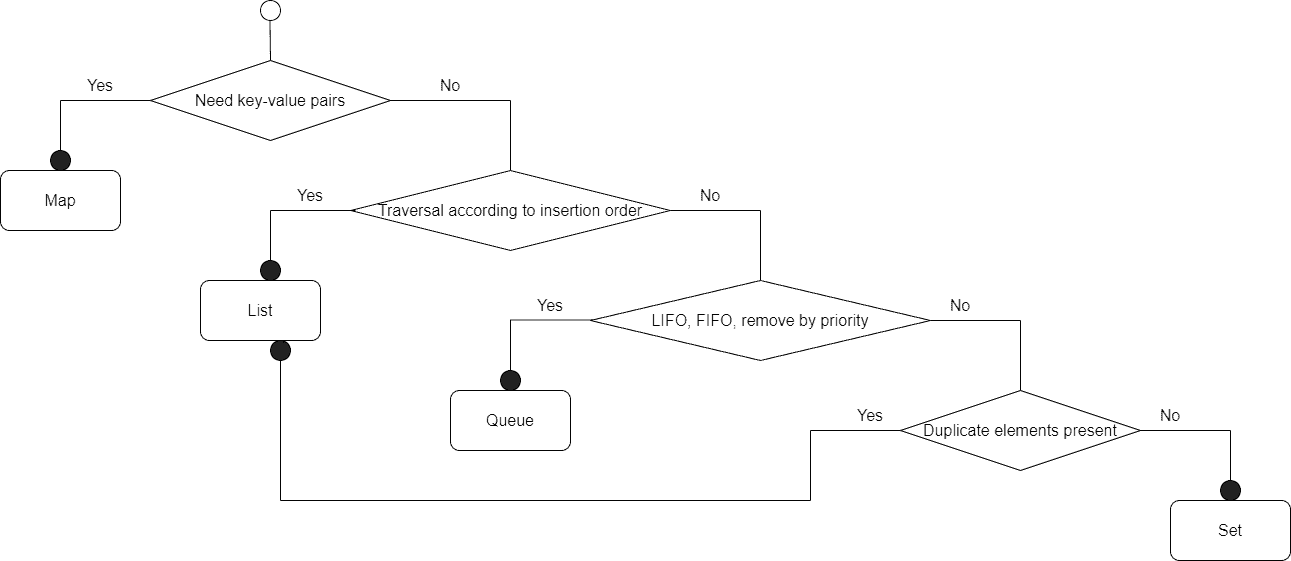
To summarize, we use lists when the insertion order of elements matters and there are duplicate elements. Sets are used when elements are treated as a set of objects, there are no duplicates, and the insertion order doesn’t matter.
Queues are used when LIFO, FIFO, or removal by priority semantics is required, and finally, maps are used when the association of keys and values is needed.
4. Choose the Right Collection Implementation
Below we can find the comparison tables of collection classes separated by the interfaces they implement. The comparisons are made based on common operations and their performance. Specifically, the performance of operations is estimated using Big-O notation. A more practical guide to operations’ duration in Java collections can be found in the benchmark of collection operations.
4.1. Lists
Let’s start with a list comparison table. Common operations for lists are adding and removing elements, accessing an element by index, traversal of the elements, and finding an element:
| Lists Comparison Table |
Add/remove element in the beginning |
Add/remove element in the middle |
Add/remove element in the end |
Get i-th element (random access) |
Find element |
Traversal order |
| ArrayList |
O(n) |
O(n) |
O(1) |
O(1) |
O(n), O(log(n)) if sorted |
as inserted |
| LinkedList |
O(1) |
O(1) |
O(1) |
O(n) |
O(n) |
as inserted |
As we can see, ArrayList is good at adding and removing elements in the end, as well as having random access to elements. Conversely, it’s bad at adding and removing elements at arbitrary positions. Meanwhile, LinkedList is good at adding and removing elements at any position. However, it doesn’t support true O(1) random access. So, regarding lists, the default choice is ArrayList until we need fast element addition and removal at any position.
4.2. Sets
For sets, we’re interested in adding and removing elements, traversal of elements, and finding an element:
| Sets Comparison Table |
Add element |
Remove element |
Find element |
Traversal order |
| HashSet |
amortized O(1) |
amortized O(1) |
O(1) |
random, scattered by the hash function |
| LinkedHashSet |
amortized O(1) |
amortized O(1) |
O(1) |
as inserted |
| TreeSet |
O(log(n)) |
O(log(n)) |
O(log(n)) |
sorted, according to elements comparison criterion |
| EnumSet |
O(1) |
O(1) |
O(1) |
according to the definition order of the enum values |
As we can see, the default choice is the HashSet collection, as it’s very fast for all the operations it supports. Furthermore, if also the insertion order of elements matters, we go with LinkedHashSet. Basically, it’s an extension of HashSet, which keeps track of elements’ insertion order by using a linked list structure internally.
If the elements need to be sorted and the sorted order needs to be preserved while adding and removing elements, then we go with TreeSet.
If the elements of the set are just enumeration values of a single enum type, then the wisest choice is EnumSet.
4.3. Queues
Queues can be divided into two groups:
- LinkedList, ArrayDeque – Queue interface implementations can act as the stack, queue, and dequeue data structures. Generally, ArrayDeque is faster than LinkedList. Hence it’s the default choice
- PriorityQueue – Queue interface implementation backed by the binary heap data structure. Used for fast (O(1)) element retrieval, which has the highest priority. Addition and removal work in O(log(n)) time
4.4. Maps
Similarly to sets, we consider the operations of adding and removing elements, traversal of elements, and finding an element for maps:
| Maps Comparison Table |
Add element |
Remove element |
Find element |
Traversal order |
| HashMap |
amortized O(1) |
amortized O(1) |
O(1) |
random, scattered by the hash function |
| LinkedHashMap |
amortized O(1) |
amortized O(1) |
O(1) |
as inserted |
| TreeMap |
O(log(n)) |
O(log(n)) |
O(log(n)) |
sorted, according to elements comparison criterion |
| EnumMap |
O(1) |
O(1) |
O(1) |
according to the definition order of the enum values |
The selection logic for maps is similar to the selection logic for sets: we use HashMap by default, LinkedHashMap if additionally, insertion order is important, TreeMap for sorting, and EnumMap when keys belong to values of a specific enum type.
Lastly, there are two implementations of the Map interface, which have very specific applications: IdentityHashMap, and WeakHashMap.
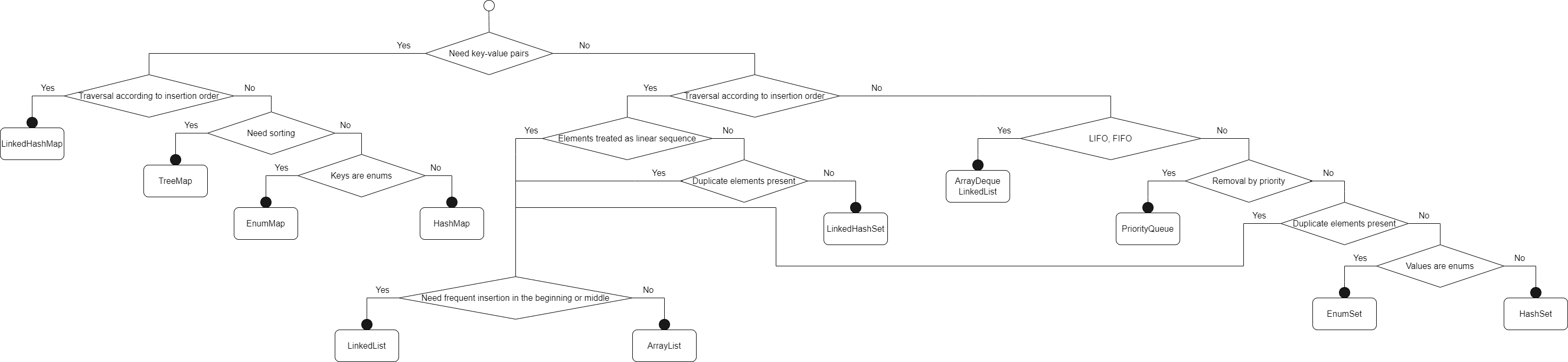
5. Concrete Collection Selection Diagram
We can extend the diagram for choosing the proper collection interface for selecting concrete collection implementations:
6. Conclusion
In this article, we went through collection interfaces and collection classes in the Java library. Moreover, we proposed methods for selecting the correct interface and implementation.



















