1. Introduction
In this tutorial, we’ll explore the EnumSet collection from the java.util package and discuss its peculiarities.
We’ll first show the main features of the collection and after that, we’ll go through the internals of the class in order to understand its benefits.
Finally, we’ll cover the main operations that it provides and implement some basic examples.
2. What Is an EnumSet
An EnumSet is a specialized Set collection to work with enum classes. It implements the Set interface and extends from AbstractSet:
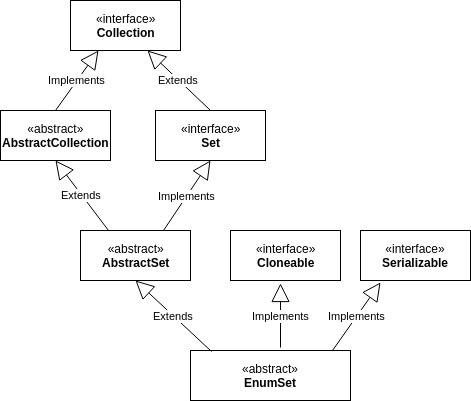
Even though AbstractSet and AbstractCollection provide implementations for almost all the methods of the Set and Collection interfaces, EnumSet overrides most of them.
When we plan to use an EnumSet we have to take into consideration some important points:
- It can contain only enum values and all the values have to belong to the same enum
- It doesn’t allow to add null values, throwing a NullPointerException in an attempt to do so
- It’s not thread-safe, so we need to synchronize it externally if required
- The elements are stored following the order in which they are declared in the enum
- It uses a fail-safe iterator that works on a copy, so it won’t throw a ConcurrentModificationException if the collection is modified when iterating over it
3. Why Use EnumSet
As a rule of thumb, EnumSet should always be preferred over any other Set implementation when we are storing enum values.
In the next sections, we’ll see what makes this collection better than others. In order to do so, we’ll briefly show the internals of the class to get a better understanding.
3.1. Implementation Details
EnumSet is a public abstract class that contains multiple static factory methods that allow us to create instances. The JDK provides 2 different implementations – are package-private and backed by a bit vector:
- RegularEnumSet and
- JumboEnumSet
RegularEnumSet uses a single long to represent the bit vector. Each bit of the long element represents a value of the enum. The i-th value of the enum will be stored in the i-th bit, so it’s quite easy to know whether a value is present or not. Since long is a 64-bit data type, this implementation can store up to 64 elements.
On the other hand, JumboEnumSet uses an array of long elements as a bit vector. This lets this implementation store more than 64 elements. It works pretty much like the RegularEnumSet but making some extra calculations to find the array index where the value is stored.
Unsurprisingly, the first long element of the array will store the 64 first values of the enum, the second element the next 64, and so on.
EnumSet factory methods create instances of one implementation or another depending on the number of elements of the enum:
if (universe.length <= 64)
return new RegularEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
else
return new JumboEnumSet<>(elementType, universe);
Keep in mind that it only takes into account the size of the enum class, not the number of elements that will be stored in the collection.
3.2. Benefits from Using an EnumSet
Due to the implementation of an EnumSet that we’ve described above, all the methods in an EnumSet are implemented using arithmetic bitwise operations. These computations are very fast and therefore all the basic operations are executed in a constant time.
If we compare EnumSet with other Set implementations like HashSet, the first is usually faster because the values are stored in a predictable order and only one bit needs to be examined for each computation. Unlike HashSet, there’s no need to compute the hashcode to find the right bucket.
Moreover, due to the nature of bit vectors, an EnumSet is very compact and efficient. Therefore, it uses less memory, with all the benefits that it brings.
4. Main Operations
The majority of the methods of an EnumSet work like any other Set, with the exception of the methods to create instances.
In the next sections, we’ll show in detail all the creational methods and we’ll cover briefly the rest of the methods.
In our examples, we’ll work with a Color enum:
public enum Color {
RED, YELLOW, GREEN, BLUE, BLACK, WHITE
}
4.1. Creational Methods
The most simple methods to create an EnumSet are allOf() and noneOf(). This way we can easily create an EnumSet containing all the elements of our Color enum:
EnumSet.allOf(Color.class);
Likewise, we can use noneOf() to do the opposite and create an empty collection of Color:
EnumSet.noneOf(Color.class);
If we want to create an EnumSet with a subset of the enum elements we can use the overloaded of() methods. It’s important to differentiate between the methods with a fixed number of parameters up to 5 different ones and the one that uses varargs:
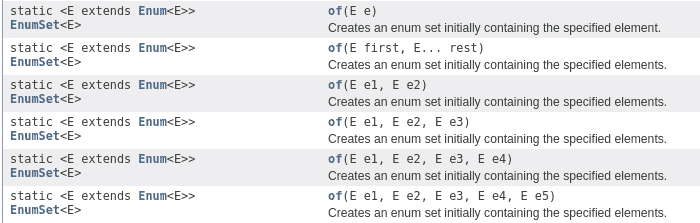
The Javadoc states that the performance of the varargs version can be slower than the others because of the creation of the array. Therefore, we should use it only if we initially need to add more than 5 elements.
Another way to create a subset of an enum is by using the range() method:
EnumSet.range(Color.YELLOW, Color.BLUE);
In the example above, the EnumSet contains all the elements from Yellow to Blue. They follow the order defined in the enum:
[YELLOW, GREEN, BLUE]
Notice that it includes both the first and last elements specified.
Another useful factory method is the complementOf() that allows us to exclude the elements passed as parameters. Let’s create an EnumSet with all the Color elements except black and white:
EnumSet.complementOf(EnumSet.of(Color.BLACK, Color.WHITE));
If we print this collection we can see that it contains all the other elements:
[RED, YELLOW, GREEN, BLUE]
Finally, we can create an EnumSet by copying all the elements from another EnumSet:
EnumSet.copyOf(EnumSet.of(Color.BLACK, Color.WHITE));
Internally, it calls the clone method.
Moreover, we can also copy all the elements from any Collection that contains enum elements. Let’s use it to copy all the elements of a list:
List<Color> colorsList = new ArrayList<>();
colorsList.add(Color.RED);
EnumSet<Color> listCopy = EnumSet.copyOf(colorsList);
In this case, the listCopy only contains the red color.
4.2. Other Operations
The rest of the operations work in the exact same way as any other Set implementation and there is no difference in how to use them.
Therefore, we can easily create an empty EnumSet and add some elements:
EnumSet<Color> set = EnumSet.noneOf(Color.class);
set.add(Color.RED);
set.add(Color.YELLOW)
Check if the collection contains a specific element:
set.contains(Color.RED);
Iterate over the elements:
set.forEach(System.out::println);
Or simply remove elements:
set.remove(Color.RED);
This, of course, among all the other operations that a Set supports.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we’ve shown the main features of EnumSet, its internal implementation and how we can benefit from using it.
We’ve also covered the main methods that it offers and implemented some examples to show how we can use them.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.


















