1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to speed up our Maven builds. We’ll present various techniques to optimize the build time and comment on their advantages and drawbacks.
2. General Recommendations
Before any optimization attempt, let’s recall that using the correct Maven phase could save us a lot of time. Why run a full install and pollute our local repository when we only need to compile the code?
On the other hand, in a multi-module project, it’s possible to rebuild only the changed modules and those that depend on them. For instance, if we make changes only in module1 and module2, we can run:
$ mvn clean install -pl module1,module2 -am
3. Using Multiple Threads
By default, the Maven build runs sequentially in a single thread. However, nowadays, all computers have multiple cores. Let’s take advantage of this to use the -T option and build our modules in parallel:
$ mvn clean install -T 1C
- -T 1C means Maven will use one thread per available core.
- -T 4 would force Maven to use four threads.
Last but not least, Maven Reactor ensures that all modules that depend on each other will run sequentially.
4. Optimizing Tests
Tests are a crucial part of software development. Nevertheless, running them less takes a lot of time.
4.1. Running Tests in Parallel
By default, the Surefire plugin runs unit tests sequentially. However, we can configure it to run them in parallel. For instance, to run all test suites in parallel and use one thread per available core, we’d run:
mvn clean install -Dparallel=all -DperCoreThreadCount=true
However, if we don’t have a lot of unit tests in our project, the overhead cost of parallelization could negate the speed gain.
4.2. Skipping Test Execution
Sometimes we don’t need to run the tests in our local environment. The Maven -DskipTests option skips the test execution while still compiling the test folder:
$ mvn clean install -DskipTests
In a highly-tested project, skipping tests when we don’t need them can save us time!
4.3. Skipping Test Compilation
Additionally, we can skip the test execution and not even compile them by using the -Dmaven.test.skip=true option:
$ mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true
This method reduces the total build time even more.
5. Optimizing JVM Parameters
By default, HotSpot JVM uses tiered compilation: it uses both the client and server compilers to optimize Java bytecode. This functioning optimizes long-lived processes on a server. However, a build is a succession of short-lived processes. Thus, let’s use the following JVM parameters:
- -XX:-TieredCompilation: the JVM won’t use tiered compilation
- -XX:TieredStopAtLevel=1: the JVM will use the client compiler only
We can have Maven use these options by creating a .mvn/jvm.config file with the following content:
-XX:-TieredCompilation -XX:TieredStopAtLevel=1
Maven uses caching and incremental build techniques to avoid recompiling unchanged code. Thus, the more new code Maven needs to compile, the more efficient this technique is.
6. Going Offline
Maven makes several round trips to the server during a build, for instance, for dependency resolution and plugin download. In particular, it will check for new snapshot updates every time. We can avoid that by going into offline mode:
$ mvn clean install -o
We can’t use offline mode when we need to update some dependencies.
7. Identifying the Bottleneck
If the previous techniques don’t help us to bring back the build time to something acceptable, we can troubleshoot our build thanks to a profiler. First, let’s create a new Maven project. Then, we’ll follow the instructions on the GitHub of the Maven Profiler project to install it. Lastly, we need to add the dependency in our pom.xml:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-profiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.7</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
We can now use it to get more insight into our build timings by launching the command:
$ mvn clean install -Dprofile
Once the build is complete, we can find the report as an HTML text inside the .profiler folder. Let’s have a look at it:
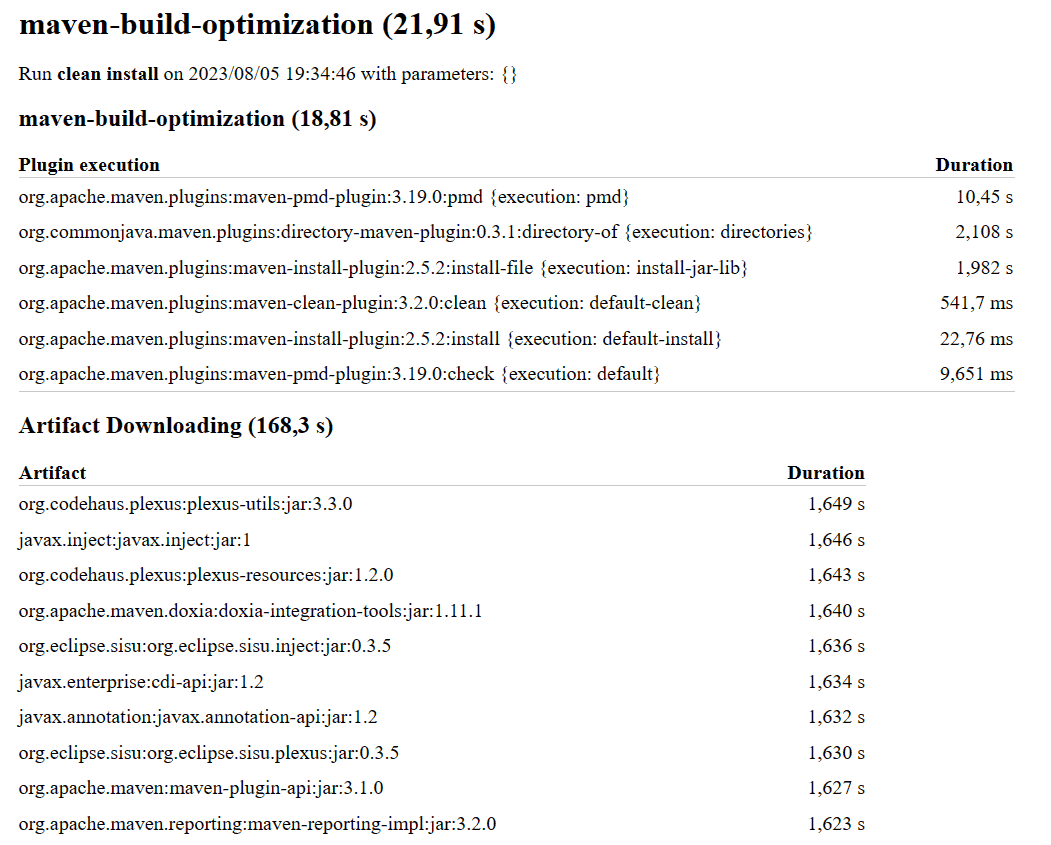
As we can see, the profiler lists all plugin executions and records the time they take. The second section lists the downloaded artifacts. This information can help us identify the plugins that take a long time to run while providing little to no value in the target environment.
8. Using Maven Profiles
Once we identify a bottleneck, we can use Maven profiles to skip them on demand and save time. For example, executing integration tests is generally very long. Moreover, running them every time in a local environment isn’t useful.
Let’s add the failsafe plugin configuration in our pom.xml:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
We can now add a profile for skipping them:
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>skipITs</id>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</profile>
</profiles>
Thanks to overriding the configuration, with the skipITs profile activated, the integration tests are now skipped:
$ mvn clean install -PskipITs
9. Using the Maven Daemon
The Maven daemon aims to improve Maven builds’ velocity. The daemon is a long-lived background process that remains active even after the build is completed. It reduces build overhead by keeping essential components in memory, enabling faster project builds by avoiding repeated startup and initialization processes. To install it, follow the instructions on the project’s GitHub page. Let’s now use it to launch the build:
$ mvnd clean install
If the daemon needs to start, the build time is slightly higher. Last but not least, we can combine the previous techniques with the Maven daemon. For instance, we can build via the daemon and skip the tests:
$ mvnd clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true
Nevertheless, let’s point out that since the Maven daemon is a long-lived process, setting up the JVM parameters as we did previously would probably do more harm than good. Let’s take a look at key Maven daemon commands:
9.1. ––status
We can use the ––status command to list all the currently running Maven daemons. Here’s what the output looks like after running the below command:
$ mvnd --status
The output provides information like Process ID, Address, Status, Resident set size (RSS), Last activity, and Java home:
ID PID Address Status RSS Last Activity Java Home
a0d06517 42987 inet:/127.0.0.1:57923 Idle 483m 2024-09-27T23:46:18.969 /opt/openjdk/Home
This output allows us to monitor the current state of all running Maven daemons and their resource usage.
9.2. ––stop
The ––stop command allows us to terminate all running Maven daemons. This is useful when we want to free up system resources. Here’s an example of what the output will look like:
$ mvnd --stop
The command stops all Maven daemons and displays the number of daemons that were terminated in the output:
Stopping 1 running daemons
10. Conclusion
In this article, we showcased various techniques to reduce the build time with Maven. In a nutshell, we should decide to start using the Maven daemon. Then, let’s remember to skip tests when we don’t need to run them. We can also profile the build and use Maven profiles to exclude time-consuming low-value tasks. If none of this is enough, we can try other techniques described in the article.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















