1. Overview
Sometimes, we may need to process a large number of elements in a for loop. Doing this sequentially may take a lot of time and keep the system underutilized.
In this tutorial, we’ll learn different ways to parallelize a for loop in Java to improve the performance of the application in such cases.
2. Sequential Processing
Let’s start by looking at how we can process elements sequentially in a for loop and measure the time taken to process the elements.
2.1. Sequential Processing With a for Loop
Firstly, we’ll create a for loop that runs 100 times and performs a heavy operation in each iteration.
Common examples of heavy operations are a database call, a network call, or CPU-intensive operation. To simulate the time taken by a heavy operation, let’s call the Thread.sleep() method in each iteration:
public class Processor {
public void processSerially() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
}
In the above code, we call the Thread.sleep() method in each iteration. This causes the execution to pause for 10 milliseconds. When we run the processSerially() method, it takes a high amount of time to process the elements sequentially.
We’ll optimize this method by parallelizing the for loop in the coming sections. And finally, we’ll compare the time taken by sequential processing and parallel processing.
3. Parallel Processing With ExecutorService
ExecutorService is an interface that represents an asynchronous execution mechanism. It allows us to submit tasks for execution and provides methods to manage them.
Let’s see how we can use the ExecutorService interface to parallelize the for loop:![]()
void processParallelyWithExecutorService() throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
List<CompletableFuture<Void>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, executorService);
futures.add(future);
}
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])).join();
executorService.shutdown();
}
Here are a few things to note in the code above:
- We create a thread pool of 10 threads using the newFixedThreadPool() method.
- Next, we submit tasks to the thread pool using the CompletableFuture.runAsync() method. The runAsync() method ensures the task supplied to it runs asynchronously in a separate thread.
- The method takes a Callable or Runnable object as an argument. In this case, we create a Runnable object using a lambda expression.
- The runAsync() method returns a CompletableFuture object. We add it to a list of CompletableFuture objects to be executed later using the thread pool in the executorService instance.
- Next, we combine the CompletableFuture objects using the CompletableFuture.allOf() method and call the join() operation on them. When join() is executed, the process waits for all CompletableFuture tasks to complete in parallel.
- Finally, we shut down the executor service using the shutdown() method. This method frees all the threads in the thread pool.
4. Parallel Processing With Streams
Java 8 introduced the Stream API, which has support for parallel processing. Let’s explore how the Stream API can parallelize the for loop.
4.1. Using Parallel Stream
Let’s see how we can use the parallel() method of the Stream API to parallelize the for loop:
void processParallelyWithStream() {
IntStream.range(0, 100)
.parallel()
.forEach(i -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
In the above code, we create a stream of integers using the IntStream.range() method. Next, we call the parallel() method to parallelize the stream.
Finally, we call the forEach() method to process the elements of the stream. For each element, we call the Thread.sleep() method to simulate a heavy operation.
4.2. Using StreamSupport
Another way to parallelize the for loop is to use the StreamSupport class. Let’s look at the code for the same:
void processParallelyWithStreamSupport() {
Iterable<Integer> iterable = () -> IntStream.range(0, 100).iterator();
Stream<Integer> stream = StreamSupport.stream(iterable.spliterator(), true);
stream.forEach(i -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
The StreamSupport class provides a stream() method that takes an Iterable object as an argument. In addition, it takes a boolean argument to indicate whether the stream should be parallel or not.
Here, we create an Iterable object using the IntStream.range() method. Next, we call the stream() method to create a stream of integers. Finally, we call the forEach() method to process the elements of the stream.
Both the parallel() method and the StreamSupport class work in a similar way. They create threads internally to process the elements of the stream. The number of threads created depends on the number of cores available in the system.
Now that we have seen different ways to parallelize the for loop, let’s compare the performance of each method. For this, let’s use Java Microbenchmark Harness (JMH). First, we need to add the JMH dependencies to our project.
Next, let’s add the @BenchmarkMode annotation to our methods and enable them to be benchmarked for average time:
@Benchmark
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
public void processSerially() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Thread.sleep(10);
}
}
Similarly, let’s do the same for all parallel processing methods.
To run the benchmarking, let’s create a main() method and set up JMH:
class Benchmark {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
org.openjdk.jmh.Main.main(new String[] { "com.baeldung.concurrent.parallel.Processor" });
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
From our main() method, we call the main() method of JMH and pass the path to our Processor class as an argument. This tells JMH to run Benchmarking on methods of the Processor class.
When we run the main() method, we see the below result:
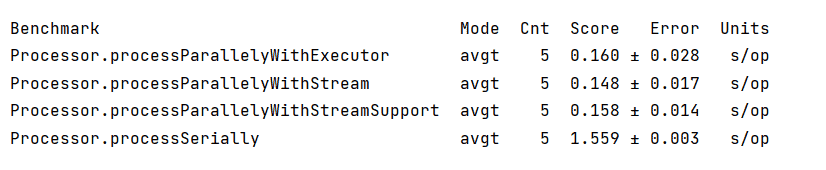
As we can see from the above results, the time taken to process the elements in parallel is much less than the time taken to process them sequentially.
Notably, the time taken to process the elements may vary from system to system. It depends on the number of cores available in the system.
Also, the time taken by each parallel method may vary in each run, and the numbers aren’t an exact comparison between these methods.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we looked at different ways to parallelize the for loop in Java. We explored how we can use the ExecutorService interface, the Stream API, and the StreamSupport utility to parallelize the for loop. Finally, we compared the performance of each method using JMH.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















