1. Overview
In this quick tutorial, we’ll show how to calculate the distance between two points in Java.
Let’s say we have two points on a plane: the first point A has the coordinates (x1, y1), and the second point B has the coordinates (x2, y2). We want to calculate AB, the distance between the points.
Firstly, let’s build a right triangle with the hypotenuse AB:
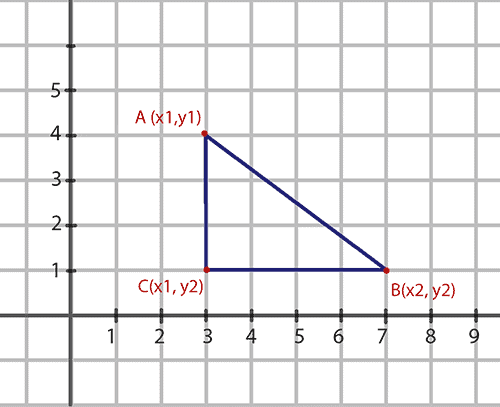
According to the Pythagorean theorem, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the triangle’s legs is the same as the square of the length of the triangle’s hypotenuse: AB2 = AC2 + CB2.
Secondly, let’s calculate AC and CB.
Obviously:
AC = y2 - y1
Similarly:
BC = x2 - x1
Let’s substitute the parts of the equation:
distance * distance = (y2 - y1) * (y2 - y1) + (x2 - x1) * (x2 - x1)
Finally, from the above equation we can calculate the distance between the points:
distance = sqrt((y2 - y1) * (y2 - y1) + (x2 - x1) * (x2 - x1))
Now let’s move on to the implementation part.
3. Java Implementation
Although java.lang.Math and java.awt.geom.Point2D packages provide ready solutions, let’s firstly implement the above formula as is:
public double calculateDistanceBetweenPoints(
double x1,
double y1,
double x2,
double y2) {
return Math.sqrt((y2 - y1) * (y2 - y1) + (x2 - x1) * (x2 - x1));
}
To test the solution, let’s take the triangle with legs 3 and 4 (as shown in the picture above). It’s clear that the number 5 is suitable as the value of the hypotenuse:
3 * 3 + 4 * 4 = 5 * 5
Let’s check the solution:
@Test
public void givenTwoPoints_whenCalculateDistanceByFormula_thenCorrect() {
double x1 = 3;
double y1 = 4;
double x2 = 7;
double y2 = 1;
double distance = service.calculateDistanceBetweenPoints(x1, y1, x2, y2);
assertEquals(distance, 5, 0.001);
}
3.2. Using java.lang.Math Package
If the result of multiplication in the calculateDistanceBetweenPoints() method is too big, overflow can occur. Unlike that, Math.hypot() method prevents intermediate overflow or underflow:
public double calculateDistanceBetweenPointsWithHypot(
double x1,
double y1,
double x2,
double y2) {
double ac = Math.abs(y2 - y1);
double cb = Math.abs(x2 - x1);
return Math.hypot(ac, cb);
}
Let’s take the same points as before and check that the distance is the same:
@Test
public void givenTwoPoints_whenCalculateDistanceWithHypot_thenCorrect() {
double x1 = 3;
double y1 = 4;
double x2 = 7;
double y2 = 1;
double distance = service.calculateDistanceBetweenPointsWithHypot(x1, y1, x2, y2);
assertEquals(distance, 5, 0.001);
}
3.3. Using java.awt.geom.Point2D Package
Finally, let’s calculate the distance with the Point2D.distance() method:
public double calculateDistanceBetweenPointsWithPoint2D(
double x1,
double y1,
double x2,
double y2) {
return Point2D.distance(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
Now let’s test the method in the same way:
@Test
public void givenTwoPoints_whenCalculateDistanceWithPoint2D_thenCorrect() {
double x1 = 3;
double y1 = 4;
double x2 = 7;
double y2 = 1;
double distance = service.calculateDistanceBetweenPointsWithPoint2D(x1, y1, x2, y2);
assertEquals(distance, 5, 0.001);
}
4. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve shown a few ways to calculate the distance between two points in Java.
As always, the code used in the examples is available over on GitHub.







