Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
Multiple Line Code Example in Javadoc Comment
Last updated: January 8, 2024
1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll explore different ways of formatting Javadoc comments. We’ll focus on analyzing the formatting of code snippets written as documentation comments.
2. Introduction
Javadoc is a tool for generating documentation for a Java class. It processes the documentation comments specified in a Java source file and generates a corresponding HTML page.
Please refer to our article to know more about Javadoc documentation.
3. Code Snippets as Javadoc Comments
We can include code snippets as part of documentation comments for a Java class. We want to view the code snippets with correct indentation and characters on the generated HTML page.
Let’s try to add a Java code snippet as part of our comments:
/**
* This is an example to show default behavior of code snippet formatting in Javadocs
*
* public class Application(){
*
* }
*
*/Corresponding HTML page:
By default, line breaks and spaces aren’t preserved in the Javadoc comments. This results in improper indentation, especially in the case of multiline code snippets.
Let’s find a way to maintain correct indentations in our comments.
3.1. Using the <pre> Tag
HTML provides the <pre> tag to indicate preformatted text. It preserves the spaces and line breaks of the enclosed text, thereby preserving the required indentation for code snippets:
/**
* This is an example to show usage of HTML pre tag while code snippet formatting in Javadocs
*
* <pre>
* public class Application(){
* List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
* }
*
* </pre>
*/Corresponding HTML page:

Here, we’ve successfully preserved the spaces and line breaks required for our code snippets. We’ve encountered a different problem now, though: We aren’t able to see the Generics entered as part of the code snippet.
As comments are parsed into an HTML page, parts of the code snippets can be misinterpreted as HTML tags, like <Integer> in the above example.
Let’s explore ways to keep correct formatting for HTML characters embedded within our comments.
3.2. Using HTML Character Entities
If our code snippet contains HTML reserved characters like ‘<’, ‘>’ or ‘&’, these can be interpreted as HTML characters while parsing the comments. To preserve these characters, we can use Character entities in place of the required characters.
For example, we can use < to denote ‘<’ character:
/**
* This is an example to show usage of HTML character entities while code snippet formatting in Javadocs
*
* <pre>
* public class Application(){
* List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
* }
*
* </pre>
*/Corresponding HTML page:

3.3. Using @code Tag
Javadoc provides a @code tag, which treats the comments embedded within brackets as source code instead of HTML characters. This enables us to use HTML reserved characters directly without escaping them using Character entities:
/**
* This is an example to show usage of javadoc code tag while code snippet formatting in Javadocs
*
* <pre>
*
* public class Application(){
* {@code List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(); }
* }
*
* </pre>
*/Corresponding HTML page:

Please note that the @code tag doesn’t address the indentation issues involved in our comments. For this, we need to use the <pre> tag additionally.
As we’ve seen above, Javadoc identifies the tags using ‘@’ characters. If we have ‘@’ as part of our code snippets, it’ll be misinterpreted by Javadoc, leading to the incorrect rendering of comments.
Let’s see this using an example:
/**
* This is an example to show issue faced while using annotations in Javadocs
*
* <pre>
*
* public class Application(){
* @Getter
* {@code List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(); }
* }
*
* </pre>
*/Corresponding HTML page:
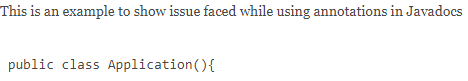
As we can see, Javadoc processes @Getter as a tag and comments aren’t rendered correctly. We can embed the annotations (or code using @ characters) within the @code tag provided by Javadoc:
/**
* This is an example to show usage of javadoc code tag for handling '@' character
*
* <pre>
*
* public class Application(){
* {@code @Getter}
* {@code List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(); }
* }
*
* </pre>
*/Corresponding HTML page:

3.4. Using @literal Tag
We can achieve similar behavior by using the @literal tag as well. The only difference between the @code tag and @literal tag is that the @code tag formats the enclosed text in code font:
/**
* This is an example to show difference in javadoc literal and code tag
*
* <p>
*
* {@literal @Getter}
* {@literal List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(); }
*
* <br />
* {@code @Getter}
* {@code List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(); }
* </p>
*/Corresponding HTML page:
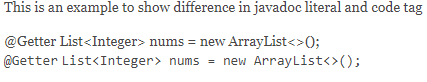
Thus, we got our code snippets rendered correctly on the HTML page.
3.5. Formatting jQuery Code Snippets
Here, we’ve taken an example of a Java code snippet. The same functionalities are applicable for any other language as well.
Let’s include a simple jQuery code snippet as documentation comment:
/**
* This is an example to illustrate a basic jQuery code snippet embedded in documentation comments
* <pre>
* {@code <script>}
* $document.ready(function(){
* console.log("Hello World!);
* })
* {@code </script>}
* </pre>
*/Corresponding HTML page:

3.6. Formatting HTML Code Snippets
So far, we’ve realized that on one hand, Javadoc enables us to use HTML tags for formatting our comments, while on the other hand, it can also lead to issues when we want to use HTML characters without markup.
For example, we may want to insert HTML code snippets in our comments.
Let’s insert an HTML code snippet as part of our documentation comment and see how it behaves:
/**
* This is an example to illustrate an HTML code snippet embedded in documentation comments
* <pre>
* <html>
* <body>
* <h1>Hello World!</h1>
* </body>
* </html>
* </pre>
*
*/Corresponding HTML page:

Here, we can see that the code snippet embedded within comments has been parsed into an HTML page with HTML markup. We can fix the issue using the @code tag as discussed above:
/**
* This is an example to illustrate an HTML code snippet embedded in documentation comments
* <pre>{@code
* <html>
* <body>
* <h1>Hello World!</h1>
* </body>
* </html>}
* </pre>
*
*/Corresponding HTML page:

4. Conclusion
We’ve explored different ways of formatting Javadoc comments. We can choose the formatting options as per our requirements to generate well-formatted documentation.
We can use HTML tags to enhance the formatting of Javadoc comments, as well as escape them whenever it suits our requirements.

















