1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll embark on an exploration of Elasticsearch and its accompanying tools.
It’s a tool that can seamlessly handle large volumes of data, scale automatically, and consistently assimilate new data.
2. Definition
Imagine we have a huge pile of documents, thousands of them, and we want to find specific information quickly and efficiently. That’s where Elasticsearch comes into play.
Imagine a super-smart librarian who deftly organizes a multitude of documents, thereby facilitating an easy search process. This is akin to Elasticsearch – an open-source search and analytics engine that is proficient in managing colossal volumes of data, delivering the precise information we seek.
Being distributed in nature and incorporating NoSQL, Elasticsearch employs JSON documents for data representation, allowing for easy integration with various programming languages and systems.
Elasticsearch stands out for its data-handling abilities, like instantly storing, searching, and examining data. Using a robust search system, Elasticsearch sorts all the words and phrases in our documents into an easy-to-search list. This means we can perform lightning-fast searches across vast amounts of data.
2.1. What About Indexes?
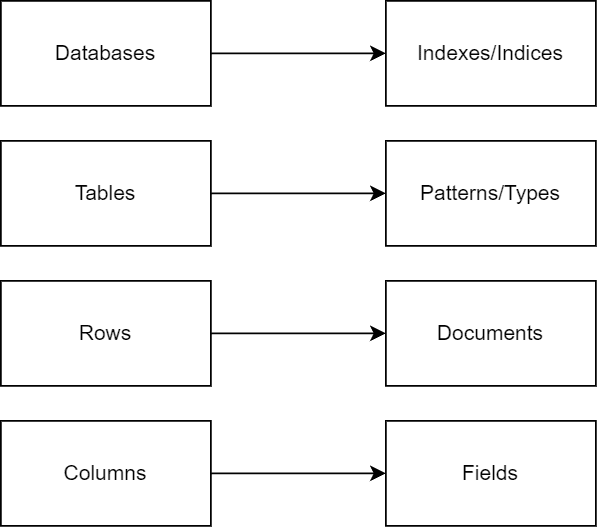
Elasticsearch has a unique way of organizing data when compared to relational database management systems (RDBMS). In RDBMS, we commonly use the term “databases”. However, in Elasticsearch, the term “indexes” is used, which is more akin to a table in a traditional database. It’s just a different term for the same concept.
Furthermore, in a relational database, we use tables to organize our data. In Elasticsearch, we have something similar, which we can think of as index patterns. In older versions, they used to be called types.
Within these databases or indexes, a relational database has tables that consist of rows and columns. In Elasticsearch, we can think of rows as documents and individual columns are referred to as fields, mirroring the structure of many NoSQL data sources.
For those used to working with relational databases like MySQL or Postgres, understanding this new document-oriented search engine is akin to expanding our existing knowledge. It helps us know how things fit together and plan our data structure. It’s like translating our current understanding into a new system with its own considerations.
Here’s a helpful table for comparison:
3. Interacting with Elasticsearch
When interacting with it, it’s fascinating to note that this is accomplished via a RESTful API. This means that all of our operations are conducted through programmatically accessible URLs, whether we’re managing indexes or dealing with different types of data.
These queries are usually made using Elasticsearch’s Query DSL, a flexible and powerful system that utilizes JSON to define queries. Importantly, Elasticsearch’s Query DSL allows for complex queries beyond simple matching, encompassing boolean logic, wildcard, range queries, and more.
It’s great for various use cases. We can gather data from different sources like logs, metrics from different systems, and even application trace data. With Elasticsearch, we can combine all this data into JSON documents and then easily search and retrieve information in real time.
4. Solving Real-World Challenges
Here are some examples illustrating how we might interact with Elasticsearch.
4.1. E-commerce Search
Now, suppose we have a bunch of documents related to customer reviews of a product. With Elasticsearch, we can quickly search for specific keywords or phrases within those reviews, giving us relevant results in no time. In addition to finding exact matches, it ranks the results based on their relevance, ensuring we receive the most important information first.
Let’s say we’re indexing a large catalog of products. Our Elasticsearch query to find all “red shirts” might look something like this:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/products/_search" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "color": "red" }},
{ "match": { "product_type": "shirt" }}
]
}
}
}'
4.2. Geospatial Search
Suppose that we’re working on a location-based application or a mapping service. We need to search for places, calculate distances, or find nearby locations. Elasticsearch has built-in support for geospatial data, allowing us to store and query location information effortlessly. Whether it’s finding the nearest coffee shop or analyzing geographic data, its geospatial capabilities make it easier to work with location-based data.
It’s not just about searching, though. It also provides some advanced features. For example, it can perform complex queries, filtering, and aggregation on our data. We can even use it to visualize and analyze our data, helping us gain insights and make informed decisions.
For a location-based search, for example, to find all coffee shops within a 1km radius of a specific location, our query might look like this:
curl -X GET "localhost:9200/places/_search" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"place_type": "coffee_shop"
}
},
"filter": {
"geo_distance": {
"distance": "1km",
"pin.location": {
"lat": 40.73,
"lon": -74.1
}
}
}
}
}
}'
4.3. Fraud Detection
Fraudulent activities, such as credit card fraud or online scams, can be a major business concern.
Elasticsearch can assist in fraud detection by analyzing large volumes of transactional data. It can identify patterns, anomalies, or suspicious behaviors using advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms.
In addition to its search capabilities, it’s highly scalable and fault-tolerant. It can distribute our data across multiple servers, ensuring that even if one server goes down, our data remains accessible. This makes it a reliable tool for handling large-scale applications or systems with high data volumes.
4. Ecosystem
Let’s move on to the whole ecosystem. If we’ve been researching Elasticsearch, chances are we’ve stumbled upon the term “Elastic Stack“, previously known as “ELK Stack”.
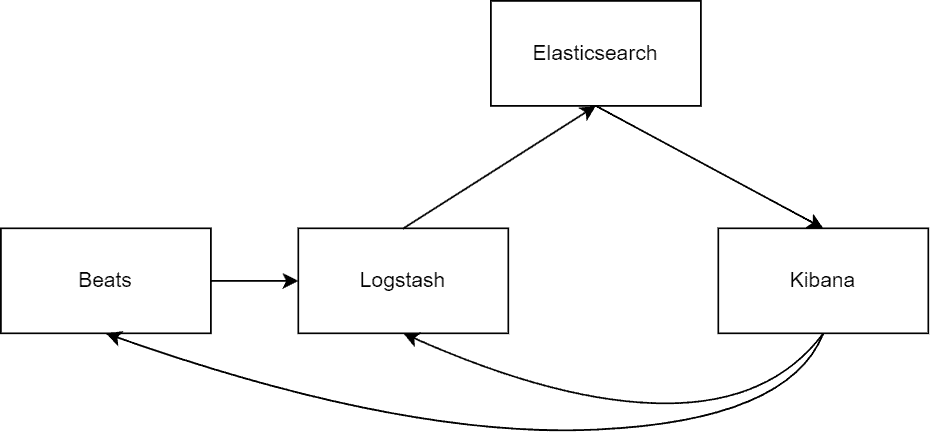
This widely used phrase brings together three potent open-source tools: Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. The term also includes Beats, a set of lightweight data shippers. Together, these components provide a comprehensive search, log analysis, and data visualization solution:
4.1. Kibana
We can think of it as a handy, web-friendly interface that lets us interact with the data in Elasticsearch. It’s kind of like our personal command center, where we can dive into and analyze all the juicy info it’s indexed for us.
With Kibana, we can create dynamic dashboards, charts, graphs, and visualizations that update in real-time as new data arrives. It serves as our primary interface for monitoring and exploring data as it flows in, helping us stay up-to-date and gain insights effortlessly.
Now, let’s discuss how data is ingested into Elasticsearch. There are two key components to consider: Logstash and Beats.
4.2. Logstash
Logstash is an open-source server-side processing pipeline. Its primary role is to handle three tasks: it takes in data, gives it a bit of a makeover, and then stores it away somewhere safe. We can configure Logstash to receive data from various sources. Like, we can format the data and send it directly to Logstash using SDKs or integrate it with different systems.
Also, while Logstash supports various data formats like JSON and CSV, it’s essential to highlight that it can deal with custom formats using its extensive plugin ecosystem.
Once the data is received, Logstash is able to conduct a range of transformations, such as formatting or structuring, before it enters the pipeline. When these tasks are completed, it forwards the refined data to its ultimate destination. For our purposes, one of those primary destinations is Elasticsearch.
4.3. Beats
Beats are lightweight data shippers. It can be thought of as agents installed on different servers to gather specific types of data. Whether we’re working with serverless architectures, files, or Windows servers, Beats serve as complementary components to Logstash. They have plugins that allow integration with various services and systems.
Here’s a cool thing about Beats – it has the capacity to shoot data straight over to Logstash for some extra processing and storage. So, Beats act as an efficient data collector that works hand in hand with Logstash to ensure seamless data flow and integration into our Elasticsearch environment.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we explored Elasticsearch as a powerful search and analytics engine that can revolutionize how we handle and make sense of data.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.


















