Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
Convert Excel Files to PDF Using Java
Last updated: March 17, 2024
1. Introduction
In this article, we’ll explore how to convert Excel files to PDF in Java using the Apache POI and iText libraries. Apache POI handles Excel file parsing and data extraction, while iText takes care of PDF document creation and formatting. By leveraging their strengths, we can efficiently convert Excel data while retaining its original formatting and styles.
2. Adding Dependencies
Before we start the implementation, we need to add the Apache POI and iText libraries to our project. In the pom.xml file, add the following dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itextpdf</groupId>
<artifactId>itextpdf</artifactId>
</dependency>The latest versions of the Apache POI and iText libraries can be downloaded from Maven Central.
3. Loading the Excel File
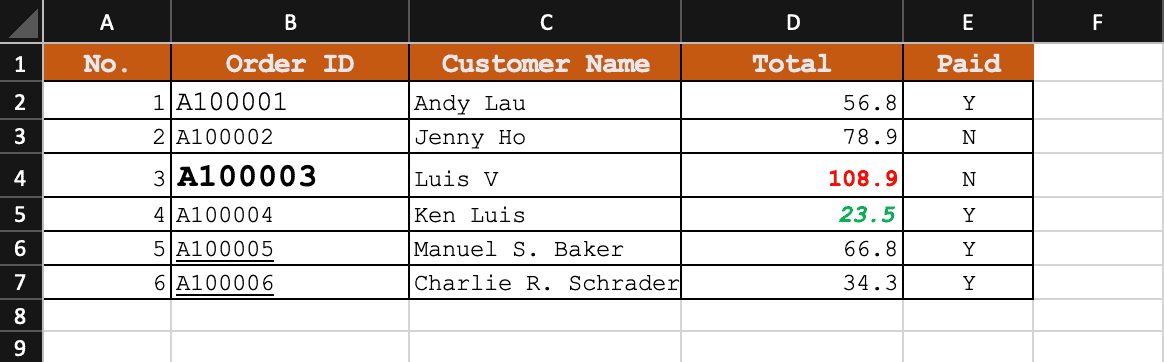
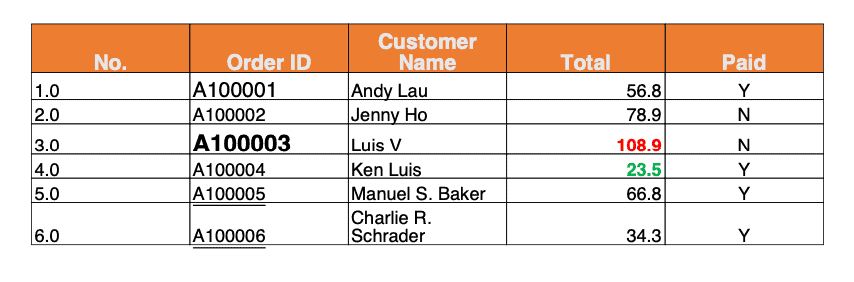
With the libraries in place, let’s load the target Excel file using Apache POI. We’ll first open the Excel file using a FileInputStream and create an XSSFWorkbook object representing the loaded workbook:
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(excelFilePath);
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);We’ll use this object to access individual sheets and their data.
4. Creating a PDF Document
Next, we’ll utilize iText to create a new PDF document:
Document document = new Document();
PdfWriter.getInstance(document, new FileOutputStream(pdfFilePath));
document.open();This creates a new Document object and associates it with a PDFWriter instance responsible for writing the PDF content. Finally, we specify the desired output location for the PDF through a FileOutputStream.
5. Parsing the Excel Data
With the document ready, we’ll iterate through each row in the worksheet to extract the cell values:
void addTableData(PdfPTable table) throws DocumentException, IOException {
XSSFSheet worksheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = worksheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext()) {
Row row = rowIterator.next();
if (row.getRowNum() == 0) {
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells(); i++) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(i);
String cellValue;
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case STRING:
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case NUMERIC:
cellValue = String.valueOf(BigDecimal.valueOf(cell.getNumericCellValue()));
break;
case BLANK:
default:
cellValue = "";
break;
}
PdfPCell cellPdf = new PdfPCell(new Phrase(cellValue));
table.addCell(cellPdf);
}
}
}The code first creates a PdfTable object matching the number of columns in the first row of the worksheet. Then, iterate through each row in the worksheet, extracting the cell values and weaving them into the PDF table. However, Excel formulas are currently not supported and will be returned with an empty string.
For each extracted cell value, we create a new PdfPCell object using a Phrase containing the extracted data. Phrase is an iText element that represents a formatted text string.
6. Preserving the Excel Styling
One of the key advantages of using Apache POI and iText is the ability to preserve the formatting and styles from the original Excel file. This includes font styles, colors, and alignments.
By accessing the relevant cell style information from Apache POI, we can apply it to the corresponding elements in the PDF document using iText. However, it’s important to note that this approach, while preserving formatting and styles, may not replicate the exact look and feel of a PDF directly exported from Excel or printed with a printer driver. For more complex formatting needs, additional adjustments may be required.
6.1. Font Styling
We’ll create a dedicated getCellStyle(Cell cell) method to extract styling information like font, color, etc., from the CellStyle object associated with each cell:
Font getCellStyle(Cell cell) throws DocumentException, IOException {
Font font = new Font();
CellStyle cellStyle = cell.getCellStyle();
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Font cellFont = cell.getSheet()
.getWorkbook()
.getFontAt(cellStyle.getFontIndexAsInt());
if (cellFont.getItalic()) {
font.setStyle(Font.ITALIC);
}
if (cellFont.getStrikeout()) {
font.setStyle(Font.STRIKETHRU);
}
if (cellFont.getUnderline() == 1) {
font.setStyle(Font.UNDERLINE);
}
short fontSize = cellFont.getFontHeightInPoints();
font.setSize(fontSize);
if (cellFont.getBold()) {
font.setStyle(Font.BOLD);
}
String fontName = cellFont.getFontName();
if (FontFactory.isRegistered(fontName)) {
font.setFamily(fontName);
} else {
logger.warn("Unsupported font type: {}", fontName);
font.setFamily("Helvetica");
}
return font;
}The Phrase object can accept a cell value and a Front object as arguments to its constructor:
PdfPCell cellPdf = new PdfPCell(new Phrase(cellValue, getCellStyle(cell));This allows us to control the content and formatting of text within a PDF cell. Note that iText’s built-in fonts are limited to Courier, Helvetica, and TimesRoman. Therefore, we should check if iText supports the extracted cell’s font family before we apply it directly. If the Excel file uses a different font family, it won’t be reflected in the PDF output.
6.2. Background Color Styling
In addition to preserving font styles, we also want to ensure that the background colors of cells in the Excel file are accurately reflected in the generated PDF. To achieve this, we’ll create a new method, setBackgroundColor(), to extract the background color information from the Excel cell and apply it to the corresponding PDF cell.
void setBackgroundColor(Cell cell, PdfPCell cellPdf) {
short bgColorIndex = cell.getCellStyle()
.getFillForegroundColor();
if (bgColorIndex != IndexedColors.AUTOMATIC.getIndex()) {
XSSFColor bgColor = (XSSFColor) cell.getCellStyle()
.getFillForegroundColorColor();
if (bgColor != null) {
byte[] rgb = bgColor.getRGB();
if (rgb != null && rgb.length == 3) {
cellPdf.setBackgroundColor(new BaseColor(rgb[0] & 0xFF, rgb[1] & 0xFF, rgb[2] & 0xFF));
}
}
}
}6.3. Alignment Styling
Apache POI provides the getAlignment() method on the CellStyle object. This returns a constant value representing the alignment. Once we have the mapped iText alignment constant, we can set it on the PdfPCell object using the setHorizontalAlignment() method.
Here’s an example of how to incorporate alignment extraction and application:
void setCellAlignment(Cell cell, PdfPCell cellPdf) {
CellStyle cellStyle = cell.getCellStyle();
HorizontalAlignment horizontalAlignment = cellStyle.getAlignment();
switch (horizontalAlignment) {
case LEFT:
cellPdf.setHorizontalAlignment(Element.ALIGN_LEFT);
break;
case CENTER:
cellPdf.setHorizontalAlignment(Element.ALIGN_CENTER);
break;
case JUSTIFY:
case FILL:
cellPdf.setVerticalAlignment(Element.ALIGN_JUSTIFIED);
break;
case RIGHT:
cellPdf.setHorizontalAlignment(Element.ALIGN_RIGHT);
break;
}
}Now, let’s update the existing code where we iterate through the cells to include the font and background color styling:
PdfPCell cellPdf = new PdfPCell(new Phrase(cellValue, getCellStyle(cell)));
setBackgroundColor(cell, cellPdf);
setCellAlignment(cell, cellPdf);Note that the resulting Excel will not look the same as a PDF exported from Excel (or a PDF print via a printer driver).
7. Saving the PDF Document
Finally, we can save the generated PDF document to the desired location. This involves closing the PDF document object and ensuring all resources are released properly:
document.add(table); document.close(); workbook.close();
8. Conclusion
We’ve learned to convert Excel files to PDF in Java using Apache POI and iText. By combining the capabilities of Apache POI for Excel handling and iText for PDF generation, we can seamlessly preserve formatting and apply styles from Excel to PDF.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.