1. Introduction
In this tutorial, we’ll consider anonymous classes in Java.
We’ll describe how we can declare and create instances of them. We’ll also briefly discuss their properties and limitations.
2. Anonymous Class Declaration
Anonymous classes are inner classes with no name. Since they have no name, we can’t use them in order to create instances of anonymous classes. As a result, we have to declare and instantiate anonymous classes in a single expression at the point of use.
We may either extend an existing class or implement an interface.
2.1. Extend a Class
When we instantiate an anonymous class from an existent one, we use the following syntax:

In the parentheses, we specify the parameters that are required by the constructor of the class that we are extending:
new Book("Design Patterns") {
@Override
public String description() {
return "Famous GoF book.";
}
}
Naturally, if the parent class constructor accepts no arguments, we should leave the parentheses empty.
2.2. Implement an Interface
We may instantiate an anonymous class from an interface as well:

Obviously, Java’s interfaces have no constructors, so the parentheses always remain empty. This is the only way we should do it to implement the interface’s methods:
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
...
}
}
Once we have instantiated an anonymous class, we can assign that instance to a variable in order to be able to reference it somewhere later.
We can do this using the standard syntax for Java expressions:
Runnable action = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
...
}
};
As we already mentioned, an anonymous class declaration is an expression, hence it must be a part of a statement. This explains why we have put a semicolon at the end of the statement.
Obviously, we can avoid assigning the instance to a variable if we create that instance inline:
List<Runnable> actions = new ArrayList<Runnable>();
actions.add(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
...
}
});
We should use this syntax with great care as it might easily suffer the code readability especially when the implementation of the run() method takes a lot of space.
3. Anonymous Class Properties
There are certain particularities in using anonymous classes with respect to usual top-level classes. Here we briefly touch the most practical issues. For the most precise and updated information, we may always look at the Java Language Specification.
3.1. Constructor
The syntax of anonymous classes does not allow us to make them implement multiple interfaces. During construction, there might exist exactly one instance of an anonymous class. Therefore, they can never be abstract. Since they have no name, we can’t extend them. For the same reason, anonymous classes cannot have explicitly declared constructors.
In fact, the absence of a constructor doesn’t represent any problem for us for the following reasons:
- we create anonymous class instances at the same moment as we declare them
- from anonymous class instances, we can access local variables and enclosing class’s members
3.2. Static Members
Anonymous classes cannot have any static members except for those that are constant.
For example, this won’t compile:
new Runnable() {
static final int x = 0;
static int y = 0; // compilation error!
@Override
public void run() {...}
};
Instead, we’ll get the following error:
The field y cannot be declared static in a non-static inner type, unless initialized with a constant expression
3.3. Scope of Variables
Anonymous classes capture local variables that are in the scope of the block in which we have declared the class:
int count = 1;
Runnable action = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Runnable with captured variables: " + count);
}
};
As we see, the local variables count and action are defined in the same block. For this reason, we can access count from within the class declaration.
Note that in order to be able to use local variables, they must be effectively final. Since JDK 8, it is not required anymore that we declare variables with the keyword final. Nevertheless, those variables must be final. Otherwise, we get a compilation error:
[ERROR] local variables referenced from an inner class must be final or effectively final
In order the compiler decides that a variable is, in fact, immutable, in the code, there should be only one place in which we assign a value to it. We might find more information about effectively final variables in our article “Why Do Local Variables Used in Lambdas Have to Be Final or Effectively Final?”
Let us just mention that as every inner class, an anonymous class can access all members of its enclosing class.
4. Anonymous Class Use Cases
There might be a big variety of applications of anonymous classes. Let’s explore some possible use cases.
4.1. Class Hierarchy and Encapsulation
We should use inner classes in general use cases and anonymous ones in very specific ones in order to achieve a cleaner hierarchy of classes in our application. When using inner classes, we may achieve a finer encapsulation of the enclosing class’s data. If we define the inner class functionality in a top-level class, then the enclosing class should have public or package visibility of some of its members. Naturally, there are situations when it is not very appreciated or even accepted.
4.2. Cleaner Project Structure
We usually use anonymous classes when we have to modify on the fly the implementation of methods of some classes. In this case, we can avoid adding new *.java files to the project in order to define top-level classes. This is especially true if that top-level class would be used just one time.
4.3. UI Event Listeners
In applications with a graphical interface, the most common use case of anonymous classes is to create various event listeners. For example, in the following snippet:
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
...
}
}
we create an instance of an anonymous class that implements interface ActionListener. Its actionPerformed method gets triggered when a user clicks the button.
Since Java 8, lambda expressions seem to be a more preferred way though.
5. General Picture
Anonymous classes that we considered above are just a particular case of nested classes. Generally, a nested class is a class that is declared inside another class or interface:
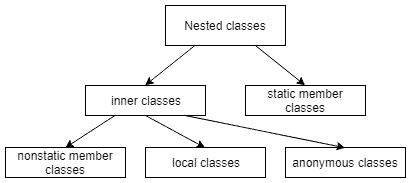
Looking at the diagram, we see that anonymous classes along with local and nonstatic member ones form the so-called inner classes. Together with static member classes, they form the nested classes.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we’ve considered various aspects of Java anonymous classes. We’ve described as well a general hierarchy of nested classes.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.



















