Learn through the super-clean Baeldung Pro experience:
>> Membership and Baeldung Pro.
No ads, dark-mode and 6 months free of IntelliJ Idea Ultimate to start with.
Last updated: June 18, 2023
The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) directly connects two network devices at the data link layer. It is typically used for internet connections and connecting remote networks via a Wide Area Network (WAN) link. PPP is adaptable, working with different physical layers protocols like serial lines, ISDN, and DSL.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore the PPP’s architecture, features, and operation while including a simple case study.
PPP is a layered protocol that operates at the data link layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model. The PPP protocol consists of a layered protocol with three primary components:
The following image depicts the PPP protocol components in the context of the OSI model:
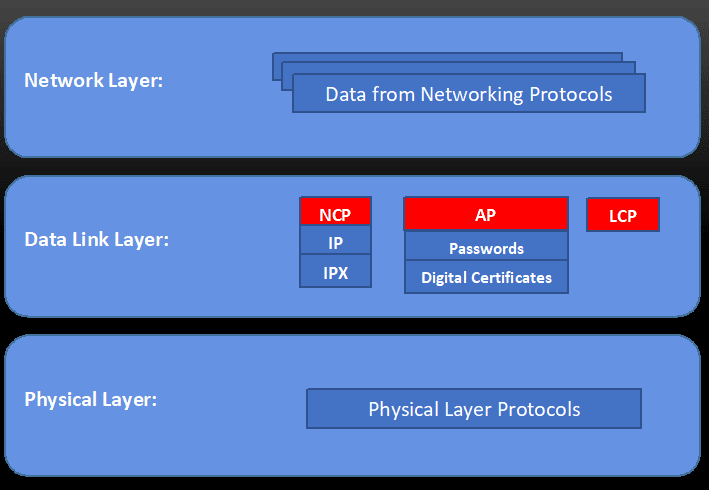
PPP provides several features that make it an attractive protocol for establishing network connections:
Generally speaking, the PPP operates by encapsulating network layer protocol packets within PPP frames, transmitting them over the physical layer protocol. Thus, the PPP frames consist of a header and a trailer, providing information about the encapsulated packet and ensuring its reliable transmission.
Moreover, the PPP header contains fields for the protocol type, address, control, and protocol identifier. In such a way, the protocol type field specifies the physical layer protocol used, like HDLC (High-level Data Link Control) or SDLC (Synchronous Data Link Control).
Furthermore, the address and control fields specify the source and destination of the PPP frame. The protocol identifier field, in turn, defines the network layer protocol being encapsulated, like IP or IPX.
Additionally, the PPP trailer contains a Frame Check Sequence (FCS) field that detects errors in transmitted data. So, the FCS field includes a checksum or a CRC calculated based on the data in the PPP frame.
Let’s check a PPP use case study. This case study has two actors: Bob (the user) and an ISP (with whom Bob communicates through a server). Thus, let’s suppose Bob wants to connect his computer to the internet using a modem, and his ISP employs PPP to establish connections:
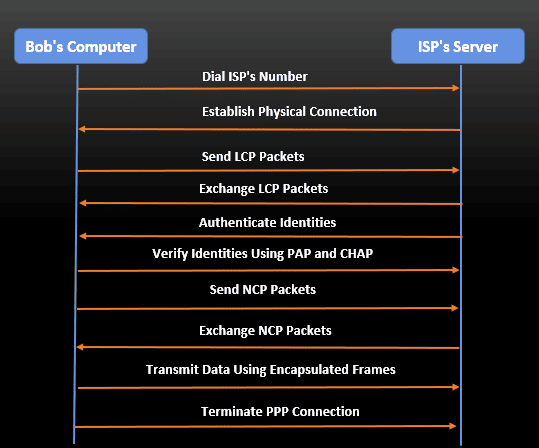
The following steps illustrate such a process:
In summary, PPP is a versatile and mature protocol with several features that make it an attractive option for establishing secure and reliable connections between network devices.
The PPP features include flexibility, error detection/correction, compression, and encryption. In this way, through PPP, two entities can successfully establish a secure and reliable connection and transmit data over the internet using the TCP/IP protocol suite, as we saw in the presented case study.