Learn through the super-clean Baeldung Pro experience:
>> Membership and Baeldung Pro.
No ads, dark-mode and 6 months free of IntelliJ Idea Ultimate to start with.
Last updated: March 18, 2024
In this tutorial, we’ll discuss the Internetwork Packet Exchange(IPX) protocol and why we use it in networking.
Novell designed the Novell Netware operating system comprising its dedicated set of protocols. Similar to the TCP/IP and OSI model, even the novel netware functions with the transferring of data in a network with its protocols.
The Netware operating system came into existence, aiming to replace the TCP/IP model. Further, the protocol suite is also called the Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX)/Sequenced Packet Exchange (SPX) protocol suite.
Let’s visualize the protocol suite of IPX/SPX:
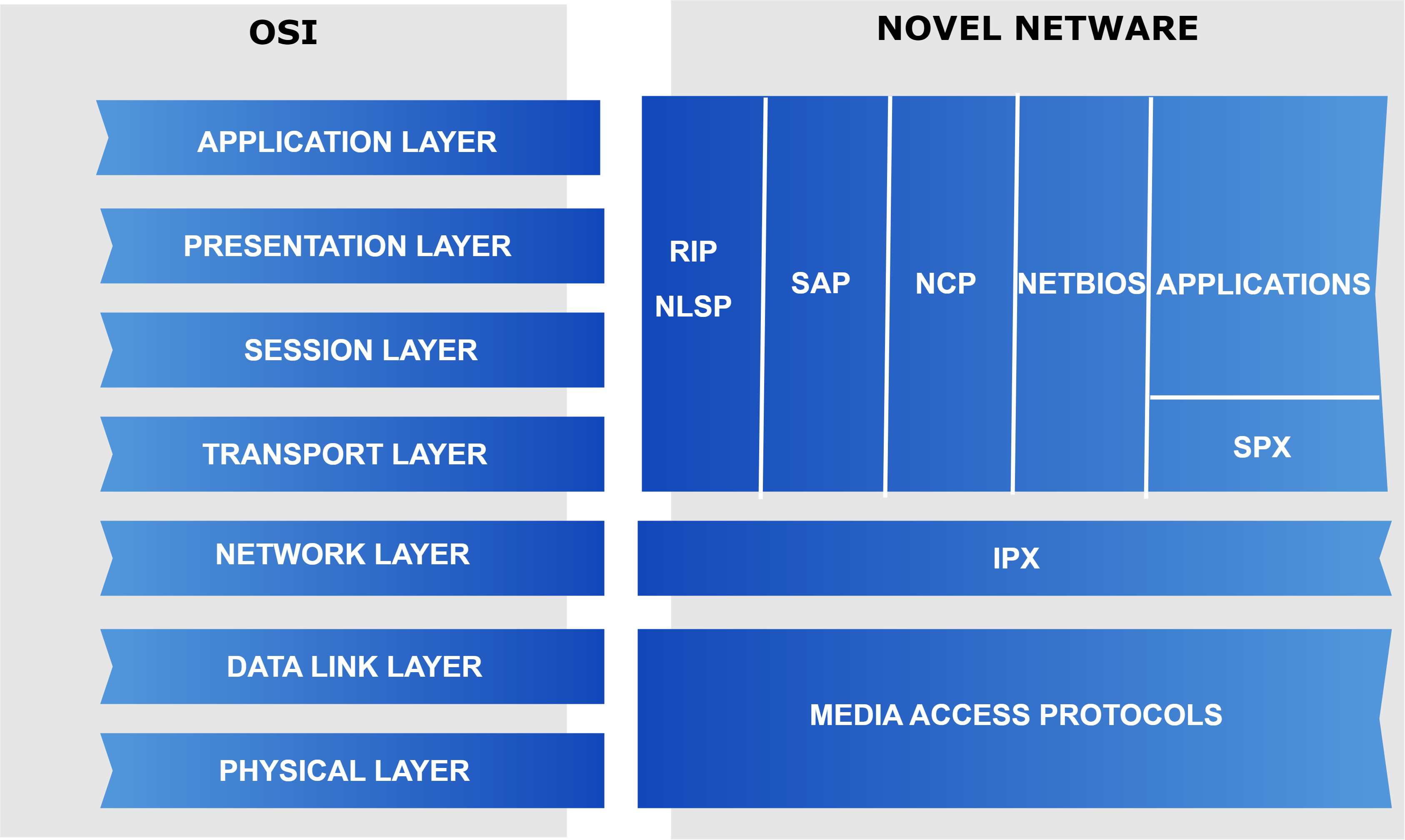
Netware Link Services Protocol (NLSP) and Routing Information Protocol (RIP) are protocols that perform the routing process. Further, the Service Advertisement Protocol (SAP) manages the information about the available resources, such as files and printers. Moreover, the routing process collects the information from SAP and creates a table holding the address and resource type.
Importantly, the Netware Core Protocol (NCP) maintains the requests from applications and the services provided as response, such as file and printer access. Further, the Network Basic Input/ Output System (NetBIOS) mimics the operations of the session layer of the OSI model. It aids in the communication between applications present in the network,
Applications act as the interface between the user and the software. Further, this serves as the medium for input and output. The IPX protocol manages the duties similar to the network layer of the OSI model. Moreover, when a connection is set up by the SPX protocol, the IPX manages the data transfer between the connected ends.
However, the media access protocols act as a combination of elements that perform operations similar to the data link layer and the physical layer. It comprises components such as Ethernet, Token Ring, and Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI).
The Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) protocol performs the tasks of a network layer of the OSI model. Additionally, it partly includes the functionalities of the transport layer.
IPX manages the path of the packets sent from one end to another, which we commonly refer to as the routing. Moreover, it holds data of both the sender and receiver in its packets. At the same time, the other models use various protocols for networking, whereas the IPX performs the tasks individually.
Let’s visualize the IPX packet structure:

Each source and destination section holds the network, node, and socket information.
The key merit of IPX protocol is that it doesn’t require a continuous connection. We refer to this as connection-less since the packets get delivered even if the connection has interruptions. This makes it ideal for locations with weaker connections.
IPX allows larger address space compared to the existing TCP/IP model. The IPX protocols are efficient for local area networks (LANs).
The key disadvantage of IPX is the high implementation cost. This makes the security costs even more expensive. Even though Netware came into existence aiming to overcome the TCP/IP model, it wasn’t efficient enough for larger networks.
IPX proved to be the medium of connecting multi-player games online. Further, it provided interruption-free communication for difficult connectable local area networks.
In this article, we discussed an important networking protocol, the Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX). We also discussed the generic idea of the IPX/SPX protocol suite.