Learn through the super-clean Baeldung Pro experience:
>> Membership and Baeldung Pro.
No ads, dark-mode and 6 months free of IntelliJ Idea Ultimate to start with.
Last updated: June 29, 2024
Blockchain, basically a system of recording data, has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about data management and financial transactions.
In this tutorial, we’ll walk through blockchain technology, analyze how it works, and discuss its strengths, weaknesses, and potential usages.
In general, a blockchain is a data structure in the form of a chain composed of a dynamic sequence of data records known as blocks that are connected and encrypted using cryptography. A crypto hashing of the preceding block, a timestamp, and transaction data are information included at every block. Also, the blockchain is developed to be immune to data alteration.
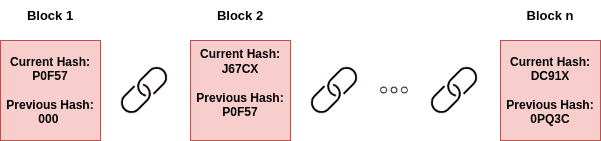
First of all, the core characteristic of the blockchain is dependent on a procedure called mining. Users who execute this process are called miners. In order for new blocks to be inserted in the chain, a certain procedure has to be followed. Miners need to complete a complex mathematical task known as a “proof of work” in their effort to add a single block to the chain. This technique requires time and entails the utilization of advanced computing technology. The first miner to achieve a certain block’s proof of work is rewarded with a set amount of cryptocurrency, and the block is added to the chain.
Following that, when a new block is inserted into the chain, it is broadcasted to the whole network and validated by other nodes/users. These nodes employ cryptography to validate the transactions of a block and guarantee that the new block is compatible with the old chain for security reasons. When a block has been validated, it can’t be changed.
Blockchain’s decentralization is a fundamental characteristic that lends to its security. Information is maintained and processed across a network of computers in a decentralized environment rather than at a sole centralized node. Each node in the network has a copy of the ledger, and any changes to the ledger must be agreed upon by a majority of the computers in the network in order to be implemented. This ensures that the ledger remains accurate and cannot be altered without the network’s consensus. This makes it far more challenging for hackers to modify the data since they would have to obtain access to a large chunk of the system.
In addition to decentralization, blockchain technology also uses cryptography to secure the data. Cryptographic hashes are employed in blockchains to protect the data at every node. This contributes to the security, immutability, and authenticity of the blockchain.
Blockchain, on the other hand, has several limits. To begin with, the decentralized structure of blockchain can make scaling problematic, particularly for applications requiring large amounts of transactions per second. Furthermore, blockchain technology can be sophisticated, making it difficult for non-technical individuals to comprehend and apply. Additionally, the proof-of-work consensus technique employed by some blockchains, such as Bitcoin, is energy-demanding and necessitates expensive hardware. Finally, blockchain is still a relatively young technology with limited use in several industries. The benefits and limitations of a blockchain can be summarized in the table below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Decentralization | Scalability |
| Immutability | Complexity |
| Security | Regulation (difficult for governments to control it) |
| Efficiency | Energy consumption and demand for expensive hardware |
This technology is based on a decentralized computer network, which implies that no one organization, like a bank or government, controls it, allowing safe financial transactions to take place without the use of middlemen. Furthermore, the transactions are recorded to a visible to every user database.
In order to connect to the bitcoin network, a unique wallet is generated that includes a single address that can be utilized to transfer and receive cryptocurrencies.
Blockchain isn’t just for cryptocurrencies. It has the power to improve several industries. Firstly, it could be employed in supply chain management to monitor the flow of items across a supply chain, increasing transparency and lowering the risk of fraud. Furthermore, in election systems, blockchain might be utilized to create safe and transparent voting systems, thereby boosting election integrity. Identification verification is an additional instance in which blockchain might be used to store and confirm identity documents such as ids and passport numbers. Further possible uses include real estate, health care, and energy trading.
In this tutorial, we introduced blockchain technology and discussed how it works. We also walked through its security, mentioned its benefits and limitations, and talked about the main applications that it has employed.