1. Overview
Swagger is a set of specifications to document and describe REST APIs. It also provides example values for the endpoint parameters.
In this tutorial, we’ll show how to produce a default example value for String arrays, as this behaviour is not enabled by default.
2. Specify an Array of Strings as Body Parameters in Swagger
The issue arises when we want to specify an array of strings as body parameters in Swagger.
Swagger’s default Example Value is a bit opaque, as we can see in the Swagger editor:
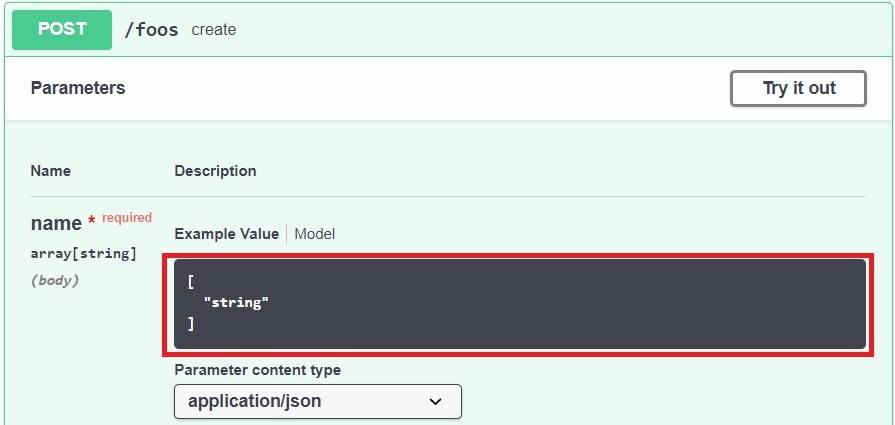
So, here we see that Swagger doesn’t really show an example of what the array contents ought to look like. Let’s see how to add one.
3. YAML
Firstly, we start by specifying the array of strings in Swagger using YAML notation. In the schema section, we include type: array with items String.
To better document the API and instruct the user, we can use the example label of how to insert values:
parameters:
- in: body
description: ""
required: true
name: name
schema:
type: array
items:
type: string
example: ["str1", "str2", "str3"]
Let’s see how our display is now more informative:
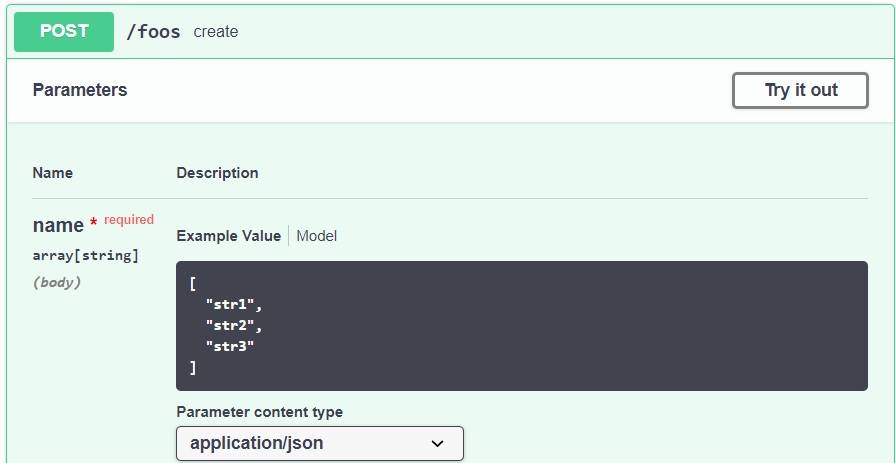
4. Springdoc
Or, we can achieve the same outcome using Springdoc.
We need to use the type: array and example in the data model with @Schema annotation:
@Schema
public class Foo {
private long id;
@Schema(name = "name", type = "array", example = "[\"str1\", \"str2\", \"str3\"]")
private List<String> name;
After that, we also need to annotate the Controller to let Swagger point to the data model.
So, let’s use @Parameters for that:
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST, value = "/foos")
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
@ResponseBody
@Parameters({ @Parameter(name = "foo", description = "List of strings") })
public Foo create(@RequestBody final Foo foo) {
And that’s it!
5. Conclusion
When documenting the REST APIs, we may have parameters that are string arrays. Ideally, we’d document these with Example Values.
We can do this in Swagger with the example property. Or, we can use the example annotation attribute in Springdoc.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















