1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll see how to display error messages originating from a Spring-based back-end application in Thymeleaf templates.
For our demonstration purposes, we’ll create a simple Spring Boot User Registration app and validate the individual input fields. Additionally, we’ll see an example of how to handle global-level errors.
First, we’ll quickly set up the back-end app and then come to the UI part.
2. Sample Spring Boot Application
To create a simple Spring Boot app for User Registration, we’ll need a controller, a repository, and an entity.
However, even before that, we should add the Maven dependencies.
2.1. Maven Dependency
Let’s add all the Spring Boot starters we’ll need – Web for the MVC bit, Validation for hibernate entity validation, Thymeleaf for the UI and JPA for the repository. Furthermore, we’ll need an H2 dependency to have an in-memory database:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<version>1.4.200</version>
</dependency>
2.2. The Entity
Here’s our User entity:
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
@NotEmpty(message = "User's name cannot be empty.")
@Size(min = 5, max = 250)
private String fullName;
@NotEmpty(message = "User's email cannot be empty.")
private String email;
@NotNull(message = "User's age cannot be null.")
@Min(value = 18)
private Integer age;
private String country;
private String phoneNumber;
// getters and setters
}
As we can see, we’ve added a number of validation constraints for the user input. Such as, fields should not be null or empty and have a specific size or value.
Notably, we haven’t added any constraint on the country or phoneNumber field. That’s because we’ll use them as an example for generating a global error, or an error not tied to a particular field.
2.3. The Repository
We’ll use a simple JPA repository for our basic use case:
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {}
2.4. The Controller
Finally, to wire everything together at the back-end, let’s put together a UserController:
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository repository;
@GetMapping("/add")
public String showAddUserForm(User user) {
return "errors/addUser";
}
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addUser(@Valid User user, BindingResult result, Model model) {
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "errors/addUser";
}
repository.save(user);
model.addAttribute("users", repository.findAll());
return "errors/home";
}
}
Here we’re defining a GetMapping at the path /add to display the registration form. Our PostMapping at the same path deals with validation when the form is submitted, with subsequent save to the repository if all goes well.
3. Thymeleaf Templates With Error Messages
Now that the basics are covered, we’ve come to the crux of the matter, that is, creating the UI templates and displaying error messages, if any.
Let’s construct the templates piecemeal based on what type of errors we can display.
3.1. Displaying Field Errors
Thymeleaf offers an inbuilt field.hasErrors method that returns a boolean depending on whether any errors exist for a given field. Combining it with a th:if we can choose to display the error if it exists:
<p th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('age')}">Invalid Age</p>
Next, if we want to add any styling, we can use th:class conditionally:
<p th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('age')}" th:class="${#fields.hasErrors('age')}? error">
Invalid Age</p>
Our simple embedded CSS class error turns the element red in color:
<style>
.error {
color: red;
}
</style>
Another Thymeleaf attribute th:errors gives us the ability to display all errors on the specified selector, say email:
<div>
<label for="email">Email</label> <input type="text" th:field="*{email}" />
<p th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('email')}" th:errorclass="error" th:errors="*{email}" />
</div>
In the above snippet, we can also see a variation in using the CSS style. Here we’re using th:errorclass, which eliminates the need for us to use any conditional attribute for applying the CSS.
Alternatively, we may choose to iterate over all validation messages on a given field using th:each:
<div>
<label for="fullName">Name</label> <input type="text" th:field="*{fullName}"
id="fullName" placeholder="Full Name">
<ul>
<li th:each="err : ${#fields.errors('fullName')}" th:text="${err}" class="error" />
</ul>
</div>
Notably, we used another Thymeleaf method fields.errors() here to collect all validation messages returned by our back-end app for the fullName field.
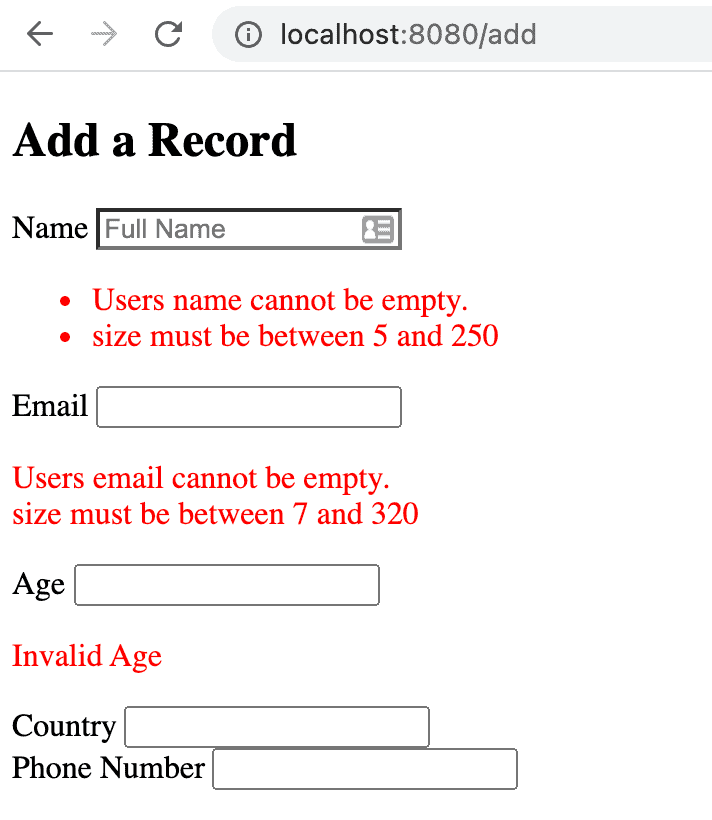
Now, to test this, let’s fire up our Boot app and hit the endpoint http://localhost:8080/add.
This is how our page looks when we don’t supply any input at all:
3.2. Displaying All Errors at Once
Next, let’s see how instead of showing every error message one by one, we can show it all in one place.
For that, we’ll use Thymeleaf’s fields.hasAnyErrors() method:
<div th:if="${#fields.hasAnyErrors()}">
<ul>
<li th:each="err : ${#fields.allErrors()}" th:text="${err}" />
</ul>
</div>
As we can see, we used another variant fields.allErrors() here to iterate over all the errors on all the fields on the HTML form.
Instead of fields.hasAnyErrors(), we could have used #fields.hasErrors(‘*’). Similarly, #fields.errors(‘*’) is an alternate to #fields.allErrors() that was used above.
Here’s the effect:

3.3. Displaying Errors Outside Forms
Next. let’s consider a scenario wherein we want to display validation messages outside an HTML form.
In that case, instead of using selections or (*{….}), we simply need to use the fully-qualified variable name in the format (${….}) :
<h4>Errors on a single field:</h4>
<div th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('${user.email}')}"
th:errors="*{user.email}"></div>
<ul>
<li th:each="err : ${#fields.errors('user.*')}" th:text="${err}" />
</ul>
This would display all error messages on the email field.
Now, let’s see how we can display all the messages at once:
<h4>All errors:</h4>
<ul>
<li th:each="err : ${#fields.errors('user.*')}" th:text="${err}" />
</ul>
And here’s what we see on the page:

3.4. Displaying Global Errors
In a real-life scenario, there might be errors not specifically associated with a particular field. We might have a use case where we need to consider multiple inputs in order to validate a business condition. These are called global errors.
Let’s consider a simple example to demonstrate this. For our country and phoneNumber fields, we might add a check that for a given country, the phone numbers should start with a particular prefix.
We’ll need to make a few changes on the back-end to add this validation.
First, we’ll add a Service to perform this validation:
@Service
public class UserValidationService {
public String validateUser(User user) {
String message = "";
if (user.getCountry() != null && user.getPhoneNumber() != null) {
if (user.getCountry().equalsIgnoreCase("India")
&& !user.getPhoneNumber().startsWith("91")) {
message = "Phone number is invalid for " + user.getCountry();
}
}
return message;
}
}
As we can see, we added a trivial case. For the country India, the phone number should start with the prefix 91.
Second, we’ll need a tweak to our controller’s PostMapping:
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addUser(@Valid User user, BindingResult result, Model model) {
String err = validationService.validateUser(user);
if (!err.isEmpty()) {
ObjectError error = new ObjectError("globalError", err);
result.addError(error);
}
if (result.hasErrors()) {
return "errors/addUser";
}
repository.save(user);
model.addAttribute("users", repository.findAll());
return "errors/home";
}
Finally, in the Thymeleaf template, we’ll add the constant global to display such type of error:
<div th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('global')}">
<h3>Global errors:</h3>
<p th:each="err : ${#fields.errors('global')}" th:text="${err}" class="error" />
</div>
Alternatively, instead of the constant, we can use methods #fields.hasGlobalErrors() and #fields.globalErrors() to achieve the same.
This is what we see on entering an invalid input:

4. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we built a simple Spring Boot Application to demonstrate how to display various types of errors in Thymeleaf.
We looked at displaying field errors one by one and then all at one go, errors outside HTML forms, and global errors.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.




















