1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll discuss Spring validation in the service layer of a Java application. Although Spring Boot supports seamless integration with custom validators, the de-facto standard for performing validation is Hibernate Validator.
Here, we’ll learn how to move our validation logic out of our controllers and into a separate service layer. Additionally, we will implement validation in the service layer in a Spring application.
2. Application Layering
Depending on the requirements, Java business applications can take several different shapes and types. For instance, we must determine which layers our application requires based on these criteria. Unless there is a specific need, many applications would not benefit from the added complexity and maintenance costs of service or repository layers.
We can fulfill all these concerns by using multiple layers. These layers are:
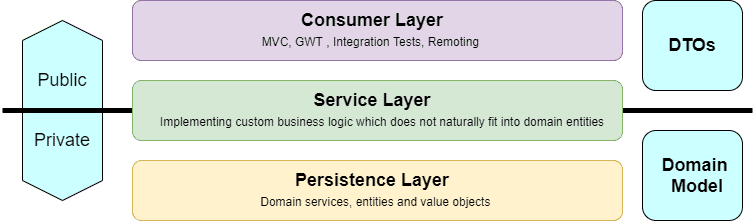
The Consumer layer or Web layer is the topmost layer of a web application. It’s in charge of interpreting the user’s inputs and providing the appropriate response. The exceptions thrown by the other layers must also be handled by the web layer. Since the web layer is our application’s entry point, it’s responsible for authentication and serves as the first line of protection against unauthorized users.
Under the web layer is the Service layer. It serves as a transactional barrier and houses both application and infrastructure services. Furthermore, the public API of the service layer is provided by the application services. They often serve as a transaction boundary and are in charge of authorizing transactions. Infrastructure services provide the “plumbing code” that connects to external tools including file systems, databases, and email servers. These approaches are often used by several application services.
A web application’s lowest layer is the persistence layer. In other words, it’s in charge of interacting with the user’s data storage.
3. Validation in the Service Layer
A service layer is a layer in an application that facilitates communication between the controller and the persistence layer. Additionally, business logic is stored in the service layer. It includes validation logic in particular. The model state is used to communicate between the controller and service layers.
There are advantages and disadvantages to treating validation as business logic, and Spring’s validation (and data binding) architecture does not preclude either. Validation, in particular, should not be bound to the web tier, should be simple to localize, and should allow for the use of any validator available.
Also, client input data does not always pass through the REST controller process, and if we don’t validate in the Service layer as well, unacceptable data can pass through, causing several issues. In this case, we’ll use the standard Java JSR-303 validation scheme.
4. Example
Let’s consider a simple user account registration form developed using Spring Boot.
4.1. Simple Domain Class
To begin with, we’ll have only the name, age, phone, and password attributes:
public class UserAccount {
@NotNull(message = "Password must be between 4 to 15 characters")
@Size(min = 4, max = 15)
private String password;
@NotBlank(message = "Name must not be blank")
private String name;
@Min(value = 18, message = "Age should not be less than 18")
private int age;
@NotBlank(message = "Phone must not be blank")
private String phone;
// standard constructors / setters / getters / toString
}
Here in the above class, we’ve used four annotations – @NotNull, @Size, @NotBlank, and @Min – to make sure that the input attributes are neither null nor blank and adhere to the size requirements.
4.2. Implementing Validation in Service Layer
There are many validation solutions available, with Spring or Hibernate handling the actual validation. On the other hand, manual validation is a viable alternative. When it comes to integrating validation into the right part of our app, this gives us a lot of flexibility.
Next, let’s implement our validation in the service class:
@Service
public class UserAccountService {
@Autowired
private Validator validator;
@Autowired
private UserAccountDao dao;
public String addUserAccount(UserAccount useraccount) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<UserAccount>> violations = validator.validate(useraccount);
if (!violations.isEmpty()) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (ConstraintViolation<UserAccount> constraintViolation : violations) {
sb.append(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
throw new ConstraintViolationException("Error occurred: " + sb.toString(), violations);
}
dao.addUserAccount(useraccount);
return "Account for " + useraccount.getName() + " Added!";
}
}
Validator is part of the Bean Validation API and responsible for validating Java objects. Furthermore, Spring automatically provides a Validator instance, which we can inject into our UserAccountService. The Validator is used to validate a passed object within the validate(..) function. The result is a Set of ConstraintViolation.
If no validation constraints are violated (the object is valid), the Set is empty. Otherwise, we throw a ConstraintViolationException.
4.3. Implementing a REST Controller
After this, let’s build the Spring REST Controller class to display the service to the client or end-user and evaluate input validation for the application:
@RestController
public class UserAccountController {
@Autowired
private UserAccountService service;
@PostMapping("/addUserAccount")
public Object addUserAccount(@RequestBody UserAccount userAccount) {
return service.addUserAccount(userAccount);
}
}
We haven’t used the @Valid annotation in the above REST controller form to prevent any validation.
4.4. Testing the REST Controller
Now, let’s test this method by running the Spring Boot application. After that, using Postman or any other API testing tool, we’ll post the JSON input to the localhost:8080/addUserAccount URL:
{
"name":"Baeldung",
"age":25,
"phone":"1234567890",
"password":"test",
"useraddress":{
"countryCode":"UK"
}
}
After confirming that the test runs successfully, let’s now check if the validation is working as per the expectation. The next logical step is to test the application with few invalid inputs. Hence, we’ll update our input JSON with invalid values:
{
"name":"",
"age":25,
"phone":"1234567890",
"password":"",
"useraddress":{
"countryCode":"UK"
}
}
We will get a response with HTTP status 400 implying a bad request and below error message. Hence, we can see how the usage of Validator is essential for validation:
Error occurred: Password must be between 4 to 15 characters, Name must not be blank
5. Pros and Cons
In the service/business layer, this is often a successful approach for validation. It isn’t restricted to method parameters and can be applied to a variety of objects. We may, for example, load an object from a database, change it, and then validate it before proceeding.
We can also use this method for unit tests so we can actually mock the Service class. In order to facilitate real validation in unit tests, we can manually generate the necessary Validator instance.
Neither case requires bootstrapping a Spring application context in our tests.
6. Conclusion
In this quick tutorial, we explored different layers of Java business applications. We learned how to move our validation logic out of our controllers and into a separate service layer. Furthermore, we implemented one approach to performing validation in the service layer of a Spring application.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















