1. Overview
In Reactive Programming, handling and transforming data streams is crucial for building responsive applications. Two commonly used methods for creating Mono instances are Mono.fromCallable and Mono.justOrEmpty. Both these methods serve their unique purpose, depending on how we want to handle nullability and lazy evaluation in our streams.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore the differences between these methods, showing how Mono.fromCallable defers execution and handles errors gracefully by wrapping computations, while Mono.justOrEmpty directly creates a Mono instance from an optional value, simplifying cases where we might have null data.
2. Introduction to Mono
Mono is a Publisher in Project Reactor, representing a stream that emits at most one value. It can be complete with a value, it can be empty, or it can terminate with an error.
Mono supports two types of publishers: cold publishers and hot publishers.
A cold publisher will only publish elements once a consumer subscribes, ensuring that each consumer receives the data from the beginning, while a hot publisher emits data as soon as it’s created, regardless of subscription.
Mono‘s fromCallable is an example of a cold publisher: It returns that Mono lazily when subscribed. Conversely, justOrEmpty is a Mono that behaves as a hot publisher, emitting its data immediately without waiting for any subscription.
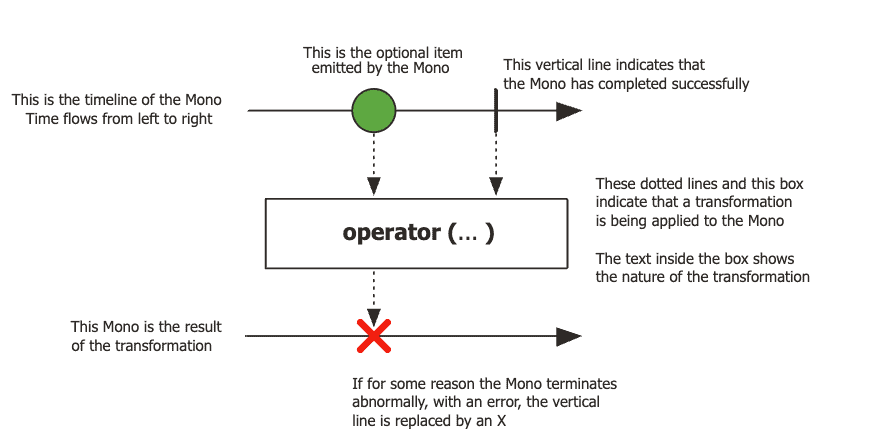
source: projectreactor.io
3. Mono.fromCallable
fromCallable takes a Callable interface and returns a Mono that delays the execution of that Callable until there’s a subscription to it. If the Callable resolves to null, the resulting Mono completes empty.
Let’s consider a sample use case where we fetch data with a consistent five-second delay between each method call. We’ll set up this logic to be deferred, so it only executes upon subscription:
public String fetchData() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return "Data Fetched";
}
Next, we’ll define a method that creates a Mono publisher using fromCallable. The timeTakenForCompletion attribute measures the duration between the start of the subscription and the receipt of the onComplete signal:
public void givenDataAvailable_whenCallingFromCallable_thenLazyEvaluation() {
AtomicLong timeTakenForCompletion = new AtomicLong();
Mono<String> dataFetched = Mono.fromCallable(this::fetchData)
.doOnSubscribe(subscription -> timeTakenForCompletion.set(-1 * System.nanoTime()))
.doFinally(consumer -> timeTakenForCompletion.addAndGet(System.nanoTime()));
StepVerifier.create(dataFetched)
.expectNext("Data Fetched")
.verifyComplete();
}
Finally, the assertion verifies that the time from subscription to receiving the onComplete signal closely aligns with the expected five-second delay, confirming that fromCallable delays execution until subscription:
assertThat(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(timeTakenForCompletion.get()))
.isCloseTo(5000L, Offset.offset(50L));
3.1. Built-in Error Handling
fromCallable also supports built-in error handling, where if the Callable throws an exception, fromCallable captures it, allowing the error to propagate through the reactive stream.
Let’s consider the same example to see the error handling of fromCallable:
public void givenExceptionThrown_whenCallingFromCallable_thenFromCallableCapturesError() {
Mono<String> dataFetched = Mono.fromCallable(() -> {
String data = fetchData();
if (data.equals("Data Fetched")) {
throw new RuntimeException("ERROR");
}
return data;
})
.onErrorResume(error -> Mono.just("COMPLETED"));
StepVerifier.create(dataFetched)
.expectNext("COMPLETED")
.verifyComplete();
}
4. Mono.justOrEmpty
justOrEmpty creates a Mono that either contains a value or completes empty if the value is null. Unlike fromCallable, it does not defer execution but evaluates as soon as Mono is created.
justOrEmpty doesn’t propagate errors since it’s designed to handle nullable values.
Let’s revisit the use case of simulating data fetching as we did previously. This time, we’ll be using the justOrEmpty method to create a Mono-type publisher.
The timeTakenToReceiveOnCompleteSignalAfterSubscription attribute tracks the time from subscription to receiving the onComplete signal. The timeTakenForMethodCompletion attribute measures the total time the method takes to complete:
public void givenDataAvailable_whenCallingJustOrEmpty_thenEagerEvaluation() {
AtomicLong timeTakenToReceiveOnCompleteSignalAfterSubscription = new AtomicLong();
AtomicLong timeTakenForMethodCompletion = new AtomicLong(-1 * System.nanoTime());
Mono<String> dataFetched = Mono.justOrEmpty(fetchData())
.doOnSubscribe(subscription -> timeTakenToReceiveOnCompleteSignalAfterSubscription
.set(-1 * System.nanoTime()))
.doFinally(consumer -> timeTakenToReceiveOnCompleteSignalAfterSubscription
.addAndGet(System.nanoTime()));
timeTakenForMethodCompletion.addAndGet(System.nanoTime());
StepVerifier.create(dataFetched)
.expectNext("Data Fetched")
.verifyComplete();
}
Let’s write an assertion that demonstrates that the time from subscription to receiving the onComplete signal is very short, confirming that the Mono was created eagerly:
assertThat(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(timeTakenToReceiveOnCompleteSignalAfterSubscription
.get())).isCloseTo(1L, Offset.offset(1L));
Next, let’s confirm that the five-second delay is included in the method’s completion time and takes place before the subscription to the Mono:
assertThat(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(timeTakenForMethodCompletion.get()))
.isCloseTo(5000L, Offset.offset(50L));
5. When to Use fromCallable
Let’s look at the use cases where we can use the Mono.fromCallable() method:
- When we need to subscribe to a publisher conditionally to save resources
- When each subscription can lead to a different outcome
- When there’s a chance the operation might throw exceptions, we want them to propagate through the reactive stream
5.1. Sample Usage
Let’s go through one sample use case where conditional deferred execution is beneficial:
public Optional<String> fetchLatestStatus() {
List<String> activeStatusList = List.of("ARCHIVED", "ACTIVE");
if (activeStatusList.contains("ARCHIVED")) {
return Optional.empty();
}
return Optional.of(activeStatusList.get(0));
}
public void givenLatestStatusIsEmpty_thenCallingFromCallableForEagerEvaluation() {
Optional<String> latestStatus = fetchLatestStatus();
String updatedStatus = "ACTIVE";
Mono<String> currentStatus = Mono.justOrEmpty(latestStatus)
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.fromCallable(()-> updatedStatus));
StepVerifier.create(currentStatus)
.expectNext(updatedStatus)
.verifyComplete();
}
In this example, the Mono publisher is defined within the switchIfEmpty method using fromCallable, allowing it to execute conditionally. As a result, the ACTIVE status will only be returned when the Mono is subscribed, making it a lazy execution.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the Mono.fromCallable method, which acts as a cold publisher, and Mono.justOrEmpty, which acts as a hot publisher. We also explored when to use the fromCallable method versus justOrEmpty, highlighting their differences and discussing example use cases.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















