1. Overview
Singleton objects are often used by developers requiring a single instance intended to be reused by many objects in the application. In Spring, we can create them by making use of Spring’s singleton beans or by implementing the singleton design pattern ourselves.
In this tutorial, we’ll first look at the singleton design pattern and its thread-safe implementation. Then, we’ll look at the singleton bean scope in Spring and compare singleton beans with objects created using the singleton design pattern.
Finally, we’ll look at some possible best practices.
2. Singleton Design Pattern
Singleton is one of the simplest design patterns published in 1994 by the Gang of Four. It is grouped under creational patterns as singleton provides a way to create an object with only one instance.
2.1. Pattern Definition
Singleton pattern involves a single class responsible for creating an object and ensuring that only a single instance ever gets created. We often use singletons to share state or to avoid the cost of setting up multiple objects.
Singleton pattern implementations ensure only one instance creation by doing these:
- Hiding all constructors by implementing a single private constructor
- Creating an instance only when it doesn’t exist and storing it in a private static variable
- Providing simple access to that instance using a public, static getter
Let’s look at an example of a few classes using a singleton object:
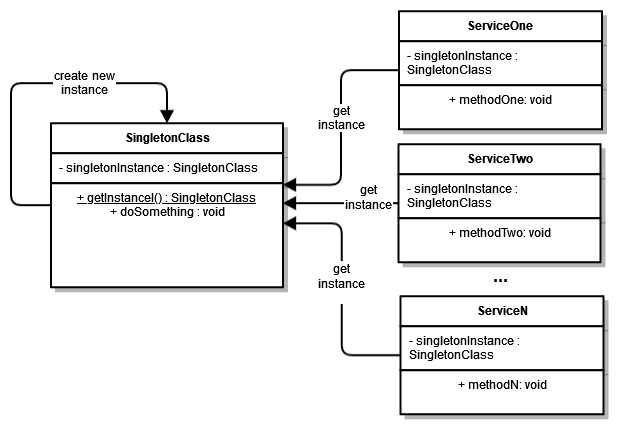
In the class diagram above, we can see how multiple services can use the same singleton instance created only once.
2.2. Lazy Initialization
Singleton pattern implementations often use lazy initialization to delay instance creation until the first time it is actually needed. To ensure lazy instantiation, we can create an instance when the static getter is first invoked:
public final class ThreadSafeSingleInstance {
private static volatile ThreadSafeSingleInstance instance = null;
private ThreadSafeSingleInstance() {}
public static ThreadSafeSingleInstance getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized(ThreadSafeSingleInstance.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ThreadSafeSingleInstance();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
//standard getters
}
In multithreaded applications, lazy instantiation can cause race conditions. Therefore, we’ve also applied double-checked locking to prevent the creation of multiple instances by different threads.
3. Singleton Beans in Spring
A bean in the Spring framework is an object created, managed, and destroyed in the Spring IoC Container.
3.1. Bean Scope
With Spring beans, we can inject an object into the Spring Container through metadata using inversion of control (IoC). In effect, an object can define its dependencies without creating them and delegate that work to the IoC Container.
The latest version of the Spring framework defines six types of scopes:
- singleton
- prototype
- request
- session
- application
- websocket
The scope of a bean defines its life cycle and visibility. It also determines how actual instances of a bean will be created. For example, we may want to create a single global instance or a different instance every time a bean is requested.
3.2. Singleton Beans
We can declare beans in Spring using the @Bean annotation located in a configuration class. The singleton scope in Spring creates one bean per bean identifier in a container:
@Configuration
public class SingletonBeanConfig {
@Bean
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON)
public SingletonBean singletonBean() {
return new SingletonBean();
}
}
Singleton is the default scope of all beans defined in Spring. So even if we didn’t specify a specific scope using the @Scope annotation, we’d still get a singleton bean. The scope is included here for illustration purposes only. It would normally be used for expressing the other scopes available.
3.3. Bean Identifier
Unlike the pure singleton design pattern, we can create multiple singleton beans from the same class:
@Bean
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON)
public SingletonBean singletonBean() {
return new SingletonBean();
}
@Bean
@Scope(value = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON)
public SingletonBean anotherSingletonBean() {
return new SingletonBean();
}
All requests for beans with a matching identifier will result in one specific bean instance being returned by the framework. When we use the @Bean annotation on a method, Spring uses the method name as a bean identifier.
When injecting beans, if more than one bean of the same type is available in the container, the framework throws NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException:
@Autowired
private SingletonBeanConfig.SingletonBean bean; //throws exception
In that case, we can make use of the @Qualifier annotation to specify the correct bean identifier to inject:
@Autowired
@Qualifier("singletonBean")
private SingletonBeanConfig.SingletonBean beanOne;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("anotherSingletonBean")
private SingletonBeanConfig.SingletonBean beanThree;
Alternatively, another annotation – @Primary – can be used to define a primary bean when multiple beans of the same type are present.
4. Comparison
Let’s now compare the two approaches and identify a best practice to follow in Spring.
4.1. Singleton Anti-Pattern
Some consider singleton to be an anti-pattern because it introduces an application-level global state. Any other object using the singleton has a direct dependency on it. That results in unnecessary inter-dependencies between classes and modules.
The Singleton pattern also violates the single-responsibility principle. As singleton objects are responsible for at least two things:
- Ensuring only one instance is created
- Performing their normal operations
In addition, singletons require special treatment in multi-threaded environments to ensure that separate threads don’t create multiple instances. They might also make unit testing and mocking harder. As many mocking frameworks rely on inheritance, the private constructor makes singleton objects hard to mock.
4.2. Recommended Approach
Using Spring’s singleton beans instead of implementing the singleton design pattern eliminates many of the above disadvantages.
Spring framework injects a bean in all classes that use it, but retains the flexibility to replace or extend it. The framework achieves that by maintaining control over the bean’s lifecycle. Therefore, it can later be replaced by another approach without any code having to change.
In addition, Spring beans make unit testing much simpler. Spring beans are easy to mock and the framework can inject them into test classes. We may choose to inject actual bean implementations or their mocks.
We should note that singleton beans will not create only one instance of a class, but one bean per bean identifier in a container.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to create singleton instances in the Spring framework. We looked at implementing the singleton design pattern, as well as making use of Spring’s singleton beans.
We explored how to implement a singleton pattern with lazy loading and thread safety. Then we investigated the singleton bean scope in Spring and explored how to implement and inject singleton beans. We also saw how singleton beans differentiate from objects created using the singleton design pattern.
Finally, we looked at how using singleton beans in Spring eliminates some disadvantages of the traditional implementation of the singleton design pattern.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















