Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
Google Cloud and Spring AI
Last updated: November 4, 2025
1. Overview
Spring AI is an application framework with a common interface for various LLMs that helps us to integrate them into our Spring Boot applications.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore how we could integrate Spring AI with the Google Cloud Vertex AI platform and adopt various models to provide chat and embedding capabilities in our applications.
2. Prerequisites
We’ll need the Spring AI Vertex AI Gemini and embedding dependencies in our pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-vertex-ai-gemini</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-vertex-ai-embedding</artifactId>
</dependency>These starter model dependencies will automatically configure Vertex AI models according to our settings in application.yml.
As a first step, we must enable the Vertex AI API in our Google Cloud console for making API calls to Vertex AI.
Once it’s enabled, we’ll need to run two additional commands in the console with Google Cloud CLI installed.
The first command sets the active project for all subsequent CLI commands:
$ gcloud config set project <PROJECT-ID>The PROJECT-ID argument is the unique ID for our Google Cloud project where Vertex AI is enabled.
The second one authenticates and gives us an OAuth2 access token that grants us access rights to the Vertex AI APIs:
$ gcloud auth application-default login <YOUR-ACCOUNT>This will open a web browser window and prompt us to sign in with our Google Cloud account. It will save the OAuth2 access token locally after we sign in.
3. Chat
Gemini is the chat model available in Vertex AI. In this section, we’ll integrate Gemini into our Spring Boot application.
3.1. Configuration
We need to add a few properties to our application.yml to integrate the chat model with Spring AI:
spring:
ai:
vertex:
ai:
gemini:
project-id: <YOUR-GOOGLE-CLOUD-PROJECT-ID>
location: "europe-west1"
model: "gemini-2.0-flash-lite"The project-id property specifies which Google Cloud project resources, including authentication and billing, should be used in our application.
The model property specifies which Gemini chat model we will integrate with. There are various Gemini models to choose from.
3.2. Service
Let’s create a simple ChatService to accept a prompt as the input argument:
@Component
@SessionScope
public class ChatService {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public ChatService(ChatModel chatModel, ChatMemory chatMemory) {
this.chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultAdvisors(MessageChatMemoryAdvisor.builder(chatMemory).build())
.build();
}
public String chat(String prompt) {
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userMessage -> userMessage.text(prompt))
.call()
.content();
}
}In this service, we inject the auto-configured Gemini ChatModel to create our ChatClient instance.
Since LLMs are stateless, they don’t have knowledge of previous conversations. Therefore, we also inject a ChatMemory instance so we can provide a conversation-like experience.
We’ll need a ChatController to accept the query for our testing purposes:
@RestController
public class ChatController {
private final ChatService chatService;
public ChatController(ChatService chatService) {
this.chatService = chatService;
}
@PostMapping("/chat")
public ResponseEntity<String> chat(@RequestBody @NotNull String prompt) {
String response = chatService.chat(prompt);
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
}This controller accepts a string in the request body and sends the prompt to the Gemini chat model via ChatService.
3.3. Test Run
Now, let’s run a test by issuing a prompt to this endpoint via Postman. We should see a response back from the Gemini:
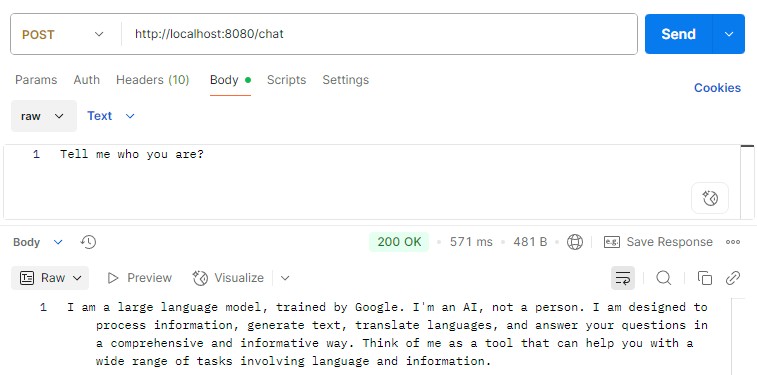
4. Text Embedding
Text embedding is the process of converting a natural language text input into a high-dimensional vector representation. The use case of embeddings could be performing similarity searches based on the contextual meaning.
4.1. Configuration
We’ll need a different model for converting text to an embedding. Let’s add a few more properties to the application.yml:
spring:
ai:
vertex:
ai:
embedding:
project-id: <YOUR-GOOGLE-CLOUD-PROJECT-ID>
location: "europe-west1"
text:
options:
model: "gemini-embedding-001"Similar to the chat model, we need to define project-id and location attributes, for which we could apply the values defined in the previous chat configuration section.
4.2. Service
Now, our application is configured to inject an EmbeddingModel into our service. We can now define a TextEmbeddingService class for converting a text to an embedding:
@Service
public class TextEmbeddingService {
private final EmbeddingModel embeddingModel;
public TextEmbeddingService(EmbeddingModel embeddingModel) {
this.embeddingModel = embeddingModel;
}
public EmbeddingResponse getEmbedding(String... texts) {
EmbeddingRequest request = new EmbeddingRequest(Arrays.asList(texts), null);
return embeddingModel.call(request);
}
}Let’s create a TextEmbeddingController as well to perform a test run:
@RestController
public class TextEmbeddingController {
private final TextEmbeddingService textEmbeddingService;
public TextEmbeddingController(TextEmbeddingService textEmbeddingService) {
this.textEmbeddingService = textEmbeddingService;
}
@PostMapping("/embedding/text")
public ResponseEntity<EmbeddingResponse> getEmbedding(@RequestBody @NotNull String text) {
EmbeddingResponse response = textEmbeddingService.getEmbedding(text);
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
}4.3. Test Run
Now, we’re ready to test our text embedding service. Let’s send some texts to this endpoint and see what it returns:
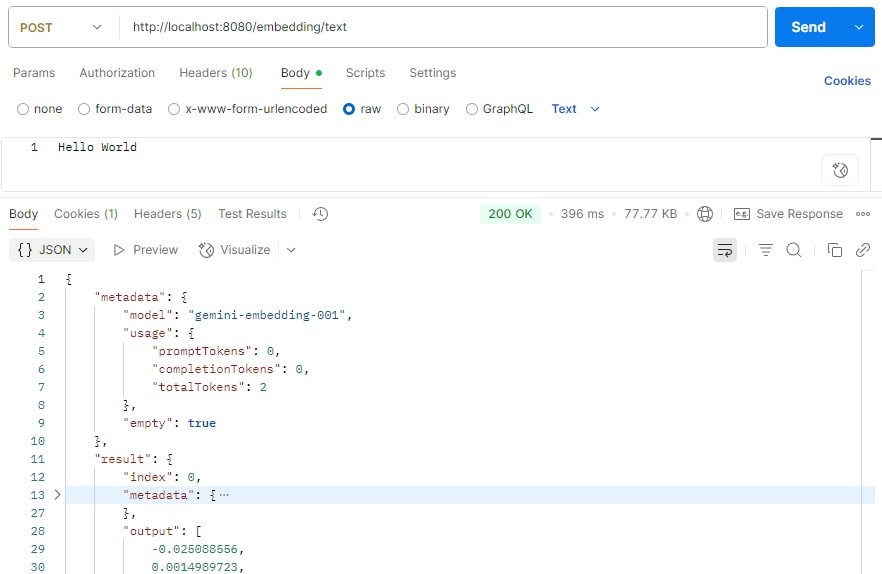
Upon completion, the endpoint returned both metadata and, most importantly, the embedding that we would find in the output attribute.
5. Multimodal Embedding
In addition to texts, Vertex AI is capable of converting various media, such as images, into embeddings.
We don’t even need any additional configurations with the multimodal embedding service. All we need is the text embedding configuration in the application.yml.
5.1. Service
Let’s create a MultiModalEmbeddingService to convert different images into embeddings:
@Service
public class MultiModalEmbeddingService {
private final DocumentEmbeddingModel documentEmbeddingModel;
public MultiModalEmbeddingService(DocumentEmbeddingModel documentEmbeddingModel) {
this.documentEmbeddingModel = documentEmbeddingModel;
}
public EmbeddingResponse getEmbedding(MimeType mimeType, Resource resource) {
Document document = new Document(new Media(mimeType, resource), Map.of());
DocumentEmbeddingRequest request = new DocumentEmbeddingRequest(List.of(document));
return documentEmbeddingModel.call(request);
}
}We’ll need the image Resource and its MIME type for converting it into an embedding. Currently, Vertex AI accepts BMP, GIF, JPG, and PNG image formats.
Let’s create a controller that accepts an image file from the request. It derives the MIME type from the request content type and sends the image file Resource along with the MIME type to the MultiModalEmbeddingService:
@RestController
public class MultiModalEmbeddingController {
private final MultiModalEmbeddingService embeddingService;
public MultiModalEmbeddingController(MultiModalEmbeddingService embeddingService) {
this.embeddingService = embeddingService;
}
@PostMapping("/embedding/image")
public ResponseEntity<EmbeddingResponse> getEmbedding(@RequestParam("image") @NotNull MultipartFile imageFile) {
EmbeddingResponse response = embeddingService.getEmbedding(
MimeType.valueOf(imageFile.getContentType()),
imageFile.getResource());
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
}5.2. Test Run
We’ll send an image instead of text to the controller endpoint this time:
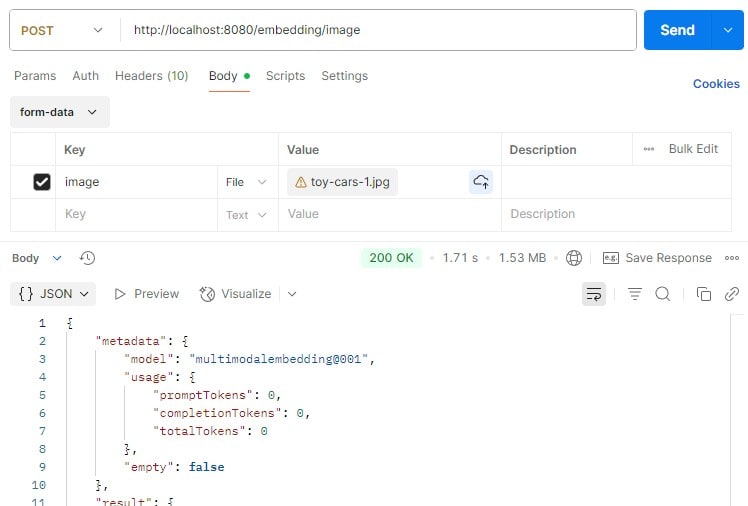
We got a similar response to the text embedding one upon completion, and we’ll find the image embedding in the output attribute of the response.
6. Conclusion
Spring AI simplifies LLMs integration with our application, which helps us adopt and switch between different LLMs with minimal development effort.
In this article, we have explored the setup of Vertex AI in a Spring Boot application. We’ve also learned how to apply the Gemini chat model and embedding models to convert texts and images into embeddings for further processing and analysis.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.
















