Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
Difference Between form-data, x-www-form-urlencoded and raw in Postman
Last updated: January 27, 2024
1. Overview
Postman provides multiple ways to interact with an API or server request with different types of body parameters. These represent different ways of sending data through an HTTP request to the API.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore the differences between using form-data, x-www-form-urlencoded, and raw for our request body.
2. form-data
Form-data represents the data sent from website forms to APIs as part of multipart/form-data. The form-data option in Postman simulates filling out a form on a website and submitting it. We can edit the form data and let it set the different key/value pairs by transforming the key-value editor in the data.
This can also be used for attaching files to the keys as well. However, we should note that using HTML5 means that the files aren’t in any history or collections. Therefore, we must select the file again at the time of sending the request body. Also, uploading multiple files with their content type isn’t supported by Postman.
Note that Postman will persist the file paths with subsequent use, i.e., when we repeatedly make an API call that sends the same file onto the server. This helps in running collections with multiple requests to upload files.
Let’s see what using form-data looks like in Postman:
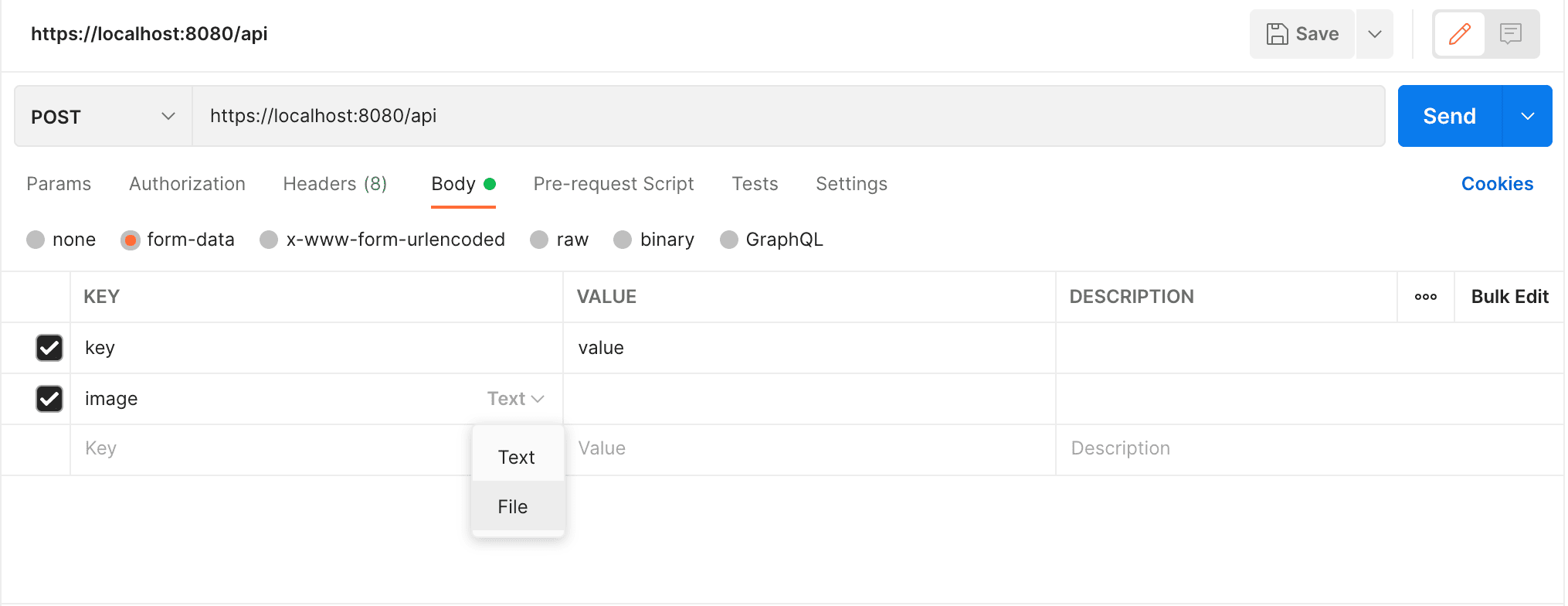
To send data as form-data, Postman generates a request like this:
curl -X POST https://localhost:8080/api
-F "key=value"
-F "image=value"3. x-www-form-urlencoded
The URL-encoded data sends encoded data to the server, and uses the same encoding as that of the URL parameters. To use it, we need to select the x-www-form-urlencoded tab in the body of the request. We need to enter the key-value pairs for sending the request body to the server, and Postman will encode the desired data before sending it. Postman encodes both the key and the value.
Note that it can’t be used for encoding files, so we need to manually do it ourselves. However, it can only encode the request body data or the URL parameters.
This is also known as the default content type. All the forms submitted with this content type follow the below encoding pattern:
- The control names and values are escaped. All space characters will be replaced by the ‘+’ symbol, and reserved characters follow the RFC 17.38 notations.
- An equal symbol, ‘=’, is used for separating the key and value, and the key/value pairs use ‘&’ to be separated from each other.
Let’s take a look at the x-www-form-urlencoded tab in Postman:
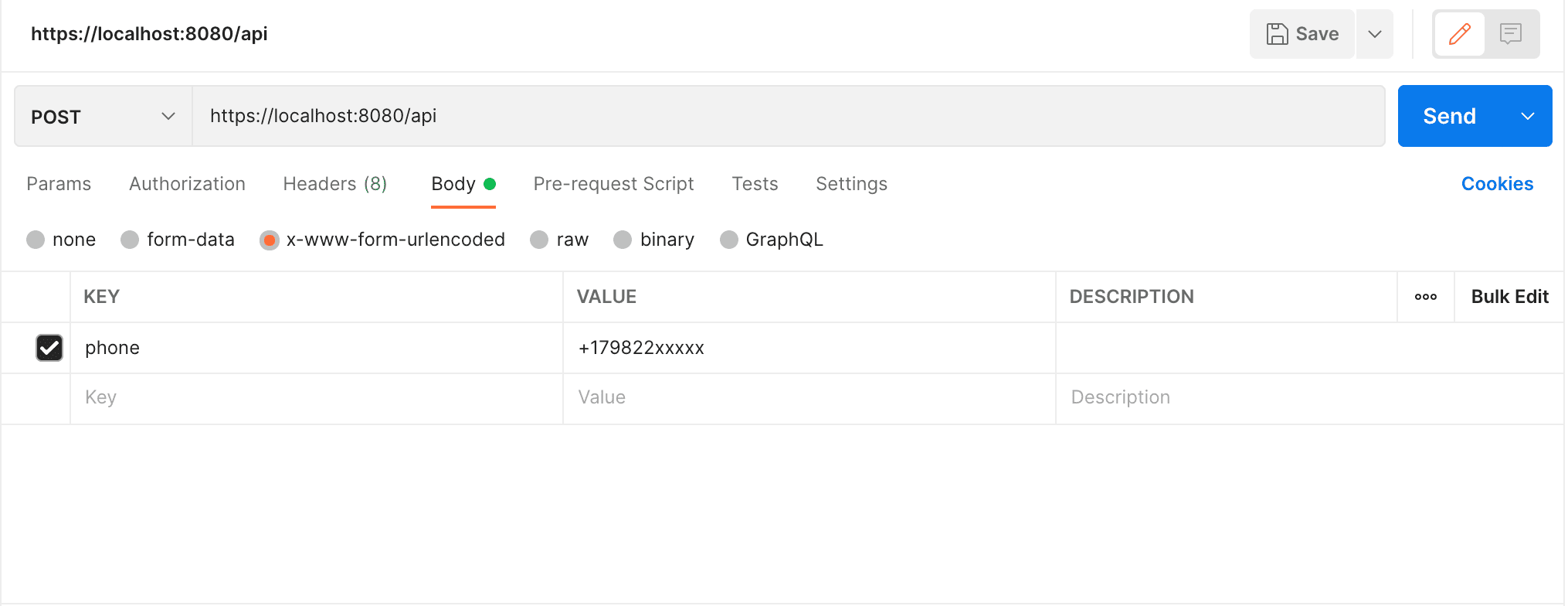
To send data as x-www-form-urlencoded, Postman generates a request like this:
curl -X POST https://localhost:8080/api/
-d "phone=+179822xxxxx"4. raw
As the name suggests, raw data can consist of anything. Postman doesn’t touch the raw string or make any type of alterations to it. The string added into the raw editor goes unmodified, except for replacing the defined environment variables. This editor lets us set different formatting styles supported by the Postman, along with the correct header that’s required to be sent with the raw body. The following types are supported:
- Text
- Javascript
- JSON
- HTML
- XML
We can also set these Content-Types manually into our request body:
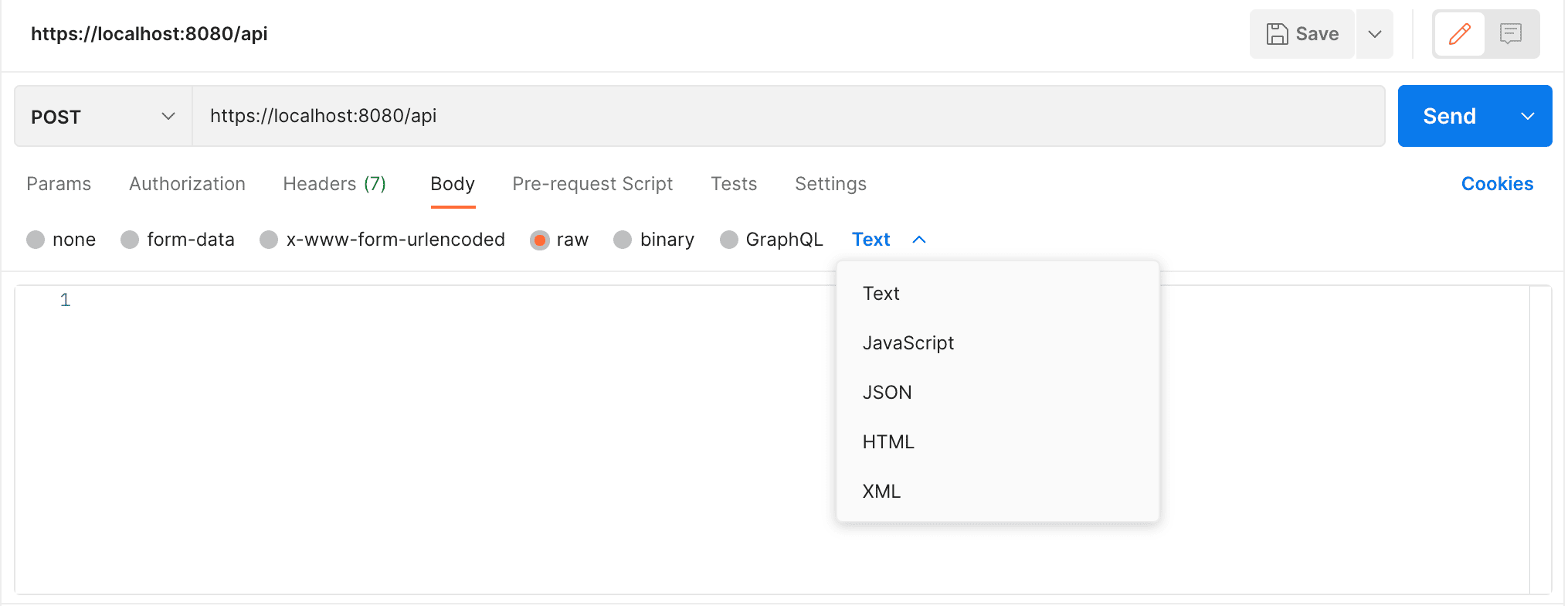
To send raw JSON data, Postman generates a request like this:
curl -X POST https://localhost:8080/api
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{"key1": "value1", "key2": "value2"}'5. Difference BETWEEN form-data, x-www-form-urlencoded and raw
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the three primary content types: form-data, x-www-form-urlencoded, and raw:
5.1. form-data
This content type is used for sending data as multipart/form-data. It is particularly useful for uploading files or sending large amounts of binary or non-ASCII data. However, form-data does not handle encoding for files and other complex structures in the request body itself.
5.2. x-www-form-urlencoded
This is the default content type for simple text form submissions. It encodes the data as key-value pairs and is similar to URL query parameters. This format is straightforward and efficient for basic form submissions. However, it has a size limit and is best used for simpler requests where the data is primarily text.
5.3. raw
The raw option provides the most flexibility, allowing us to send any type of data without modifications. It supports various content types, such as JSON, XML, and plain text. This format is ideal for sending complex or custom-formatted data, including JavaScript functions and markup languages. Unlike form-data and x-www-form-urlencoded, raw data is sent as-is, with no additional encoding or alteration by Postman.
5.4. Summary Table
The following table highlights their key characteristics and use cases:
| Aspect | form-data | x-www-form-urlencoded | raw |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encoding | Multipart form-data | URL encoding | No encoding (data sent as-is) |
| File Uploads | Supports file uploads | Doesn’t support file uploads | Not applicable |
| Data Types | Text and binary data (files) | Key-value pairs (text only) | Custom data formats (e.g., JSON, XML, plain text) |
| Use Cases | Uploading files, complex forms | Simple form submissions | Sending JSON objects, XML documents, scripts |
| Size Limitation | No significant size limitation | Limited by URL length and server configuration | Generally unrestricted by size limitations |
6. Conclusion
In this article, we examined a few of the request body data types supported by Postman.
We also outlined the differences between form-data, x-www-form-urlencoded and raw in Postman. However, we only gained a basic understanding of the requests. If you want to understand these request body types more deeply, you can explore the Postman online documentation.

















