Learn through the super-clean Baeldung Pro experience:
>> Membership and Baeldung Pro.
No ads, dark-mode and 6 months free of IntelliJ Idea Ultimate to start with.
Last updated: January 28, 2025
Digital pens and touch screens have drastically changed the way we interact with phones, tablets, and laptops. They enable users to digitize creativity and productivity, from sketching and note-taking to annotation, graphic design, and professional illustrations. However, many Linux users find it challenging to discover software that effectively supports digital pens. Luckily, there are some viable open-source note-taking and drawing options available for Linux users to maximize the potential of their digital pens.
In this tutorial, we’ve curated a list of top software alternatives for utilizing digital pens on Linux. Notably, these apps are listed without any specific ranking order.
In all cases when using Snap or Flatpak commands, the appropriate packaging system should be available beforehand.
Xournal++ is a popular open-source note-taking software that supports macOS, Windows, and Linux. It’s basically a modern and advanced version of the Xournal application.
Xournal++ enables users to handwrite notes, sketch, and journal using a stylus and drawing tablet. Additionally, users can write their scientific and mathematical works using its built-in LaTeX editor.
Moreover, Xournal++ lets users record their notes and listen to the recordings later for better clarity.
Of course, we can install Xournal++ on Linux by executing the appropriate command, depending on the distribution of the system:
$ sudo apt install xournalpp # Debian-based systems
$ sudo dnf install xournalpp # Fedora-based systems
$ sudo pacman -S xournalpp # Arch-based systemsAlternatively, we can install Xournal++ using the Snap or Flatpak commands:
$ flatpak install flathub com.github.xournalpp.xournalpp # Flatpak
$ sudo snap install xournalpp # SnapAfter installing Xournal++, we can launch it and enjoy creating digital handwritten notes:
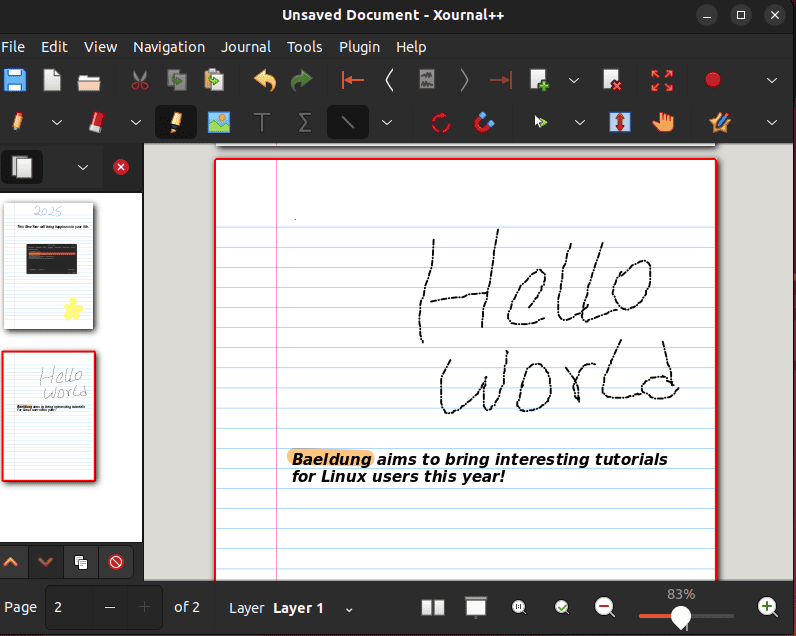
Here, we see the interface of Xournal++.
So, let’s cover some of the features Xournal++ offers:
Additionally, it’s available in more than 20 languages.
Depending on the installation method, we should be able to remove Xournal++ from the Linux system fairly easily:
$ sudo apt remove --purge xournalpp # Debian-based systems
$ sudo dnf remove xournalpp # Fedora-based systems
$ sudo pacman -Rns xournalpp # Arch-based systems
$ flatpak uninstall com.github.xournalpp.xournalpp # Flatpak
$ sudo snap remove xournalpp # SnapOverall, Xournal++ is a versatile note-taking, annotation, and sketching tool suitable for students, educators, and professionals.
Krita is an open-source, fully-featured painting software primarily used for digital art and 2D animation. It was originally created for Linux but now supports other major platforms, including Android, macOS, and Windows.
Additionally, Krita offers numerous advanced brush engines, color spaces, and amazing filters for vector art, sketching, and painting.
To install Krita on a Debian-based Linux distribution, we can use the APT command:
$ sudo apt install kritaAlternatively, we can use a Snap command to install the software:
$ sudo snap install kritaAfterward, we launch Krita and enjoy drawing or sketching:
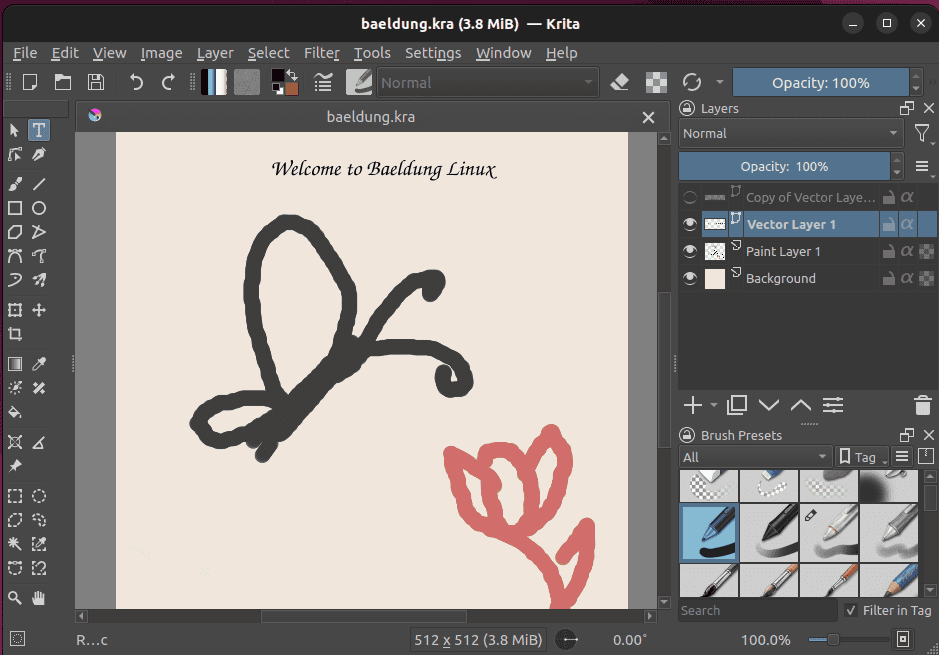
Here, we can see the fairly standard interface of Krita.
Moving forward, let’s highlight some features of the Krita application:
Additionally, Krita is one of the few painting software options that support opening, storing, editing, and creating HDR and scene-referred images.
Lastly, we can remove Krita from a Linux system by running any of the respective commands, depending on the installation method:
$ sudo apt remove krita --purge # Debian-based system
$ sudo snap remove krita # SnapOverall, Krita offers excellent brush engines, pressure sensitivity, and features tailored for art creation, making it a favorite among digital artists, illustrators, and animators.
LibreDraw is part of the well-known LibreOffice suite that comes by default in the majority of Linux distributions. It offers all the basic tools users would need for creating and editing graphics, diagrams, and document layouts. Not only can it handle simple drawings, but it can also manage complex technical diagrams.
Additionally, it provides basic tools for document manipulation, such as a spell checker, autocorrect, thesaurus, and hyphenation mode.
To begin with, we can install LibreOffice in the Linux system using the Snap or Flatpak commands:
$ flatpak install flathub org.libreoffice.LibreOffice # Flatpak
$ sudo snap install libreoffice # SnapAfterward, we can create diagrams, charts, and basic designs as part of document workflows:
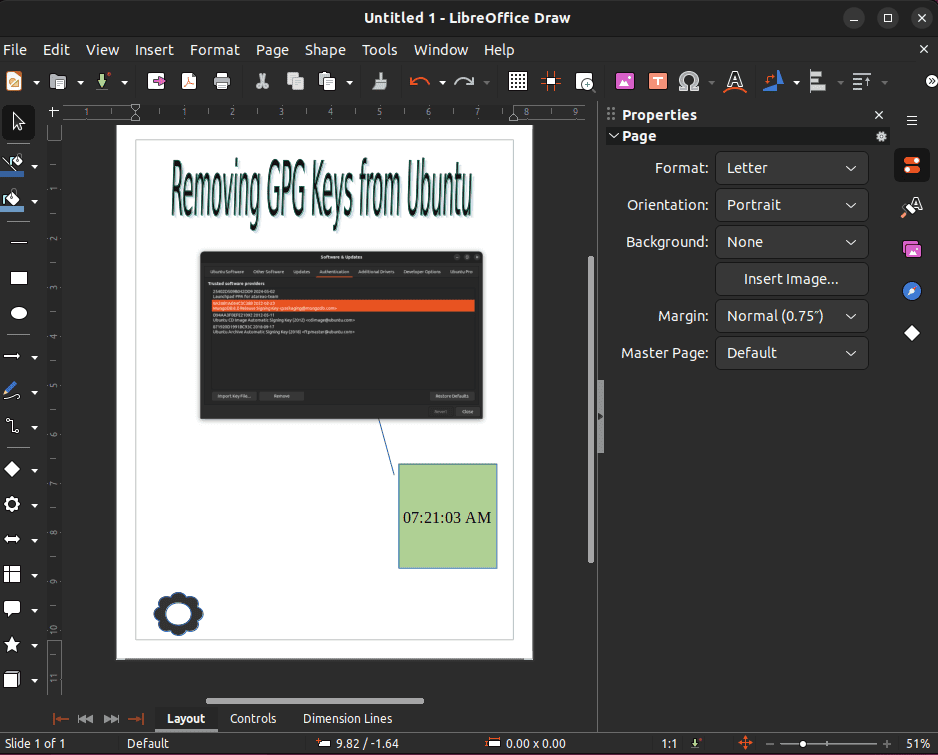
Thus, we see the interface of LibreDraw.
At this point, let’s highlight some features of LibreDraw:
Moreover, Linux users enable users to add tables, charts, and formulas into files.
Lastly, we can uninstall LibreOffice from the Linux system using the appropriate Snap or Flatpak command, depending on how it was installed:
$ flatpak uninstall flathub org.libreoffice.LibreOffice # Flatpak
$ sudo snap remove libreoffice # SnapOverall, LibreDraw is ideal for creating simple diagrams and presentations, especially for users who already rely on LibreOffice for other tasks.
GIMP (stands for GNU Image Manipulation Program) is an open-source, cross-platform graphic editing software. It enables users to manipulate and edit images and graphics, as well as create free-form drawings.
We can install GIMP using the Flatpak command:
$ flatpak install flathub org.gimp.GIMPSo, after installing GIMP, we can edit photos, design graphics, and create visual content:
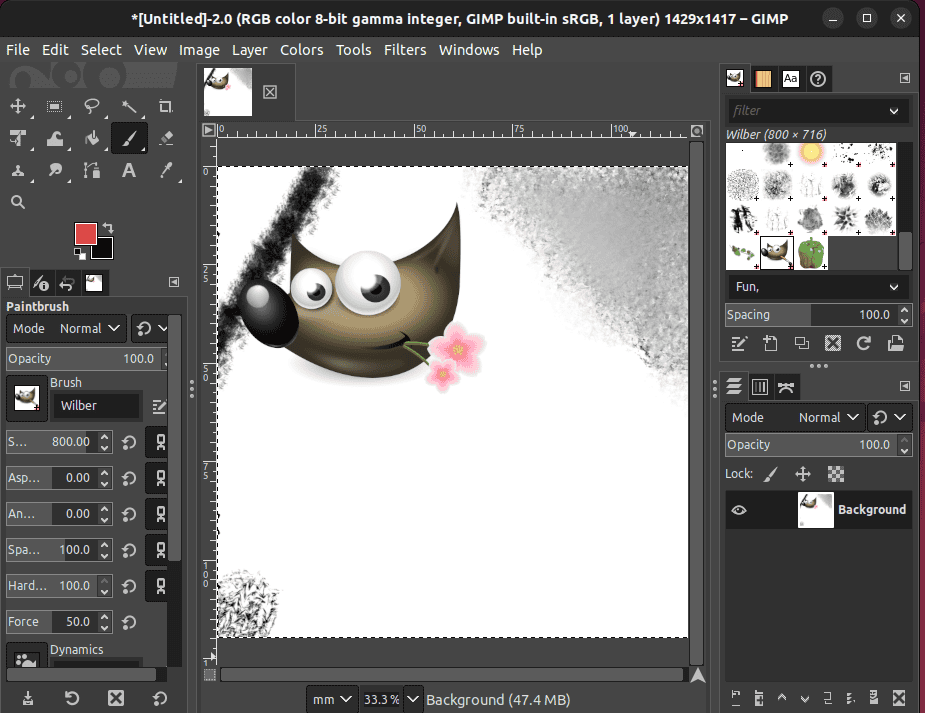
Above, we can see the main interface of GIMP.
So, let’s list some features GIMP offers:
Moreover, it offers customization options and supports numerous third-party plugins.
Lastly, we can remove GIMP from Linux by executing the respective Flatpak command:
$ flatpak uninstall flathub org.gimp.GIMPOverall, GIMP is suitable for professional graphic designers, photographers, and users requiring advanced image editing capabilities.
Joplin is a popular open-source note-taking and to-do list tool available for mobile, tablet, and desktop. It enables users to create notes with a variety of multimedia, such as images, videos, PDFs, and audio files. Moreover, it supports synchronizing user data across various devices and sharing notes with others using Joplin Cloud.
So, we can install Joplin on Linux by running either the Snap or Flatpak command:
$ flatpak install flathub net.cozic.joplin_desktop # Flatpak
$ sudo snap install joplin-desktop # SnapAfterward, we can use Joplin to organize notes and create to-do lists, all while syncing data across devices for productivity:
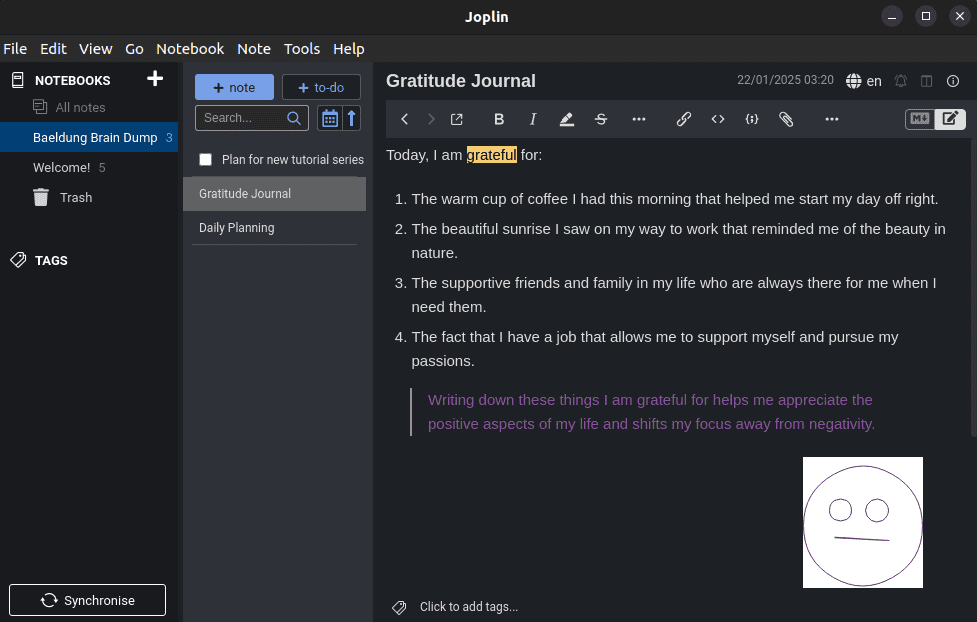
In this case, we can observe the interface of Joplin.
Let’s list some features of Joplin:
Moreover, users can create handwritten notes using Joplin.
Lastly, we can remove Joplin from Linux by running any of the following commands, depending on the way it was installed:
$ flatpak uninstall flathub net.cozic.joplin_desktop # Flatpak
$ sudo snap remove joplin-desktop # SnapOverall, Joplin is suitable for professionals, students, and users seeking an encrypted note-taking app with cross-platform synchronization.
In this article, we listed note-taking and drawing software alternatives for utilizing digital pens on Linux. Each application is suited for a specific use case and audience.
Xournal++ is ideal for note-taking and annotations, while Joplin offers secure note-taking with synchronization support. On the other hand, Krita is perfect for digital art, GIMP excels in advanced image editing, and LibreOffice Draw is suitable for diagram creation.