1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll examine how to use the replaceAll() provided in the String class to replace text using regular expressions. Additionally, we’ll learn two methods, back reference and lookaround, to perform the same operation and then compare their performance.
Let’s begin by describing the first method.
2. Using Back Reference With replaceAll()
To understand back reference, we first need to learn about matching groups. In short, a group is nothing but multiple characters seen as a single unit. So, back-references is a feature in regular expressions that allows us to refer back to previously matched groups within the same regex. Typically, we denote them with numbers that refer to the capturing group in the pattern, like \1, \2, etc.
For example, the regex (a)(b)\1 uses \1 to refer back to the first captured group, which in our case is (a).
In string replacement operations, we use these references to replace the matching text with the one we want. When using the replaceAll() method, we refer to a capturing group in the replacement string as $1, $2, etc.
Now, to understand better, let’s consider the following use case. We want to remove all the asterisk symbols within a string. So, the task is to preserve asterisks only if they appear at the beginning or the end of a string while removing all others. For example, *text* remains unaltered while **te*x**t** becomes *text*.
2.1. Implement Back Reference
To complete our task, we’ll use the replaceAll() method with a regular expression and use the backreference in:
String str = "**te*xt**";
String replaced = str.replaceAll("(^\\*)|(\\*$)|\\*", "$1$2");
assertEquals("*text*", replaced);
Above, we are defining the regular expression “(^\\*)|(\\*$)|\\*” which is made of three parts. The first group (^\\*) captures the asterisk at the beginning of the string. The second group (\\*$) captures the asterisk at the end of the string. The third group \\* captures all the rest of the asterisks. So, the regex only selects certain parts of the string, and only those selected parts will be replaced. We highlight the different parts with different colors:
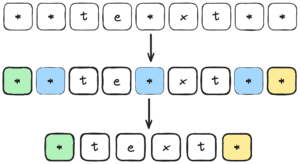
In short, the replacement string $1$2 returns all the selected characters in that group so they are kept in the final string.
Let’s look at a different approach to solving the same task.
3. Using Lookaround With replaceAll()
An alternative approach to back reference is using lookarounds, which allow us to ignore the surrounding characters when doing the match in the regular expression. In our example, we can remove the asterisks within the string in a more intuitive way:
String str = "**te*xt**";
String replacedUsingLookaround = str.replaceAll("(?<!^)\\*+(?!$)", "");
assertEquals("*text*", replacedUsingLookaround);
In this example, (?<!^)\\*+ captures one or more asterisks (\\*+) that don’t have the start of the string before them ((?<!^)). In short, we are doing a negative look behind. Next, the (?!$) part is a negative lookahead that we define to ignore asterisks that are followed by the end of the string. Finally, the empty replacement string here removes all the matching characters. Therefore, this method is more easy to reason about as we are selecting all the characters we want to remove:
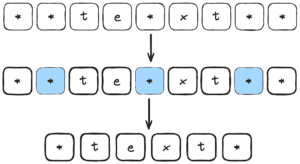
Apart from readability, these two methods differ in performance. Let’s check them out next.
To compare the performance of both of these methods, we’ll use the JMH library to benchmark and measure the average execution time required for each method to process a large number of string replacements.
For our performance test, we’ll use the same asterisk example from the previous task. In short, we’ll repeatedly use the replaceAll() function with the two regex methods 1000 times.
For this test, we’ll configure 2 warmup iterations and 5 measurement iterations. Additionally, we’ll measure the average time taken to complete the task:
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
@Fork(1)
@Warmup(iterations = 2)
@Measurement(iterations = 5)
public class RegexpBenchmark {
private static final int ITERATIONS_COUNT = 1000;
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
public static class BenchmarkState {
String testString = "*example*text**with*many*asterisks**".repeat(ITERATIONS_COUNT);
}
@Benchmark
public void backReference(BenchmarkState state) {
state.testString.replaceAll("(^\\*)|(\\*$)|\\*", "$1$2");
}
@Benchmark
public void lookaround(BenchmarkState state) {
state.testString.replaceAll("(?<!^)\\*+(?!$)", "");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Options opt = new OptionsBuilder().include(RegexpBenchmark.class.getSimpleName())
.build();
new Runner(opt).run();
}
}
The resulting output of this example states clearly that the lookaround method is more performant:
Benchmark Mode Cnt Score Error Units
RegexpBenchmark.backReference avgt 5 0.504 ± 0.011 ms/op
RegexpBenchmark.lookaround avgt 5 0.315 ± 0.006 ms/op
So, back reference is slower because it requires an overhead to capture the groups individually and then replace those groups with the replacement string. While lookaround, as explained previously, selects the characters directly and removes them.
5. Conclusion
In this article, we saw how to use the replaceAll() method with back references and lookarounds in regular expressions. While back references are useful for reusing parts of the matched string, they can be slower due to the overhead of capturing groups. To demonstrate this, we performed a benchmark to compare the two methods.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.



















