1. Overview
JSR 354 – “Currency and Money” addresses the standardization of currencies and monetary amounts in Java.
Its goal is to add a flexible and extensible API to the Java ecosystem and make working with monetary amounts simpler and safer.
The JSR did not make its way into JDK 9 but is a candidate for future JDK releases.
2. Setup
First, let’s define the dependency into our pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.javamoney</groupId>
<artifactId>moneta</artifactId>
<version>1.1</version>
</dependency>
The latest version of the dependency can be checked here.
3. JSR-354 Features
The goals of “Currency and Money” API:
- To provide an API for handling and calculating monetary amounts
- To define classes representing currencies and monetary amounts, as well as monetary rounding
- To deal with currency exchange rates
- To deal with formatting and parsing of currencies and monetary amounts
4. Model
Main classes of the JSR-354 specification, are depicted in the following diagram:
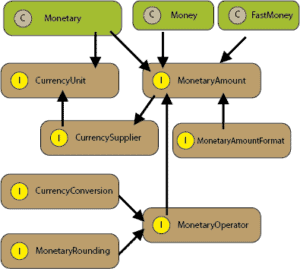
The model holds two main interfaces CurrencyUnit and MonetaryAmount, explained in the following sections.
5. CurrencyUnit
CurrencyUnit models the minimal properties of a currency. Its instances can be obtained using the Monetary.getCurrency method:
@Test
public void givenCurrencyCode_whenString_thanExist() {
CurrencyUnit usd = Monetary.getCurrency("USD");
assertNotNull(usd);
assertEquals(usd.getCurrencyCode(), "USD");
assertEquals(usd.getNumericCode(), 840);
assertEquals(usd.getDefaultFractionDigits(), 2);
}
We create CurrencyUnit using a String representation of the currency, this could lead to a situation where we try to create a currency with nonexistent code. Creating currencies with nonexistent codes raise an UnknownCurrency exception:
@Test(expected = UnknownCurrencyException.class)
public void givenCurrencyCode_whenNoExist_thanThrowsError() {
Monetary.getCurrency("AAA");
}
6. MonetaryAmount
MonetaryAmount is a numeric representation of a monetary amount. It’s always associated with CurrencyUnit and defines a monetary representation of a currency.
The amount can be implemented in different ways, focusing on the behavior of a monetary representation requirements, defined by each concrete use cases. For example. Money and FastMoney are implementations of the MonetaryAmount interface.
FastMoney implements MonetaryAmount using long as numeric representation, and is faster than BigDecimal at the cost of precision; it can be used when we need performance and precision isn’t an issue.
A generic instance can be created using a default factory. Let’s show the different way of obtaining MonetaryAmount instances:
@Test
public void givenAmounts_whenStringified_thanEquals() {
CurrencyUnit usd = Monetary.getCurrency("USD");
MonetaryAmount fstAmtUSD = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory()
.setCurrency(usd).setNumber(200).create();
Money moneyof = Money.of(12, usd);
FastMoney fastmoneyof = FastMoney.of(2, usd);
assertEquals("USD", usd.toString());
assertEquals("USD 200", fstAmtUSD.toString());
assertEquals("USD 12", moneyof.toString());
assertEquals("USD 2.00000", fastmoneyof.toString());
}
7. Monetary Arithmetic
We can perform monetary arithmetic between Money and FastMoney but we need to be careful when we combine instances of these two classes.
For example, when we compare one Euro instance of FastMoney with one Euro instance of Money the result is that they are not the same:
@Test
public void givenCurrencies_whenCompared_thanNotequal() {
MonetaryAmount oneDolar = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory()
.setCurrency("USD").setNumber(1).create();
Money oneEuro = Money.of(1, "EUR");
assertFalse(oneEuro.equals(FastMoney.of(1, "EUR")));
assertTrue(oneDolar.equals(Money.of(1, "USD")));
}
We can perform add, subtract, multiply, divide and other monetary arithmetic operations using the methods provided by the MonetaryAmount class.
Arithmetic operations should throw an ArithmeticException, if the arithmetic operations between amounts outperform the capabilities of the numeric representation type used, for example, if we try to divide one by three, we get an ArithmeticException because the result is an infinite number:
@Test(expected = ArithmeticException.class)
public void givenAmount_whenDivided_thanThrowsException() {
MonetaryAmount oneDolar = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory()
.setCurrency("USD").setNumber(1).create();
oneDolar.divide(3);
}
When adding or subtracting amounts, it’s better to use parameters which are instances of MonetaryAmount, as we need to ensure that both amounts have the same currency to perform operations between amounts.
7.1. Calculating Amounts
A total of amounts can be calculated in multiple ways, one way is simply to chain the amounts with:
@Test
public void givenAmounts_whenSummed_thanCorrect() {
MonetaryAmount[] monetaryAmounts = new MonetaryAmount[] {
Money.of(100, "CHF"), Money.of(10.20, "CHF"), Money.of(1.15, "CHF")};
Money sumAmtCHF = Money.of(0, "CHF");
for (MonetaryAmount monetaryAmount : monetaryAmounts) {
sumAmtCHF = sumAmtCHF.add(monetaryAmount);
}
assertEquals("CHF 111.35", sumAmtCHF.toString());
}
Chaining can also be applied to subtracting:
Money calcAmtUSD = Money.of(1, "USD").subtract(fstAmtUSD);
Multiplying:
MonetaryAmount multiplyAmount = oneDolar.multiply(0.25);
Or dividing:
MonetaryAmount divideAmount = oneDolar.divide(0.25);
Let’s compare our arithmetic results using Strings, given that with Strings because the result also contains the currency:
@Test
public void givenArithmetic_whenStringified_thanEqualsAmount() {
CurrencyUnit usd = Monetary.getCurrency("USD");
Money moneyof = Money.of(12, usd);
MonetaryAmount fstAmtUSD = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory()
.setCurrency(usd).setNumber(200.50).create();
MonetaryAmount oneDolar = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory()
.setCurrency("USD").setNumber(1).create();
Money subtractedAmount = Money.of(1, "USD").subtract(fstAmtUSD);
MonetaryAmount multiplyAmount = oneDolar.multiply(0.25);
MonetaryAmount divideAmount = oneDolar.divide(0.25);
assertEquals("USD", usd.toString());
assertEquals("USD 1", oneDolar.toString());
assertEquals("USD 200.5", fstAmtUSD.toString());
assertEquals("USD 12", moneyof.toString());
assertEquals("USD -199.5", subtractedAmount.toString());
assertEquals("USD 0.25", multiplyAmount.toString());
assertEquals("USD 4", divideAmount.toString());
}
8. Monetary Rounding
Monetary rounding is nothing else than a conversion from an amount with an undetermined precision to a rounded amount.
We’ll use the getDefaultRounding API provided by the Monetary class to make the conversion. The default rounding values are provided by the currency:
@Test
public void givenAmount_whenRounded_thanEquals() {
MonetaryAmount fstAmtEUR = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory()
.setCurrency("EUR").setNumber(1.30473908).create();
MonetaryAmount roundEUR = fstAmtEUR.with(Monetary.getDefaultRounding());
assertEquals("EUR 1.30473908", fstAmtEUR.toString());
assertEquals("EUR 1.3", roundEUR.toString());
}
9. Currency Conversion
Currency conversion is an important aspect of dealing with money. Unfortunately, these conversions have a great variety of different implementations and use cases.
The API focuses on the common aspects of currency conversion based on the source, target currency, and exchange rate.
Currency conversion or the access of exchange rates can be parametrized:
@Test
public void givenAmount_whenConversion_thenNotNull() {
MonetaryAmount oneDollar = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory().setCurrency("USD")
.setNumber(1).create();
CurrencyConversion conversionEUR = MonetaryConversions.getConversion("EUR");
MonetaryAmount convertedAmountUSDtoEUR = oneDollar.with(conversionEUR);
assertEquals("USD 1", oneDollar.toString());
assertNotNull(convertedAmountUSDtoEUR);
}
A conversion is always bound to currency. MonetaryAmount can simply be converted by passing a CurrencyConversion to the amount’s with method.
The formatting allows the access of formats based on java.util.Locale. Contrary to the JDK, the formatters defined by this API are thread-safe:
@Test
public void givenLocale_whenFormatted_thanEquals() {
MonetaryAmount oneDollar = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory()
.setCurrency("USD").setNumber(1).create();
MonetaryAmountFormat formatUSD = MonetaryFormats.getAmountFormat(Locale.US);
String usFormatted = formatUSD.format(oneDollar);
assertEquals("USD 1", oneDollar.toString());
assertNotNull(formatUSD);
assertEquals("USD1.00", usFormatted);
}
Here we’re using the predefined format and creating a custom format for our currencies. The use of the standard format is straightforward using the method format of the MonetaryFormats class. We defined our custom format setting the pattern property of the format query builder.
As before because the currency is included in the result we test our results using Strings:
@Test
public void givenAmount_whenCustomFormat_thanEquals() {
MonetaryAmount oneDollar = Monetary.getDefaultAmountFactory()
.setCurrency("USD").setNumber(1).create();
MonetaryAmountFormat customFormat = MonetaryFormats.getAmountFormat(AmountFormatQueryBuilder.
of(Locale.US).set(CurrencyStyle.NAME).set("pattern", "00000.00 ¤").build());
String customFormatted = customFormat.format(oneDollar);
assertNotNull(customFormat);
assertEquals("USD 1", oneDollar.toString());
assertEquals("00001.00 US Dollar", customFormatted);
}
11. Summary
In this quick article, we’ve covered the basics of the Java Money & Currency JSR.
Monetary values are used everywhere, and Java provides is starting to support and handle monetary values, arithmetic or currency conversion.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















