Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
HMAC in Java
Last updated: March 26, 2025
1. Overview
Let’s consider a scenario in which two parties want to communicate, and they need an approach to verify that the messages they receive haven’t been tampered with. Hash-based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) is a good solution.
In this tutorial, we look at how to work with the HMAC algorithm in Java.
2. Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC)
HMAC is a cryptographic method that guarantees the integrity of the message between two parties.
HMAC algorithm consists of a secret key and a hash function. The secret key is a unique piece of information or a string of characters. It is known both by the sender and the receiver of the message.
The hash function is a mapping algorithm that converts one sequence to another sequence.
The below figure shows the high-level HMAC algorithm:
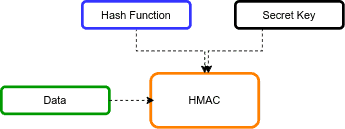
HMAC uses cryptographic hash functions such as MD5 and SHA-*.
3. HMAC Using JDK APIs
Java provides a built-in Mac class for HMAC generating. After initializing the Mac object, we call the doFinal() method to perform the HMAC operation. This method returns a byte array containing the HMAC result.
Let’s define a method for calculating the HMAC with the various hashing algorithms, such as MD5, SHA-1, SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512:
public static String hmacWithJava(String algorithm, String data, String key)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException {
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(), algorithm);
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(algorithm);
mac.init(secretKeySpec);
return bytesToHex(mac.doFinal(data.getBytes()));
}Let’s write an example test to illustrate HMAC calculation:
@Test
public void givenDataAndKeyAndAlgorithm_whenHmacWithJava_thenSuccess()
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException {
String hmacSHA256Value = "5b50d80c7dc7ae8bb1b1433cc0b99ecd2ac8397a555c6f75cb8a619ae35a0c35";
String hmacSHA256Algorithm = "HmacSHA256";
String data = "baeldung";
String key = "123456";
String result = HMACUtil.hmacWithJava(hmacSHA256Algorithm, data, key);
assertEquals(hmacSHA256Value, result);
}In this test, we’re using the HmacSHA512 algorithm with simple string data and keys. Then, we assert that the HMAC result is equal to the expected data.
4. Apache Commons Library
The Apache Commons library also provides a utility class for HMAC calculation.
4.1. Adding the Maven Dependency
To use the Apache Commons utility class, we’ll need to add the commons-codec to our pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-codec</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-codec</artifactId>
<version>1.15</version>
</dependency>
4.2. HmacUtils Class
For calculating an HMAC, we can use the HmacUtils class. After initializing the HmacUtils object, we call the hmacHex() method to perform the HMAC operation. This method returns a hexadecimal string containing the HMAC result.
Let’s create a method for generating the HMAC:
public static String hmacWithApacheCommons(String algorithm, String data, String key) {
String hmac = new HmacUtils(algorithm, key).hmacHex(data);
return hmac;
}Let’s write an example test:
@Test
public void givenDataAndKeyAndAlgorithm_whenHmacWithApacheCommons_thenSuccess() {
String hmacMD5Value = "621dc816b3bf670212e0c261dc9bcdb6";
String hmacMD5Algorithm = "HmacMD5";
String data = "baeldung";
String key = "123456";
String result = HMACUtil.hmacWithApacheCommons(hmacMD5Algorithm, data, key);
assertEquals(hmacMD5Value, result);
}In this test, we’re using the HmacMD5 algorithm.
5. BouncyCastle Library
Similarly, we can also use the BouncyCastle library. BouncyCastle is a collection of cryptographic APIs that we can use in Java.
5.1. Adding the Maven Dependency
Before we start working with the library, we need to add the bcpkix-jdk15to18 dependency to our pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.bouncycastle</groupId>
<artifactId>bcpkix-jdk15to18</artifactId>
<version>1.69</version>
</dependency>5.2. Hmac Class
We’ll start by instantiating the HMac class based on the hashing algorithm we want to use. Then we’ll update the HMAC object with input data using the update() method. Finally, we’ll call the doFinal() method to generate an HMAC code:
public static String hmacWithBouncyCastle(String algorithm, String data, String key) {
Digest digest = getHashDigest(algorithm);
HMac hMac = new HMac(digest);
hMac.init(new KeyParameter(key.getBytes()));
byte[] hmacIn = data.getBytes();
hMac.update(hmacIn, 0, hmacIn.length);
byte[] hmacOut = new byte[hMac.getMacSize()];
hMac.doFinal(hmacOut, 0);
return bytesToHex(hmacOut);
}
private static Digest getHashDigest(String algorithm) {
switch (algorithm) {
case "HmacMD5":
return new MD5Digest();
case "HmacSHA256":
return new SHA256Digest();
case "HmacSHA384":
return new SHA384Digest();
case "HmacSHA512":
return new SHA512Digest();
}
return new SHA256Digest();
}Below is an example that produces an HMAC for a string data and then verifies it:
@Test
public void givenDataAndKeyAndAlgorithm_whenHmacWithBouncyCastle_thenSuccess() {
String hmacSHA512Value = "b313a21908df55c9e322e3c65a4b0b7561ab1594ca806b3affbc0d769a1" +
"290c1922aa6622587bea3c0c4d871470a6d06f54dbd20dbda84250e2741eb01f08e33";
String hmacSHA512Algorithm = "HmacSHA512";
String data = "baeldung";
String key = "123456";
String result = HMACUtil.hmacWithBouncyCastle(hmacSHA512Algorithm, data, key);
assertEquals(hmacSHA512Value, result);
}In this test, we’re using the HmacSHA512 algorithm.
6. Conclusion
The HMAC provides a data integrity check. In this article, we learned how to generate HMAC for input strings data using the HMAC algorithm in Java. Additionally, we discussed the usage of the Apache Commons and BouncyCastle libraries in HMAC calculation.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.
















