Yes, we're now running our Black Friday Sale. All Access and Pro are 33% off until 2nd December, 2025:
Forward Chaining vs. Backward Chaining in Drools
Last updated: August 17, 2025
1. Overview
Drools is a powerful, open-source business rule management system (BRMS) written in Java. It allows developers to separate business logic from application code by writing rules in a declarative format. Most notably, this includes providing a forward chaining and backward chaining inference-based rule engine, a DMN decision engine, and other projects.
In this tutorial, we’ll primarily focus on forward chaining and backward chaining, highlighting differences, use cases, and performance implications. If just getting started with Drools, check out our introduction and Spring integration articles, as we’ll be basing our example code on them.
2. Forward Chaining
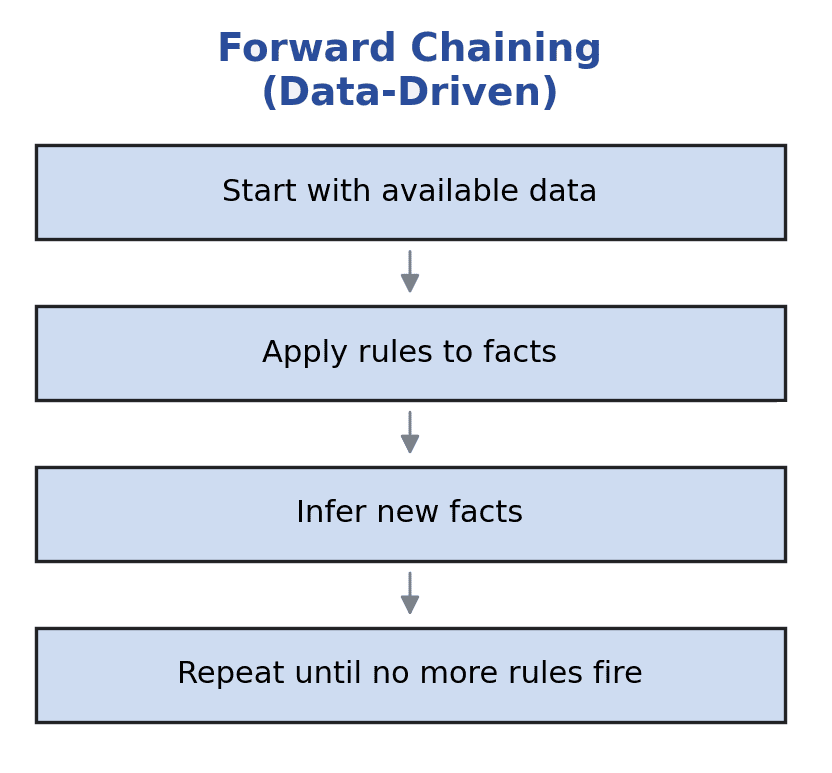
Forward chaining begins with known facts and actively applies rules to generate new ones. The engine evaluates all available data, fires matching rules, and continues this process until it can no longer draw additional conclusions.
In a data-driven approach, inserting facts into Drools’ working memory immediately triggers rules whose conditions match those facts. These rules create new facts, which in turn activate further rules, creating a cascading chain of inferences. Consequently, forward chaining responds dynamically to changing data, making it ideal for environments such as monitoring systems, real-time analytics, or stream-based processing:
For example, in a telecom provisioning engine, adding a customer with a specific plan instantly initiates a sequence of configurations—updating billing, programming switches, adjusting records, and coordinating across multiple systems.
Let’s have a look at a few rules designed for forward chaining:
dialect "mvel"
rule "Suggest Manager Role"
when
Applicant(experienceInYears > 10)
Applicant(currentSalary > 1000000 && currentSalary <= 2500000)
then
suggestedRole.setRole("Manager");
end
rule "Suggest Senior Developer Role"
when
Applicant(experienceInYears > 5 && experienceInYears <= 10)
Applicant(currentSalary > 500000 && currentSalary <= 1500000)
then
suggestedRole.setRole("Senior developer");
end
rule "Suggest Developer Role"
when
Applicant(experienceInYears > 0 && experienceInYears <= 5)
Applicant(currentSalary > 200000 && currentSalary <= 1000000)
then
suggestedRole.setRole("Developer");
endWith the rules set, let’s see forward chaining in action:
private void forwardChaining() {
KieSession ksession = new DroolsBeanFactory().getKieSession();
Applicant applicant = new Applicant("Daniel", 38, 1_600_000.0, 11);
SuggestedRole suggestedRole = new SuggestedRole();
ksession.setGlobal("suggestedRole", suggestedRole);
ksession.insert(applicant);
int fired = ksession.fireAllRules();
System.out.println("Rules fired: " + fired);
System.out.println("Suggested role: " + suggestedRole.getRole());
ksession.dispose();
}Based on our set rules, the console should show that one rule was fired, and the suggested role is Manager.
3. Backwards Chaining
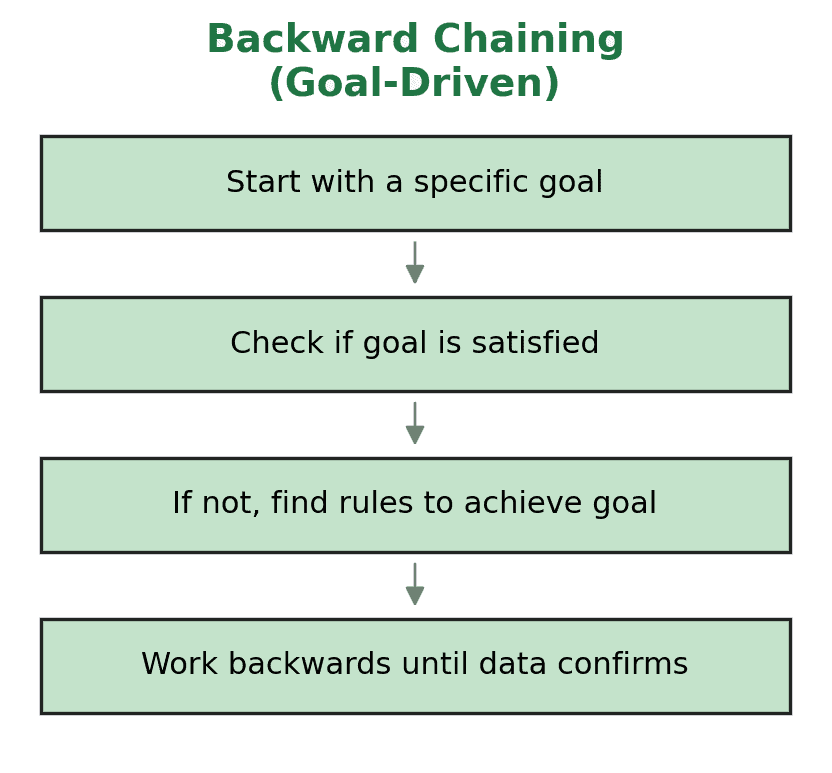
Backward chaining takes the opposite approach. Instead of starting with data, it begins with a goal or query. The engine then works backward to determine what facts or rules can support that conclusion.
In Drools, backward chaining is implemented using queries and logical insertions. When a rule or query requests a fact, Drools searches for rules that could logically infer that fact. If it finds a match, it attempts to satisfy the conditions needed to fire those rules, working recursively toward the initial goal:
It’s especially effective in interrogative systems, such as diagnostic tools or query-driven applications. For example, we might use backward chaining in insurance to identify which policies are covered under a specific reinsurance contract.
Let’s look at a few rules and queries to demonstrate backward chaining:
dialect "mvel"
query belongsTo(String x, String y)
Fact(x, y;)
or
(Fact(z, y;) and belongsTo(x, z;))
end
rule "Great Wall of China BELONGS TO Planet Earth"
when
belongsTo("Great Wall of China", "Planet Earth";)
then
result.setValue("Decision one taken: Great Wall of China BELONGS TO Planet Earth");
end
rule "print all facts"
when
belongsTo(element, place;)
then
result.addFact(element + " IS ELEMENT OF " + place);
endNow, let’s run the rules:
public Result backwardChaining() {
Result result = new Result();
KieSession ksession = new DroolsBeanFactory().getKieSession();
ksession.setGlobal("result", result);
ksession.insert(new Fact("Asia", "Planet Earth"));
ksession.insert(new Fact("China", "Asia"));
ksession.insert(new Fact("Great Wall of China", "China"));
ksession.fireAllRules();
return result;
}As a result, we should see the following flow:
Decision one taken: Great Wall of China BELONGS TO Planet Earth
Great Wall of China IS ELEMENT OF China
Asia IS ELEMENT OF Planet Earth
China IS ELEMENT OF Asia
Great Wall of China IS ELEMENT OF Planet Earth
Great Wall of China IS ELEMENT OF Asia
China IS ELEMENT OF Planet Earth4. Hybrid Reasoning
Drools supports hybrid reasoning, allowing us to mix both chaining methods within the same rule set. We can process incoming data reactively using forward chaining while querying specific conditions using backward chaining. For instance, we could use backward chaining to verify a condition and then trigger a forward chaining rule to insert a new fact, bridging both modes for more flexible, efficient solutions.
Let’s have a look at a visual diagram illustrating how forward chaining and backward chaining work:
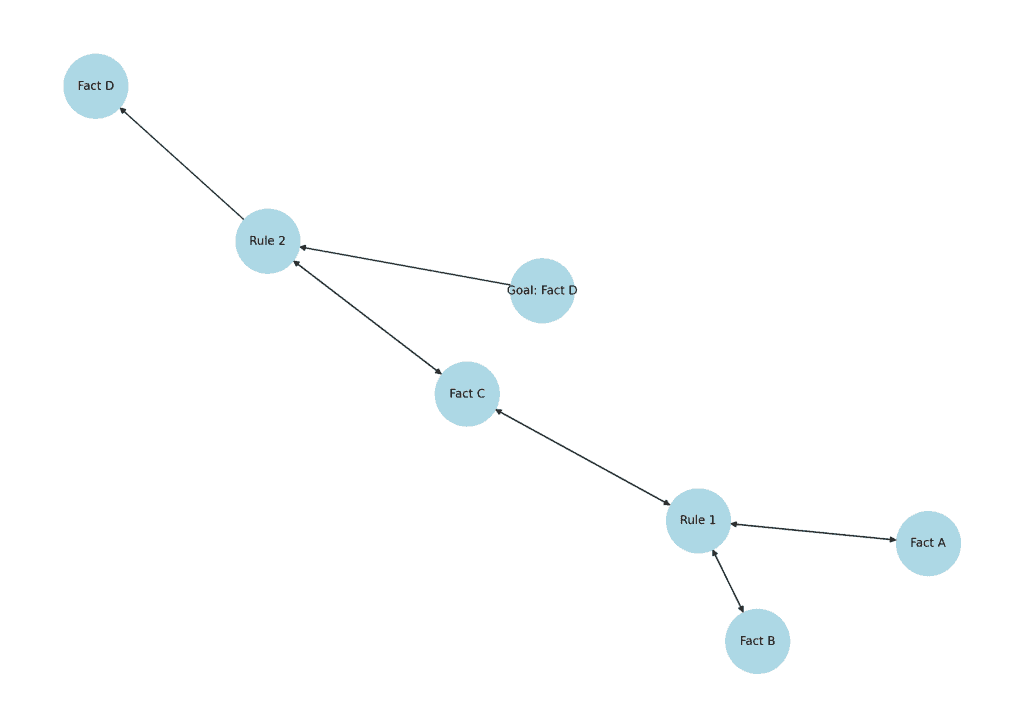
Forward chaining starts with known facts (Fact A, Fact B), triggers Rule 1, infers Fact C, which then triggers Rule 2, and finally infers Fact D.
Backward chaining starts from a goal (Fact D), looks for rules that could lead to it, checks Rule 2, which needs Fact C, and recursively evaluates the necessary facts and rules.
5. Performance Considerations
Since forward chaining reacts to all relevant facts globally, it may suffer performance bottlenecks if your rule base is extensive and data flows are frequent. The Rete algorithm helps optimize pattern matching, though it still requires consideration when scaling.
Meanwhile, backward chaining, being goal‑specific, typically executes fewer rules and is leaner for targeted logic queries—but it doesn’t automatically respond to new data unless prompted.
Therefore, we pick forward chaining for real‑time, auto‑reactive environments, and backward chaining when precision and minimized rule traversal matter.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored what forward and backward chaining are, how and when to implement them, as well as the key differences between them.

















