1. Overview
Having high performance and availability are essential parts of modern software development.
One way to achieve this is through non-blocking and asynchronous programming. In Java, the CompletableFuture class provides a way to write non-blocking code. But is it truly non-blocking?
In this tutorial, we’ll examine the situations when CompletableFuture is blocking and when it is non-blocking.
2. CompletableFuture
Firstly, let’s take a brief look at CompletableFuture class. It’s a powerful class introduced in Java 8 as part of the Concurrent API.
Moreover, it implements the Future interface and represents the primary implementation of the CompletionStage interface. Thus, it offers nearly 50 different methods for creating and executing asynchronous computations.
Why did we need CompletableFurure in the first place? Using the Future interface, we could only retrieve the result by calling the get() method. However, this method represents a blocking operation. In other words, it’ll block the current thread until the result of the task becomes available.
If we need to perform additional actions on the result, we’ll end up with blocking operations.
On the other hand, thanks to CompletionStage, CompletableFuture provides the ability to chain multiple computations together that can run concurrently. This functionality allows us to create a chain of tasks where the next task is triggered when the current task is completed.
Furthermore, we can specify what should happen once we get the result from the future without blocking the current thread.
The CompletableFuture class represents both the stage in dependent processes, where one stage’s completion triggers another, and its result.
3. Blocking vs. Non-blocking
Next, let’s understand the difference between blocking and non-blocking processing.
In the blocking operation, the calling thread waits until the operation in another thread completes before continuing with its execution:
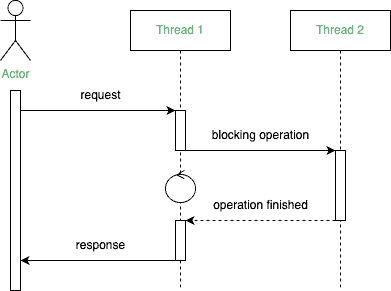
Here, the tasks execute sequentially. Thread 1 is blocked by Thread 2. In other words, Thread 1 can’t continue with its execution until Thread 2 finishes processing its tasks.
We can look at the blocking processing as synchronous operations.
However, blocking operations in our system can cause performance issues, especially in applications that require high availability and scalability.
In contrast, a non-blocking operation allows threads to perform multiple computations simultaneously without having to wait for each task to complete.
The current thread can continue with its execution while the other threads perform tasks in parallel:
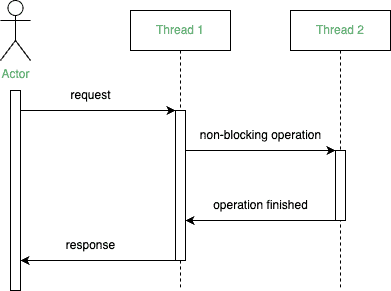
In the example above, Thread 2 isn’t blocking the execution of Thread 1. Furthermore, both threads are running their tasks concurrently.
Besides improving the performance, we can decide what to do with the result once the non-blocking operation finishes with execution.
4. CompletableFuture and Non-blocking Operations
The main advantage of using CompletableFuture is its ability to chain multiple tasks together that will be executed without blocking the current thread. Therefore, we can say the CompletableFuture is non-blocking.
Additionally, it provides several methods that allow us to perform tasks in a non-blocking way, including:
- supplyAsync(): executes a task asynchronously and returns a CompletableFuture representing the result
- thenApply(): applies a function to the result of a previous task and returns a CompletableFuture representing the transformed result
- thenCompose(): executes a task that returns a CompletableFuture and returns a CompletableFuture representing the result of the nested task
- allOf(): executes several tasks in parallel and returns a CompletableFuture representing the completion of all tasks
Next, let’s see a simple example. For instance, suppose we have two tasks we’d like to execute as non-blocking:
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Baeldung")
.thenApply(String::length)
.thenAccept(s -> logger.info(String.valueOf(s)));
After the task completes, it’ll print the number 8 on the standard output.
The computation runs in the background and returns a future. If we have multiple dependent actions, each action is represented by the stage. After one stage completes, it triggers the computation of other dependent stages.
5. When Is CompletableFuture Blocking?
Although CompletableFuture is used to perform non-blocking operations, it can still end up blocking the current thread in certain scenarios.
In asynchronous communication, we usually have a callback mechanism to retrieve the result of the computation. However, CompletableFuture doesn’t notify us upon its completion.
If needed, we can retrieve the result in the calling thread using the get() method.
Nevertheless, we need to be aware the get() method returns the result using blocking processing. If required, it waits for the computation to complete and then returns the result.
Therefore, we’ll end up blocking the current thread until the future completes:
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "Baeldung")
.thenApply(String::toUpperCase);
assertEquals("BAELDUNG", completableFuture.get());
Similarly, calling the join() method will block the current thread as well:
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> "Blocking")
.thenApply(s -> s + " Operation")
.thenApply(String::toLowerCase);
assertEquals("blocking operation", completableFuture.join());
The main difference between these two methods is that the join() method doesn’t throw checked exceptions if the future completes exceptionally.
Additionally, we can call the isDone() method to check whether the future is completed before obtaining the result.
However, when it’s necessary to obtain the computation result in the calling thread, we can create CompletableFuture, do other work in the current thread, and then call the get() or join() method. By giving it more time, it’s more likely the Future will finish with computations before we get the result. But there’s still no guarantee that the retrieval won’t end up blocking the thread.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we examined the scenarios when CompletableFuture is non-blocking and when it’s not.
To sum up, CompletableFuture is non-blocking most of the time. However, if we call the get() or the join() methods to retrieve the result, they will block the current thread.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.


















