Yes, we're now running our Black Friday Sale. All Access and Pro are 33% off until 2nd December, 2025:
Guide to Eureka Self Preservation and Renewal
Last updated: January 27, 2024
1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’re going to learn about Eureka Self Preservation and Renewal.
We’ll start by creating a Eureka server alongside multiple Eureka client instances.
Then, we’ll register these clients with our Eureka server to show how self-preservation works.
2. Eureka Self-Preservation
Before talking about self-preservation, let’s understand how the Eureka server maintains the client instance registry.
During the start-up, the clients trigger a REST call with the Eureka server to self-register to the server’s instance registry. When a graceful shutdown occurs after use, the clients trigger another REST call so that the server can wipe out all the data related to the caller.
To handle ungraceful client shutdowns the server expects heartbeats from the client at specific intervals. This is called renewal. If the server stops receiving the heartbeat for a specified duration, then it will start evicting the stale instances.
The mechanism that stops evicting the instances when the heartbeats are below the expected threshold is called self-preservation. This might happen in the case of a poor network partition, where the instances are still up, but just can’t be reached for a moment or in the case of an abrupt client shutdown.
And when the server activates self-preservation mode it holds the instance eviction until the renewal rate is back above the expected threshold.
Let’s see this in action.
3. Creating the Server
Let’s first, create the Eureka server by annotating our Spring Boot main class with @EnableEurekaServer:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
public class EurekaServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApplication.class, args);
}
}But now, let’s add the basic configurations for us to start up the server:
eureka.client.registerWithEureka=false
eureka.client.fetchRegistry=false
eureka.instance.hostname=localhostSince we don’t want our Eureka server to register with itself, we’ve set the property eureka.client.registerWithEureka as false. Here the property eureka.instance.hostname=localhost is particularly important since we’re running it in a local machine. Otherwise, we may end up creating an unavailable replica within the Eureka server – messing up the client’s heartbeat counts.
Now let’s take a look at all the configuration and its relevance in the context of self-preservation in the next section.
3.1. Self-Preservation Configurations
By default, Eureka servers run with self-preservation enabled.
However, for the sake of our understanding, let’s go through each of these configurations on the server-side.
- eureka.server.enable-self-preservation: Configuration for disabling self-preservation – the default value is true
- eureka.server.expected-client-renewal-interval-seconds: The server expects client heartbeats at an interval configured with this property – the default value is 30
- eureka.instance.lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: Indicates the time in seconds that the Eureka server waits since it received the last heartbeat from a client before it can remove that client from its registry – the default value is 90
- eureka.server.eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: This property tells the Eureka server to run a job at this frequency to evict the expired clients – the default value is 60 seconds
- eureka.server.renewal-percent-threshold: Based on this property, the server calculates the expected heartbeats per minute from all the registered clients – the default value is 0.85
- eureka.server.renewal-threshold-update-interval-ms: This property tells the Eureka server to run a job at this frequency to calculate the expected heartbeats from all the registered clients at this minute – the default value is 15 minutes
In most cases, the default configuration is sufficient. But for specific requirements, we might want to change these configurations. Utmost care needs to be taken in those cases to avoid unexpected consequences like wrong renew threshold calculation or delayed self-preservation mode activation.
4. Registering Clients
Now, let’s create a Eureka Client and spin up six instances:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
public class EurekaClientApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaClientApplication.class, args);
}
}Here are the client’s configurations:
spring.application.name=Eurekaclient
server.port=${PORT:0}
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka
eureka.instance.preferIpAddress=true
eureka.instance.lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds=30This configuration allows us to spin up multiple instances of the same client with the PORT program argument. The configuration eureka.instance.lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds indicates the interval of heartbeats that the client sends to the server. The default value is 30 seconds which means that the client will send one heartbeat every 30 seconds.
Let’s now start these six client instances with the port numbers starting from 8081 to 8086 and navigate to http://localhost:8761 to inspect whether these instances are registered with the Eureka server.
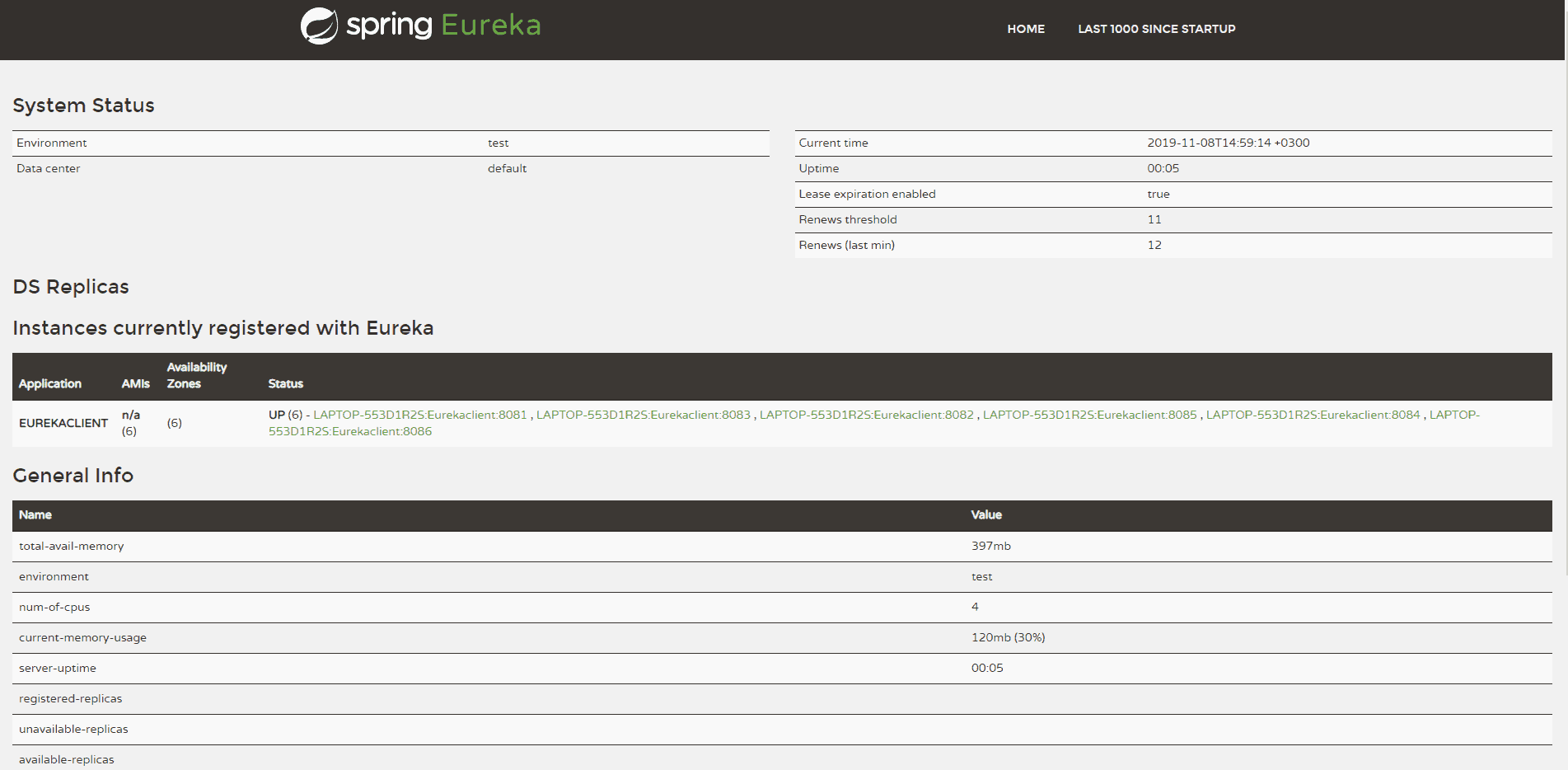
From the screenshot, we can see that our Eureka server has six registered client instances and the total renewal threshold is 11. The threshold calculation is based on three factors:
- Total number of registered client instances – 6
- Configured client renewal interval – 30 seconds
- The configured renewal percentage threshold – 0.85
Considering all these factors, in our case, the threshold is 11.
5. Testing Self-Preservation
In order to simulate a temporary network problem, let’s set the property eureka.client.should-unregister-on-shutdown as false at the client-side and stop one of our client instances. Because we set the should-unregister-on-shutdown flag as false, the client won’t invoke the unregister call and the server assumes that this is an ungraceful shutdown.
Let’s now wait for 90 seconds, set by our eureka.instance.lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds property, and navigate again to http://localhost:8761. The red bold text indicates that the Eureka Server is now in self-preservation mode and stopped evicting instances.
Let’s now inspect the registered instances section to see if the stopped instance is still available or not. As we can see, it is available but with the status as DOWN:
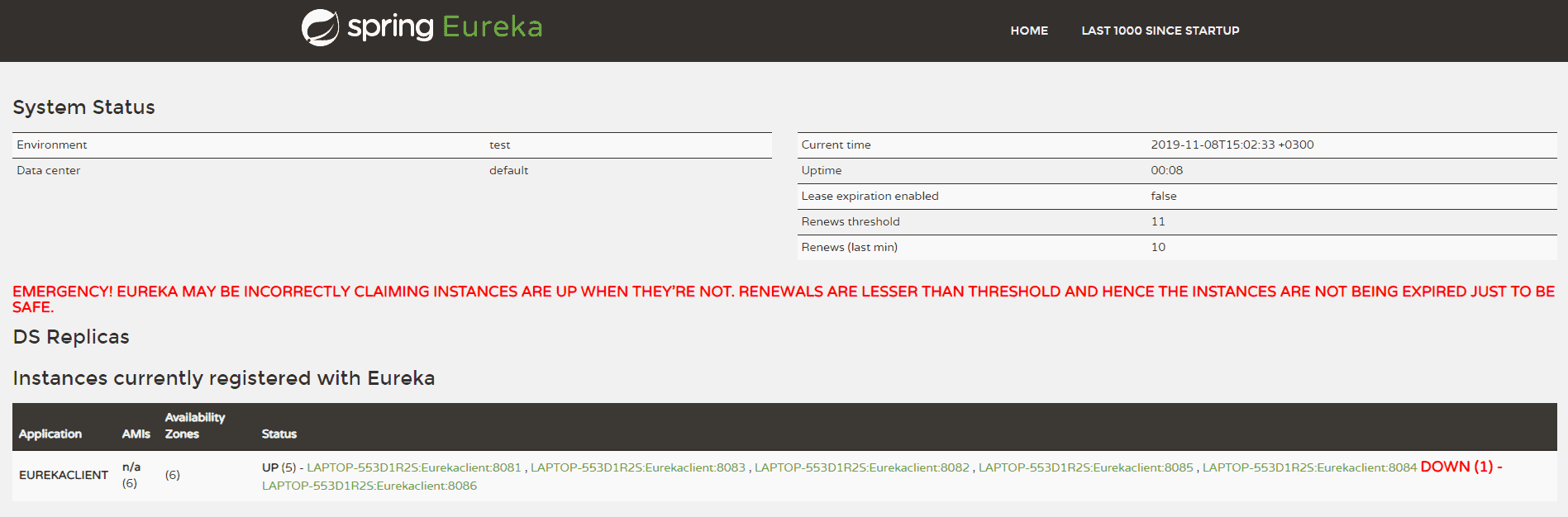
The only way the server can get out of self-preservation mode is either by starting the stopped instance or by disabling self-preservation itself. If we repeat the same steps by setting the flag eureka.server.enable-self-preservation as false, then the Eureka server will evict the stopped instance from the registry after the configured lease expiration duration property.
6. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we’ve learned how Eureka self-preservation works and how can we configure different options related to self-preservation.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.

















