1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll learn about the pigeonhole sorting algorithm.
2. What Is Pigeonhole Sort?
Pigeonhole sort is appropriate for sorting arrays of elements where the number of elements in the array () is close to the range of possible values inside the array (
).
For example, if we had an array with elements ,
is 9, and
is 1 through 9, which equals 9. Therefore, we can use pigeonhole sort since
is equal to
.
Furthermore, pigeonhole sort requires time.
3. How Does It Work?
Now let’s see how the sorting algorithm works.
3.1. Find the Range
First, we should find the range of possible values inside the array:
Now we can create pigeonholes with a size equal to .
3.2. Fill the Pigeonholes
Now let’s create the pigeonholes and fill them:
The first line creates an array of vectors with the size of . Each vector is a pigeonhole that keeps equal elements.
After that, we go through the original array and put each element inside a pigeonhole with index .
3.3. Fill the Original Array
Now that we have sorted the elements and put them into the pigeonholes, we should put them in the original array:
The above code iterates through the pigeonholes and copies each element into the original array.
4. An Example
Let’s assume we have .
In the first step, we calculate ,
, and
.
In the second step, we create the pigeonholes and fill them:
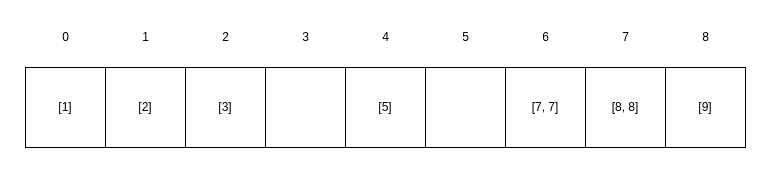
In the third step, we copy the elements from the pigeonholes into the original array:
We’ve successfully sorted the array.
5. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how the pigeonhole sorting algorithm works and when it’s appropriate to use it.