Learn through the super-clean Baeldung Pro experience:
>> Membership and Baeldung Pro.
No ads, dark-mode and 6 months free of IntelliJ Idea Ultimate to start with.
In this article, we’re going to learn the binary tree data structure and its properties. Next, we’ll learn six types of binary trees with an illustration.
Finally, we’ll explore different applications of a binary tree.
A binary tree is a hierarchal data structure in which each node has at most two children. The child nodes are called the left child and the right child.
To start with, let’s describe the linked list representation of a binary tree in which each node has three fields:
Let’s see an example of a binary tree:
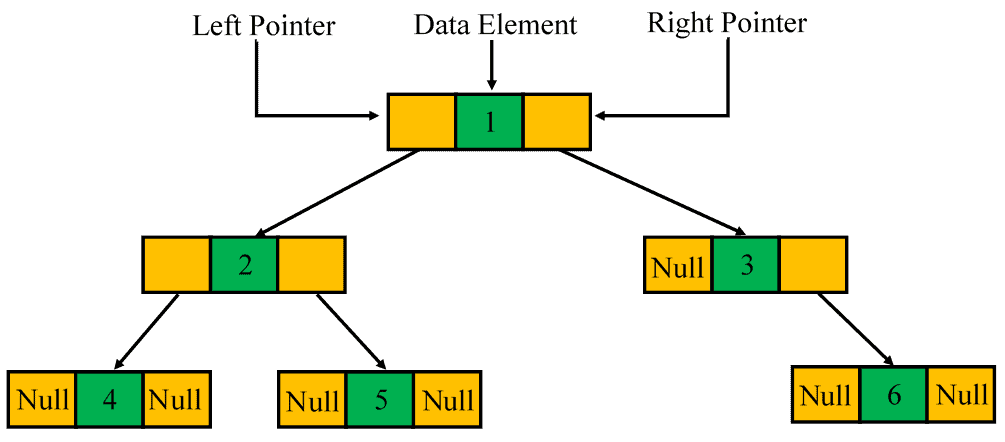
Let’s now focus on some basic properties of a binary tree:
In this section, we’re going to discuss six types of binary trees and describe each with an illustration.
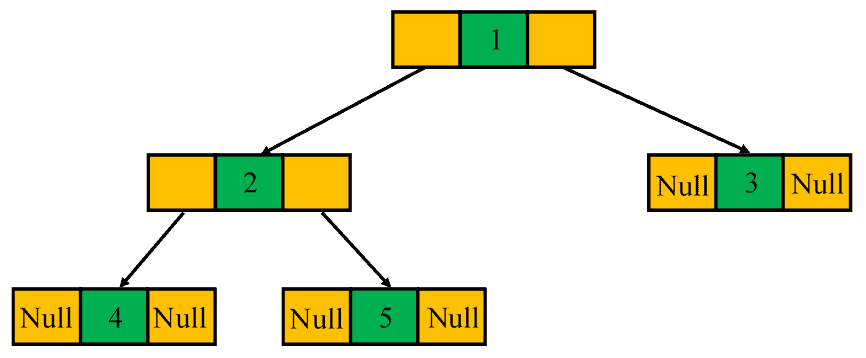
A binary tree is said to be a full binary tree when each internal node has zero or two children:
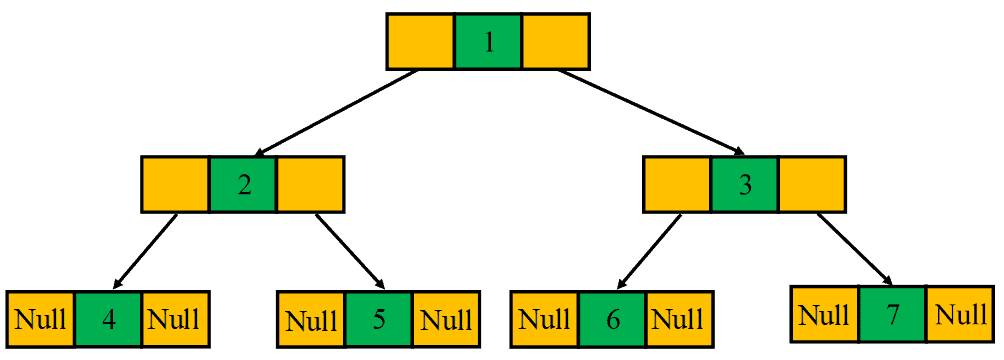
A perfect binary tree is a special type of binary tree in which all the leaf nodes are at the same level, and each internal node has two children:
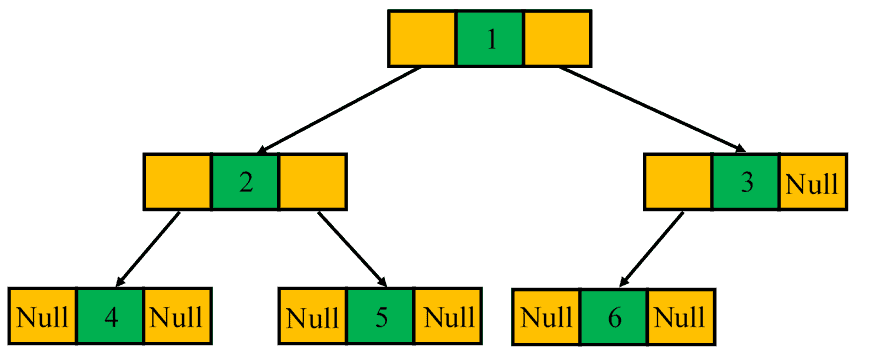
A binary tree is referred to as a complete binary tree when all of its levels are completely filled. The only exception is possibly the lowest level in which the nodes must lean as left as possible:
A degenerate or pathological tree is a type of binary tree in which each internal node has a single child, either the left child or the right child:
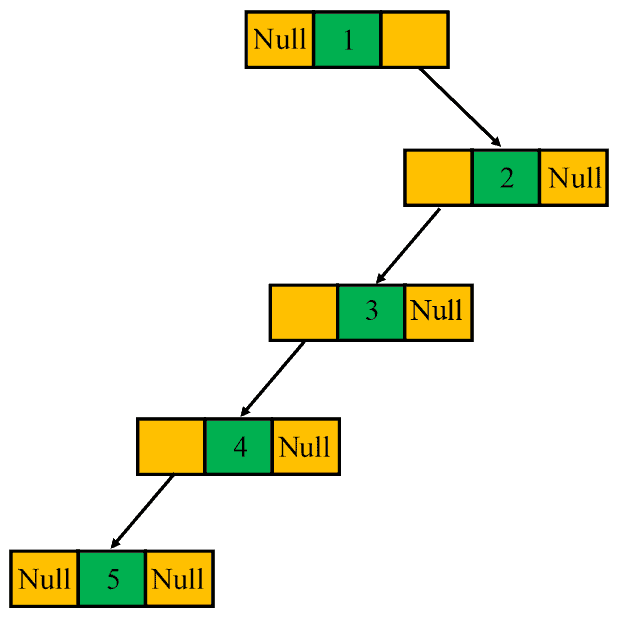
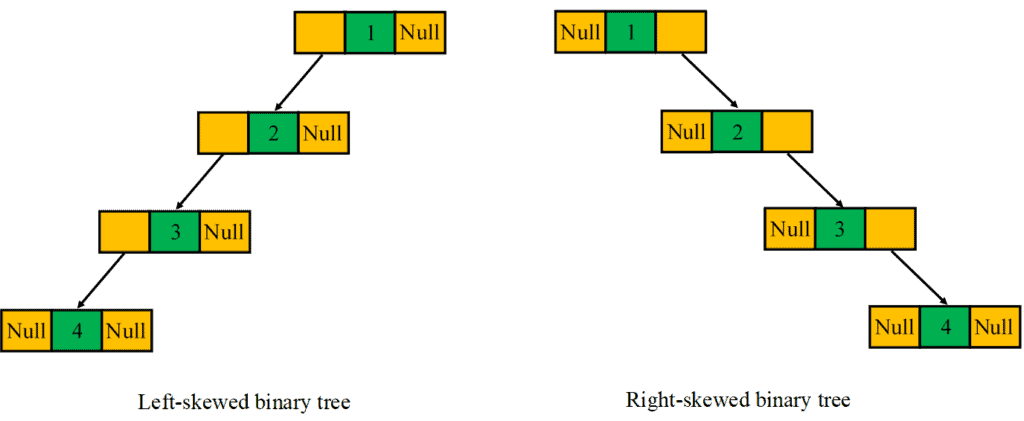
A binary tree is said to be a skewed binary tree if all of its internal nodes have exactly one child, and either left children or right children dominate the tree. In particular, there exist two types of skewed binary trees: left-skewed binary tree and the right-skewed binary tree:
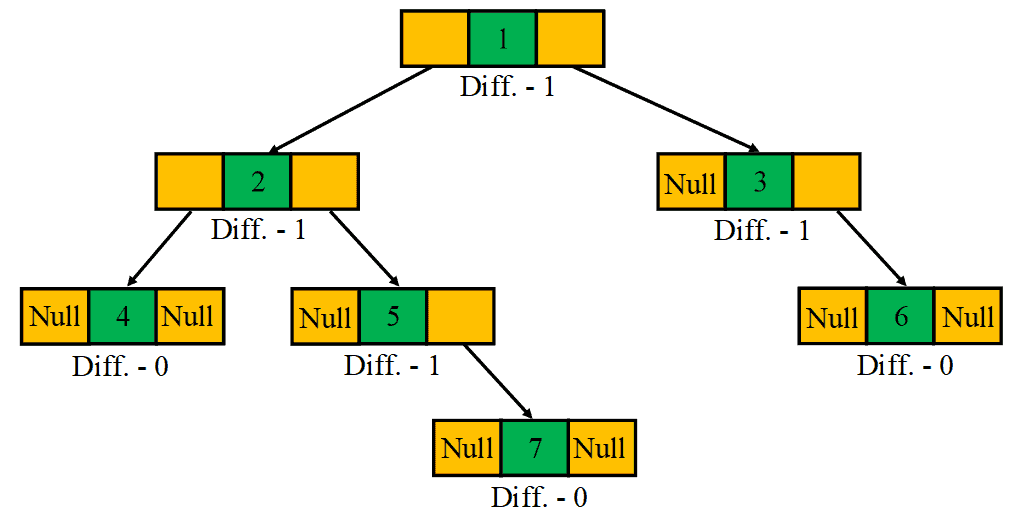
A balanced binary tree is also a special type of binary tree in which the difference of height between the left and the right subtrees for each node is at most one:
There are many other data structures that are derived from the idea of a binary tree, such as binary search tree, syntax tree, heap, hash tree, red-black tree, binary trie, AVL tree, GGM tree, T-tree, and Treap.
Other real-life applications of a binary tree include binary space partition, heap sort, Huffman coding, virtual memory management, and indexing.
In this article, we’ve learned the binary tree data structure along with its basic properties.
Then, we’ve discussed six types of binary trees with illustrative examples. At last, we’ve listed various applications of a binary tree.