Learn through the super-clean Baeldung Pro experience:
>> Membership and Baeldung Pro.
No ads, dark-mode and 6 months free of IntelliJ Idea Ultimate to start with.
Last updated: March 18, 2024
Artificial intelligence, the cutting-edge technology that simulates human intelligence in machines, has revolutionized various industries and continues to shape our future. Artificial intelligence agents have evolved significantly over time, from early expert systems in 1970 to the advent of machine learning algorithms and deep neural networks in recent decades.
In this tutorial, we’ll delve into the realm of Artificial Intelligence Agents, exploring their environment, types, and examples.
An artificial intelligence agent can be defined as a program that makes decisions and takes action based on the decisions. These agents are designed to mimic or replicate human intelligence and decision-making capabilities. The critical components of Artificial Intelligence agents include:
Artificial Intelligence agents perceive and gather information about their environment through various sensors, such as cameras, microphones, or text input. They can analyze and interpret the data they receive to understand the state of the environment or extract relevant features.
Artificial Intelligence agents use reasoning and decision-making algorithms to analyze the available information and determine the best course of action to achieve their goals. They may use techniques like rule-based systems, logical reasoning, machine learning, or reinforcement learning to make decisions and select appropriate actions.
Artificial Intelligence agents can act in their environment based on their decisions and goals. These actions can range from simple tasks like moving an object in a physical environment to complex interactions in virtual or social environments.
Artificial Intelligence agents can learn from their experiences and adapt their behaviour based on the feedback they receive. They can update their knowledge, improve their decision-making capabilities, and adjust their actions to achieve better performance over time.
Artificial Intelligence agents can communicate and interact with humans or other agents through various modalities, such as speech, text, or gestures. They can understand and generate natural language, engage in conversations, and respond to queries or requests.
Artificial Intelligence agents can operate in various environments, depending on their specific tasks and applications. Here are some common types of environments in which Artificial Intelligence agents can operate:
Artificial Intelligence agents can operate in simulated or virtual environments, which are computer-generated environments that mimic real-world scenarios. These environments provide a controlled setting for training and testing Artificial Intelligence agents without the risks or costs associated with physical environments. Let’s now take a look at some examples:
Artificial Intelligence agents can also operate in physical environments, which are the real-world spaces where they perform tasks. These environments range from factories and warehouses to homes, hospitals, and outdoor spaces. Artificial Intelligence agents in physical environments often use sensors (such as cameras, lidar, or microphones) to perceive their surroundings and actuators (such as robotic arms or wheels) to interact with the environment.
Here are some examples:
Artificial Intelligence agents can interact with web-based environments and the internet. Artificial Intelligence agents can browse websites, extract information, analyze data, perform natural language processing, and interact with users through chatbots or virtual assistants. Here are some examples:
Artificial Intelligence agents can operate in text-based environments, processing and generating natural language text. These environments can involve tasks like language translation, sentiment analysis, text summarization, question-answering, and chat-based interactions. Let’s now take a look at some examples:
Artificial Intelligence agents can be trained and operate in-game environments, ranging from classic board games like chess and Go to complex video games. Game environments provide well-defined rules and objectives, making them suitable for developing Artificial Intelligence algorithms and evaluating agent performance. Here’re some examples:
Artificial Intelligence agents can be designed to operate in social environments, interacting and collaborating with humans or other agents. Social environments can involve tasks like social chatbots, virtual companions, collaborative robots, and multi-agent systems. Here’re some examples:
Agents are classified into five classes based on their agent programs. Let’s discover those classes.
Simple Reflex (SR) agents make decisions based on the current percept or input without considering the history or future consequences. SR agents operate correctly only in the fully observable environment, here’s the leading architecture of SR agents:
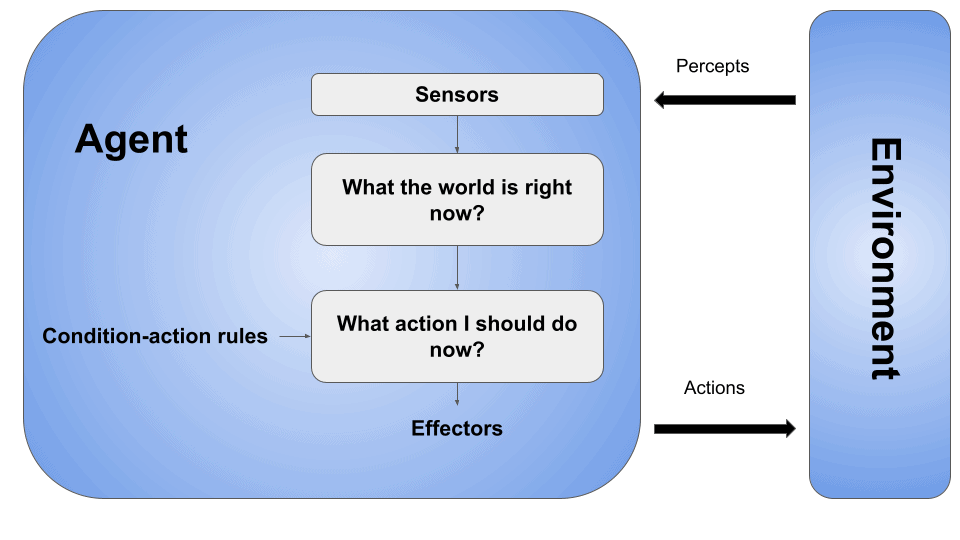
These agents have internal models or representations of the world, enabling them to consider the history of percepts to make more informed decisions, here’s the main architecture of a model-based agent:
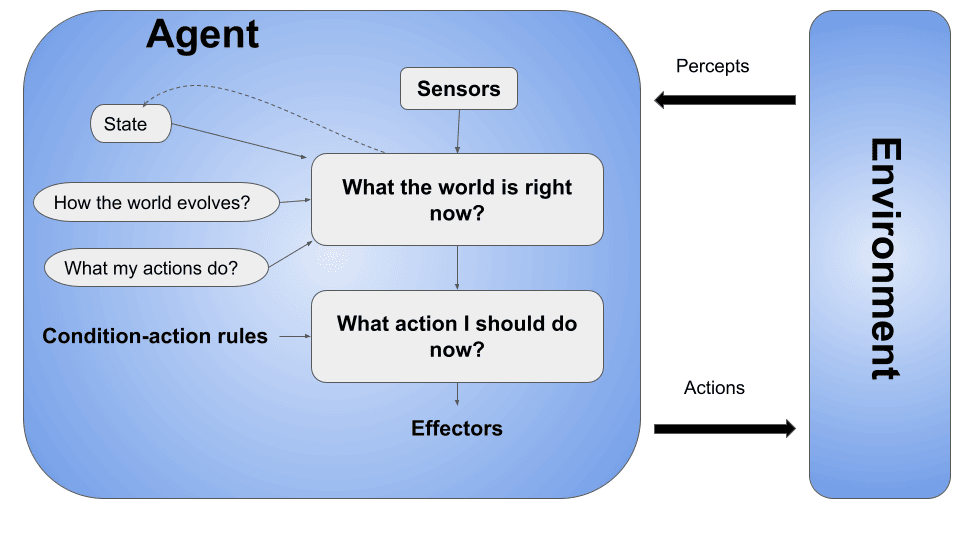
These agents have specific goals or objectives they strive to achieve. They use their internal models to plan and take actions that are likely to lead them toward their goals. Here’s the central architecture of the SR agent:
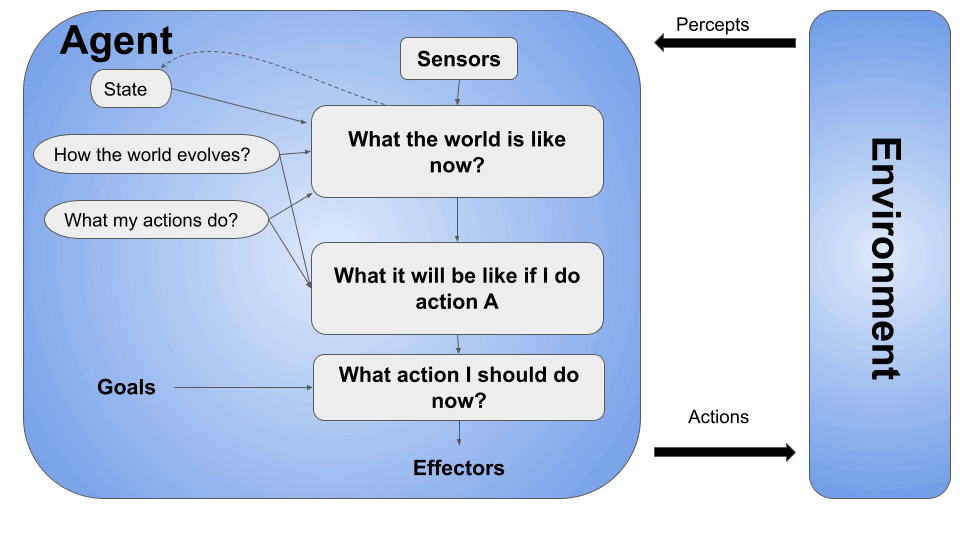
These agents consider their goals and the desirability or utility of different outcomes. Moreover, They make decisions based on the expected utility of different actions. Here’s the main architecture of a Utility-based agent:
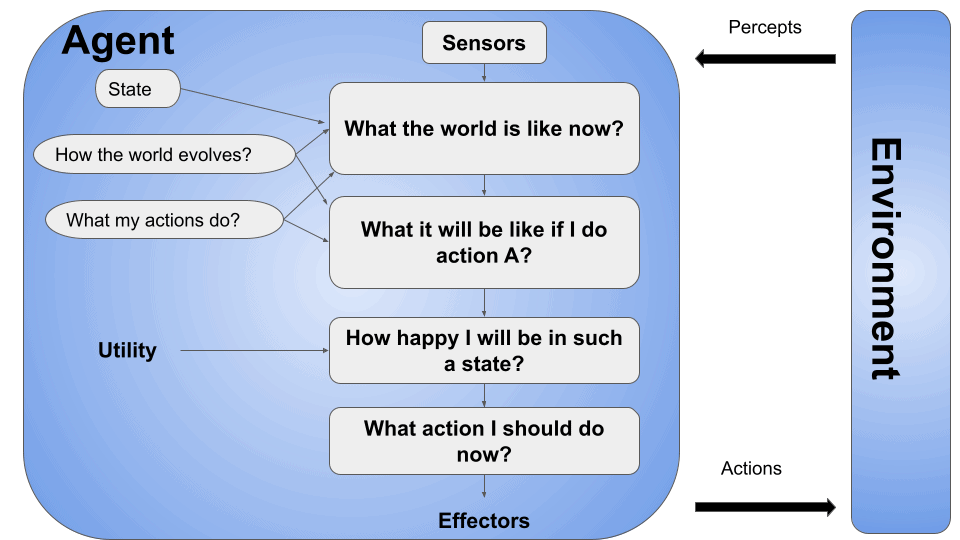
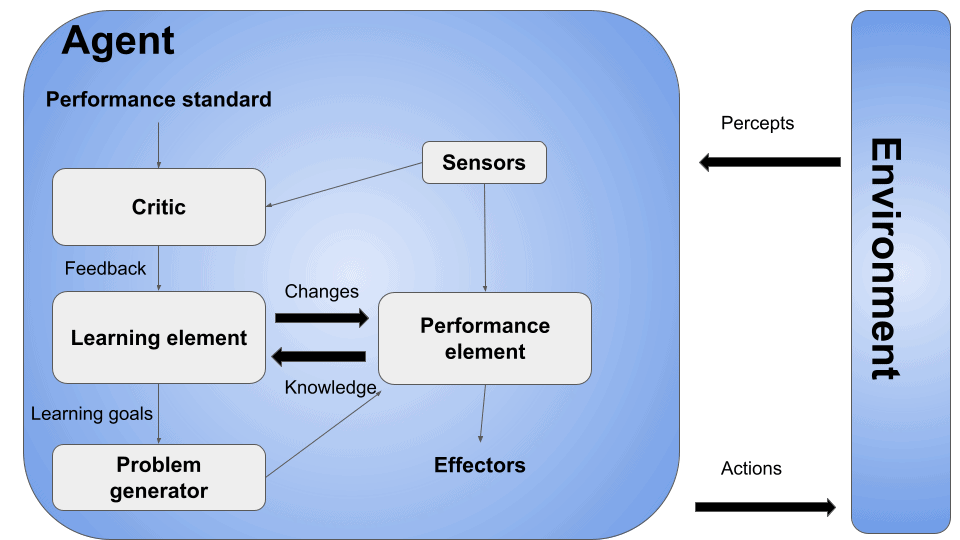
These agents can learn from their environment and past experiences. Furthermore, they can adapt and improve their performance over time by updating their internal models or adjusting their decision-making strategies. However, a learning agent has mainly four conceptual components, which are:
Chatbots are Artificial Intelligence agents that interact with humans through text or speech. On the other hand, they can understand natural language inputs and provide relevant responses. here’re some examples:
Self-driving cars and autonomous drones are Artificial Intelligence agents that perceive their environment through sensors such as cameras and lidar, process the data to make decisions, and control their actions accordingly. Here’re some examples:
These agents analyze user preferences and behavior to provide personalized recommendations. Examples include the recommendation algorithms used by streaming platforms, here’re some examples:
Artificial Intelligence agents have demonstrated remarkable performance in various games, here’re some examples:
We use Artificial Intelligence agents to assist in medical diagnosis by analyzing patient data, symptoms, and medical records to provide recommendations or predictions for disease identification and treatment. Let’s take a look at some examples:
We use artificial intelligence agents in robotic systems for tasks like object recognition, motion planning, and human-robot interaction. Let’s take a look at some examples:
In conclusion, we have explored the concept of artificial intelligence agents and their role in various environments. As a result, we design Artificial Intelligence agents are software systems to perform specific tasks or interact with their environment using artificial intelligence techniques.