Learn through the super-clean Baeldung Pro experience:
>> Membership and Baeldung Pro.
No ads, dark-mode and 6 months free of IntelliJ Idea Ultimate to start with.
Last updated: March 25, 2025
In Jenkins, restarting the server is important as it is frequently required for updating the configurations and plugins to newer versions. Additionally, we want to approach this in a way that doesn’t disrupt our CI/CD pipeline. So, updating Jenkins needs a safe way to restart to avoid any bugs and errors as ongoing builds might get stuck during the restart.
In this tutorial, we’ll look at different ways to restart Jenkins safely to avoid job interruption and provide data integrity.
Jenkins is an open-source project that updates very frequently. So, we frequently need to update various components of the server, including the config or plugins. Let’s also look at various reasons to update the Jenkins server:
Hence, restarting the Jenkins server needs to be done very carefully to ensure stability and prevent unexpected downtime.
Jenkins provides a built-in safe restart option which is used to restart the server without interrupting the running jobs. To demonstrate, let’s look at the following steps:
Jenkins provides a restart banner for other Jenkins pages. Here, we can create a custom message that will appear on every page:
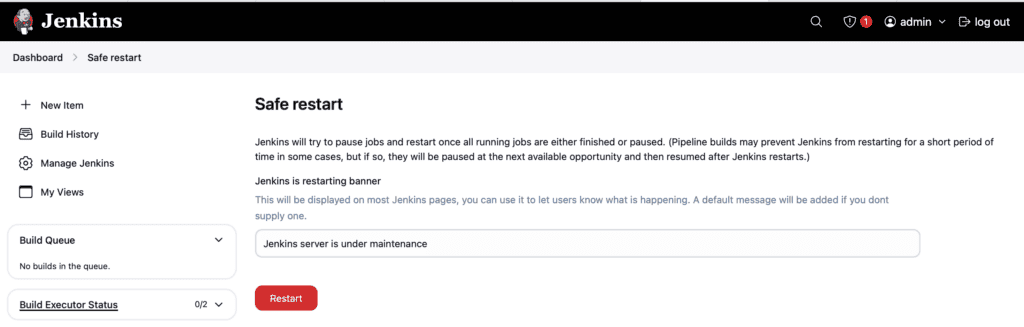
No new jobs will start and when all running jobs finish, the server will restart.
The Jenkins CLI provides a way to programmatically restart the Jenkins server safely during automated tasks.
The Jenkins CLI is bundled as a JAR. We can download it from our deployment at https://jenkins.example.org/jnlpJars/jenkins-cli.jar link. To demonstrate, let’s take a look at the command:
$ java -jar jenkins-cli.jar -s https://jenkins.example.org -auth baeldung:baeldung_admin safe-restart
This will trigger the safe restart mode as before, meaning that no new jobs will start and the server will restart after all running jobs finish. This method is useful for remote management of Jenkins instances.
Another approach to restarting Jenkins is using a scripted job. This method is beneficial as it allows automated, scheduled restarts directly within Jenkins jobs without relying on external tools.
To restart Jenkins safely with Groovy within a scheduled job, we can use the Jenkins Groovy plugin. It provides the required System Groovy script build step.
Now, let’s look at the steps to create a freestyle job and restart the server:
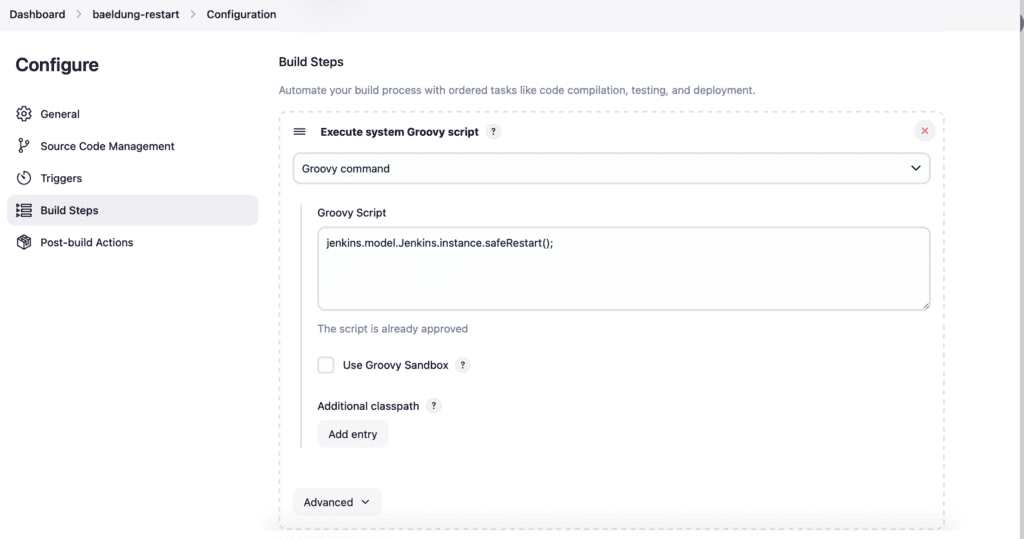
Finally, for the script content, we need a fully-qualified reference to the safeRestart() system function:
jenkins.model.Jenkins.instance.safeRestart();The above script will safely restart the Jenkins server on each run.
To automatically trigger the job, let’s configure the cron trigger in this job:
This scheduling also works across platforms without requiring additional installations and ensures the automatic and safe restart of the Jenkins server.
In this article, we explored several different ways to restart the Jenkins server safely. This includes the Jenkins UI, Jenkins CLI, or system Groovy scripts.
Finally, these methods let us restart Jenkins to finish server, plugin, or configuration updates without impacting existing running jobs.