Yes, we're now running our Black Friday Sale. All Access and Pro are 33% off until 2nd December, 2025:
Introduction to DHCP
Last updated: March 18, 2024
1. Introduction
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a client-server protocol that automatically assigns an Internet Protocol (IP) address to a device as well as other related configurations.
In this tutorial, we’ll discuss this protocol and explore various aspects such as how it works and the benefits it offers.
2. What Is DHCP?
Every computer on a network must have an IP address to communicate with other devices. An IP address is an identifier for a computer or device on a network.
There are two ways an IP address is assigned to a computer – static and dynamic. A static IP is where a user assigns an IP address manually to a computer. However, this process is tedious and error-prone as it requires manual intervention every time a device joins the network. Dynamic IP assignment resolves this issue.
A dynamic IP is where a computer receives an IP address from a DHCP server. Moreover, a DHCP server also assigns a device a subnet mask, default gateway, and the Domain Name System (DNS) server in addition.
3. How Does DHCP Work?
DHCP is a Client-Server protocol. In a network, each device will have a DHCP client installed. Additionally, there’s a DHCP server, which is responsible for the automatic assignment of addresses as requested by the DHCP clients:
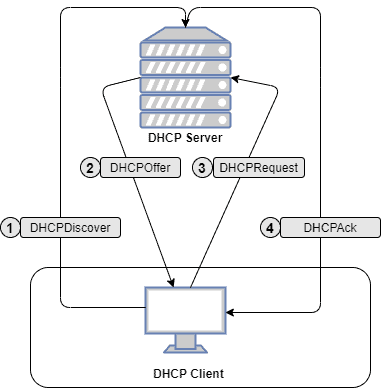
The assignment between the DHCP client and server follows four steps:
- Server Discovery: Once a device joins a network and requires an IP address, it broadcasts a message to the network asking for it. The DHCP server will process this request and all other devices in the network will ignore this message
- DHCP Offer: The DHCP server looks for an available IP address from its pool of addresses and offers one to the requesting device
- DHCP Request: The device responds to the DHCP server by confirming the provided IP address
- Acknowledgment: The DHPC server provides the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and the DNS server details to the device
4. DHCP Lease Time Management
The IP address information assigned by DHCP is only valid for a limited period of time and is known as a DHCP lease and the period of validity is called the DHCP lease time.
When the lease expires, the client can no longer use the IP address and has to stop all communication with the IP network unless it requests to extend the lease via the DHCP lease renewal cycle.
To avoid impacts of the DHCP server not being available at the end of the lease time, clients generally start renewing their lease halfway through the lease period. This renewal process ensures robust IP address allocation to devices.
5. Benefits of DHCP
DHCP offers several benefits over static IP configuration:
- Reliable IP address management: DHCP minimizes configuration errors caused by manual IP address configuration, such as typographical errors, or address conflicts caused by the assignment of an IP address to more than one computer at the same time
- Reduced Manual Intervention: DHCP lets network administrators centralize and automate the IP address configuration process. DHCP lets efficient management of IP addresses. For example, if a device leaves the network or moves to a different location, the assigned IP address is removed and assigned to another device
6. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we discussed the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, or DHCP.
First, we discussed IP address management options and explored the importance of dynamically managing the IP addresses of devices. We then learned how DHCP works and the communication happens between a DHCP server and a client. We also discussed the lease management technique.
Finally, we concluded the tutorial by providing the benefits of using DHCP.