1. Overview
Most of the time, when we’re implementing graph-based algorithms, we also need to implement some utility functions.
JGraphT is an open-source Java class library which not only provides us with various types of graphs but also many useful algorithms for solving most frequently encountered graph problems.
In this article, we’ll see how to create different types of graphs and how convenient it is to use the provided utilities.
2. Maven Dependency
Let’s start by adding the dependency to our Maven project:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jgrapht</groupId>
<artifactId>jgrapht-core</artifactId>
<version>1.0.1</version>
</dependency>
The latest version can be found at the Maven Central.
3. Creating Graphs
JGraphT supports various types of graphs.
3.1. Simple Graphs
For starters, let’s create a simple graph with a vertex of type String:
Graph<String, DefaultEdge> g
= new SimpleGraph<>(DefaultEdge.class);
g.addVertex(“v1”);
g.addVertex(“v2”);
g.addEdge(v1, v2);
3.2. Directed/Undirected Graphs
It also allows us to create directed/undirected graphs.
In our example, we’ll create a directed graph and use it to demonstrate other utility functions and algorithms:
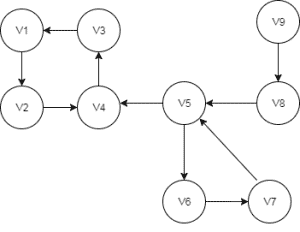
DirectedGraph<String, DefaultEdge> directedGraph
= new DefaultDirectedGraph<>(DefaultEdge.class);
directedGraph.addVertex("v1");
directedGraph.addVertex("v2");
directedGraph.addVertex("v3");
directedGraph.addEdge("v1", "v2");
// Add remaining vertices and edges
3.3. Complete Graphs
Similarly, we can also generate a complete graph:
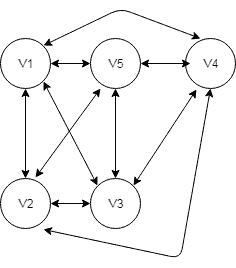
public void createCompleteGraph() {
completeGraph = new SimpleWeightedGraph<>(DefaultEdge.class);
CompleteGraphGenerator<String, DefaultEdge> completeGenerator
= new CompleteGraphGenerator<>(size);
VertexFactory<String> vFactory = new VertexFactory<String>() {
private int id = 0;
public String createVertex() {
return "v" + id++;
}
};
completeGenerator.generateGraph(completeGraph, vFactory, null);
}
3.4. Multi-Graphs

Other than simple-graphs, API also provides us with multigraphs (graphs with multiple paths between two vertices).
Besides, we can have weighted/unweighted or user-defined edges in any graph.
Let’s create a multigraph with weighted edges:
public void createMultiGraphWithWeightedEdges() {
multiGraph = new Multigraph<>(DefaultWeightedEdge.class);
multiGraph.addVertex("v1");
multiGraph.addVertex("v2");
DefaultWeightedEdge edge1 = multiGraph.addEdge("v1", "v2");
multiGraph.setEdgeWeight(edge1, 5);
DefaultWeightedEdge edge2 = multiGraph.addEdge("v1", "v2");
multiGraph.setEdgeWeight(edge2, 3);
}
In addition to this, we can have unmodifiable (read-only) and listenable (allows external listeners to track modifications) graphs as well as subgraphs. Also, we can always create all compositions of these graphs.
Further API details can be found here.
4. API Algorithms
Now, that we’ve got full fledge graph objects, let’s look at some common problems and their solutions.
4.1. Graph Iteration
We can traverse the graph using various iterators such as BreadthFirstIterator, DepthFirstIterator, ClosestFirstIterator, RandomWalkIterator as per the requirement.
We simply need to create an instance of respective iterators by passing graph objects:
DepthFirstIterator depthFirstIterator
= new DepthFirstIterator<>(directedGraph);
BreadthFirstIterator breadthFirstIterator
= new BreadthFirstIterator<>(directedGraph);
Once we get the iterator objects, we can perform the iteration using hasNext() and next() methods.
4.2. Finding the Shortest Path
It provides implementations of various algorithms such as Dijkstra, Bellman-Ford, Astar, and FloydWarshall in the org.jgrapht.alg.shortestpath package.
Let’s find the shortest path using Dijkstra’s algorithm:
@Test
void whenGetDijkstraShortestPath_thenGetNotNullPath() {
DijkstraShortestPath dijkstraShortestPath
= new DijkstraShortestPath(directedGraph);
List<String> shortestPath = dijkstraShortestPath
.getPath("v1","v4").getVertexList();
assertNotNull(shortestPath);
}
Similarly, to get the shortest path using the Bellman-Ford algorithm:
@Test
void whenGetBellmanFordShortestPath_thenGetNotNullPath() {
BellmanFordShortestPath bellmanFordShortestPath
= new BellmanFordShortestPath(directedGraph);
List<String> shortestPath = bellmanFordShortestPath
.getPath("v1", "v4")
.getVertexList();
assertNotNull(shortestPath);
}
4.3. Finding Strongly Connected Subgraphs
Before we get into the implementation, let’s briefly look at what strongly connected subgraphs mean. A subgraph is said to be strongly connected only if there is a path between each pair of its vertices.
In our example, {v1,v2,v3,v4} can be considered a strongly connected subgraph if we can traverse to any vertex irrespective of what the current vertex is.
We can list four such subgraphs for the directed graph shown in the above image:
{v9},{v8},{v5,v6,v7},{v1,v2,v3,v4}
Implementation to list out all strongly connected subgraphs:
@Test
void whenGetStronglyConnectedSubgraphs_thenPathExists() {
StrongConnectivityAlgorithm<String, DefaultEdge> scAlg
= new KosarajuStrongConnectivityInspector<>(directedGraph);
List<DirectedSubgraph<String, DefaultEdge>> stronglyConnectedSubgraphs
= scAlg.stronglyConnectedSubgraphs();
List<String> stronglyConnectedVertices
= new ArrayList<>(stronglyConnectedSubgraphs.get(3)
.vertexSet());
String randomVertex1 = stronglyConnectedVertices.get(0);
String randomVertex2 = stronglyConnectedVertices.get(3);
AllDirectedPaths<String, DefaultEdge> allDirectedPaths
= new AllDirectedPaths<>(directedGraph);
List<GraphPath<String, DefaultEdge>> possiblePathList
= allDirectedPaths.getAllPaths(
randomVertex1, randomVertex2, false,
stronglyConnectedVertices.size());
assertTrue(possiblePathList.size() > 0);
}
4.4. Eulerian Circuit
A Eulerian Circuit in a graph G is a circuit that includes all vertices and edges of G. A graph which has it is a Eulerian Graph.
Let’s have a look at the graph:
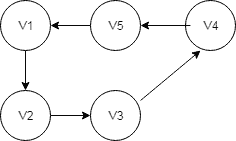
public void createGraphWithEulerianCircuit() {
SimpleWeightedGraph<String, DefaultEdge> simpleGraph
= new SimpleWeightedGraph<>(DefaultEdge.class);
IntStream.range(1,5)
.forEach(i-> simpleGraph.addVertex("v" + i));
IntStream.range(1,5)
.forEach(i-> {
int endVertexNo = (i + 1) > 5 ? 1 : i + 1;
simpleGraph.addEdge("v" + i,"v" + endVertexNo);
});
}
Now, we can test whether a graph contains Eulerian Circuit using the API:
@Test
void givenGraph_whenCheckEluerianCycle_thenGetResult() {
HierholzerEulerianCycle eulerianCycle
= new HierholzerEulerianCycle<>();
assertTrue(eulerianCycle.isEulerian(simpleGraph));
}
@Test
void whenGetEulerianCycle_thenGetGraphPath() {
HierholzerEulerianCycle eulerianCycle
= new HierholzerEulerianCycle<>();
GraphPath path = eulerianCycle.getEulerianCycle(simpleGraph);
assertTrue(path.getEdgeList()
.containsAll(simpleGraph.edgeSet()));
}
4.5. Hamiltonian Circuit
A GraphPath that visits each vertex exactly once is known as Hamiltonian Path.
A Hamiltonian cycle (or Hamiltonian circuit) is a Hamiltonian Path such that there is an edge (in the graph) from the last vertex to the first vertex of the path.
We can find optimal Hamiltonian Cycle for complete graph with HamiltonianCycle.getApproximateOptimalForCompleteGraph() method.
This method will return an approximate minimal traveling salesman tour (Hamiltonian cycle). The optimal solution is NP-complete, so this is a decent approximation that runs in polynomial time:
void whenGetHamiltonianCyclePath_thenGetVerticeSequence() {
List<String> verticeList = HamiltonianCycle
.getApproximateOptimalForCompleteGraph(completeGraph);
assertEquals(verticeList.size(), completeGraph.vertexSet().size());
}
4.6. Cycle Detector
We can also check if there are any cycles in the graph. Currently, CycleDetector only supports directed graphs:
@Test
void whenCheckCycles_thenDetectCycles() {
CycleDetector<String, DefaultEdge> cycleDetector
= new CycleDetector<String, DefaultEdge>(directedGraph);
assertTrue(cycleDetector.detectCycles());
Set<String> cycleVertices = cycleDetector.findCycles();
assertTrue(cycleVertices.size() > 0);
}
5. Graph Visualization
JGraphT allows us to generate visualizations of graphs and save them as images, first let’s add the jgrapht-ext extension dependency from Maven Central:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jgrapht</groupId>
<artifactId>jgrapht-ext</artifactId>
<version>1.0.1</version>
</dependency>
Next, let’s create a simple directed graph with 3 vertices and 3 edges:
@BeforeEach
public void createGraph() {
File imgFile = new File("src/test/resources/graph.png");
imgFile.createNewFile();
DefaultDirectedGraph<String, DefaultEdge> g =
new DefaultDirectedGraph<String, DefaultEdge>(DefaultEdge.class);
String x1 = "x1";
String x2 = "x2";
String x3 = "x3";
g.addVertex(x1);
g.addVertex(x2);
g.addVertex(x3);
g.addEdge(x1, x2);
g.addEdge(x2, x3);
g.addEdge(x3, x1);
}
We can now visualize this graph:
@Test
void givenAdaptedGraph_whenWriteBufferedImage_thenFileShouldExist() throws IOException {
JGraphXAdapter<String, DefaultEdge> graphAdapter =
new JGraphXAdapter<String, DefaultEdge>(g);
mxIGraphLayout layout = new mxCircleLayout(graphAdapter);
layout.execute(graphAdapter.getDefaultParent());
BufferedImage image =
mxCellRenderer.createBufferedImage(graphAdapter, null, 2, Color.WHITE, true, null);
File imgFile = new File("src/test/resources/graph.png");
ImageIO.write(image, "PNG", imgFile);
assertTrue(imgFile.exists());
}
Here we have created a JGraphXAdapter which receives our graph as a constructor argument and we have applied a mxCircleLayout to it. This lays the visualization out in a circular manner.
Furthermore, we use a mxCellRenderer to create a BufferedImage and then write the visualization to a png file.
We can see the final image in a browser or our favorite renderer:
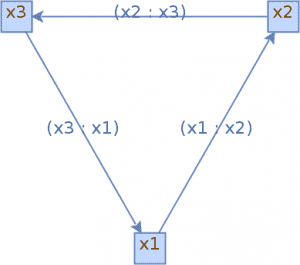
We can find more details in the official documentation.
6. Conclusion
JGraphT provides almost all types of graphs and variety of graph algorithms. We covered how to use few popular APIs. However, you can always explore the library on the official page.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're
logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.





















