Let's get started with a Microservice Architecture with Spring Cloud:
Efficient Word Frequency Calculator in Java
Last updated: December 19, 2017
1. Overview
In this tutorial, we’ll show various ways of implementing a word counter in Java.
2. Counter Implementations
Let’s start by simply calculating the word count of words in this array:
static String[] COUNTRY_NAMES
= { "China", "Australia", "India", "USA", "USSR", "UK", "China",
"France", "Poland", "Austria", "India", "USA", "Egypt", "China" };
If we want to process huge files, we need to go for other options described here.
2.1. Map With Integers
One of the simplest solutions would be to create a Map, store words as keys and the number of occurrences as values:
Map<String, Integer> counterMap = new HashMap<>();
for (String country : COUNTRY_NAMES) {
counterMap.compute(country, (k, v) -> v == null ? 1 : v + 1);
}
assertEquals(3, counterMap.get("China").intValue());
assertEquals(2, counterMap.get("India").intValue());We simply used Map‘s handy compute method, which increments the counter or initializes it with 1 if the key isn’t present.
However, this method of creating a counter isn’t efficient as Integer is immutable, so every time we increment the counter, we create a new Integer object.
2.2. Stream API
Now, let’s leverage Java 8 Stream API, parallel Streams, and the groupingBy() collector:
@Test
public void whenMapWithLambdaAndWrapperCounter_runsSuccessfully() {
Map<String, Long> counterMap = new HashMap<>();
Stream.of(COUNTRY_NAMES)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(k -> k, ()-> counterMap,
Collectors.counting());
assertEquals(3, counterMap.get("China").intValue());
assertEquals(2, counterMap.get("India").intValue());
}
Similarly, we could use a parallelStream:
@Test
public void whenMapWithLambdaAndWrapperCounter_runsSuccessfully() {
Map<String, Long> counterMap = new HashMap<>();
Stream.of(COUNTRY_NAMES).parallel()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(k -> k, ()-> counterMap,
Collectors.counting());
assertEquals(3, counterMap.get("China").intValue());
assertEquals(2, counterMap.get("India").intValue());
}
2.3. Map With an Integer Array
Next, let’s use a Map that wraps a counter within an Integer array used as a value:
@Test
public void whenMapWithPrimitiveArrayCounter_runsSuccessfully() {
Map<String, int[]> counterMap = new HashMap<>();
counterWithPrimitiveArray(counterMap);
assertEquals(3, counterMap.get("China")[0]);
assertEquals(2, counterMap.get("India")[0]);
}
private void counterWithPrimitiveArray(Map<String, int[]> counterMap) {
for (String country : COUNTRY_NAMES) {
counterMap.compute(country, (k, v) -> v == null ?
new int[] { 0 } : v)[0]++;
}
}
Note how we created a simple HashMap with int arrays as values.
In the counterWithPrimitiveArray method, while iterating over each value of the array, we:
- invoke a get on the counterMap by passing the country name as a key
- check whether a key was already present or not. If the entry is already present, we create a new instance of a primitive integer array with a single “1”. If the entry is absent, we increment the counter value present in the array
This method is better than the wrapper implementation – as it creates fewer objects.
2.4. Map With a MutableInteger
Next, let’s create a wrapper object which embeds a primitive integer counter as below:
private static class MutableInteger {
int count = 1;
public void increment() {
this.count++;
}
// getter and setter
}
Let’s see how we can make use of the above class as a counter:
@Test
public void whenMapWithMutableIntegerCounter_runsSuccessfully() {
Map<String, MutableInteger> counterMap = new HashMap<>();
mapWithMutableInteger(counterMap);
assertEquals(3, counterMap.get("China").getCount());
assertEquals(2, counterMap.get("India").getCount());
}
private void counterWithMutableInteger(
Map<String, MutableInteger> counterMap) {
for (String country : COUNTRY_NAMES) {
counterMap.compute(country, (k, v) -> v == null
? new MutableInteger(0) : v).increment();
}
}In the mapWithMutableInteger method, while iterating over each country in the COUNTRY_NAMES array, we:
- invoke a get on the counterMap by passing the country name as a key
- check whether the key is already present or not. If an entry is absent, we create an instance of MutableInteger, which sets the counter value to 1. We increment the counter value present in the MutableInteger if the country is present in the map
This method of creating a counter is better than the previous one – as we’re reusing the same MutableInteger and thereby creating fewer objects.
This is how Apache Collections HashMultiSet works where it embeds a HashMap with value as MutableInteger internally.
3. Performance Analysis
Here’s the chart that compares the performance of every method listed above.
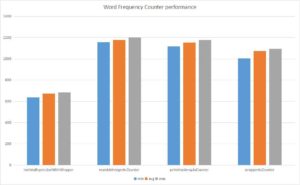
The above chart is created using JMH, and here’s the code that created the statistics above:
Map<String, Integer> counterMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, MutableInteger> counterMutableIntMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, int[]> counterWithIntArrayMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Long> counterWithLongWrapperMap = new HashMap<>();
@Benchmark
public void wrapperAsCounter() {
counterWithWrapperObject(counterMap);
}
@Benchmark
public void lambdaExpressionWithWrapper() {
counterWithLambdaAndWrapper(counterWithLongWrapperMap );
}
@Benchmark
public void parallelStreamWithWrapper() {
counterWithParallelStreamAndWrapper(counterWithLongWrapperStreamMap);
}
@Benchmark
public void mutableIntegerAsCounter() {
counterWithMutableInteger(counterMutableIntMap);
}
@Benchmark
public void mapWithPrimitiveArray() {
counterWithPrimitiveArray(counterWithIntArrayMap);
}
4. Conclusion
In this quick article, we illustrated various ways of creating word counters using Java.
The code backing this article is available on GitHub. Once you're logged in as a Baeldung Pro Member, start learning and coding on the project.
















