1. Overview
In this quick article, we’ll describe the different popular servers for Java development.
2. Web vs. Application Server
We’re going to see what are the differences between a web and application servers and which Java EE specifications they support.
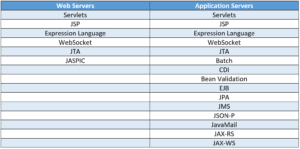
Simply put, the core difference is that application servers have full support for the Java EE spec, whereas web servers support a small subset of that functionality:
3. Apache Tomcat
One of the more popular web servers in the Java ecosystem is Apache Tomcat.
You can check the latest version of Apache Tomcat and the support Java version(s) on the project’s website.
Here’s a nice table with the exact specs Tomcat supports in each version.
You can also contribute to the project here.
4. Jetty
The Jetty web server is developed under the Eclipse Foundation.
Because it’s so lightweight, it can be easily embedded in devices, frameworks, and application servers. Some of the products that use Jetty are Apache ActiveMQ, Eclipse, Google App Engine, Apache Hadoop and Atlassian Jira.
Naturally, the project is open-source and you can contribute to it here.
Let’s now move on from web servers to application servers.
5. Apache TomEE
The Apache TomEE is a full application server built on top of the standard Apache Tomcat, and primarily supported by Tomitribe. You can check the website here for the latest version.
TomEE enables us to use some of the features of Java EE that aren’t supported by Tomcat.
This application server is, as the name suggests, under the umbrella of the Apache Foundation.
You can contribute to the project here.
6. Oracle WebLogic
WebLogic 12 is also worth mentioning, as it’s the primary application server offering from Oracle.
The latest release and supported Java versions can be found here.
7. WebSphere
IBM has also developed its own application server, called WebSphere. The latest release and supported Java versions can be found here.
WebSphere is not an open-source project, but it has given the WebSphere Liberty application to Eclipse – which makes some essential code of WebSphere open for developers to use and contribute to.
You can contribute to that project here.
8. WildFly
Wildfly is an open-source Java application server, developed by Red Hat.
Wildfly is gaining popularity for Java EE applications, with the latest release version to be found here.
You can also contribute to the project here.
9. Apache Geronimo
Apache Geronimo is developed by the Apache Software Foundation under the Apache license, which makes it an open-source project so we can also contribute, the same as in the previous application servers.
The latest release available can be found here.
You can contribute to the project here.
10. GlassFish
Glassfish is an open-source application server, also sponsored by Oracle. The latest release available can be found here.
You can contribute to the project here.
11. Conclusion
In this quick, list-style article, we had a very high-level look at the web and application server landscape in the Java ecosystem.






